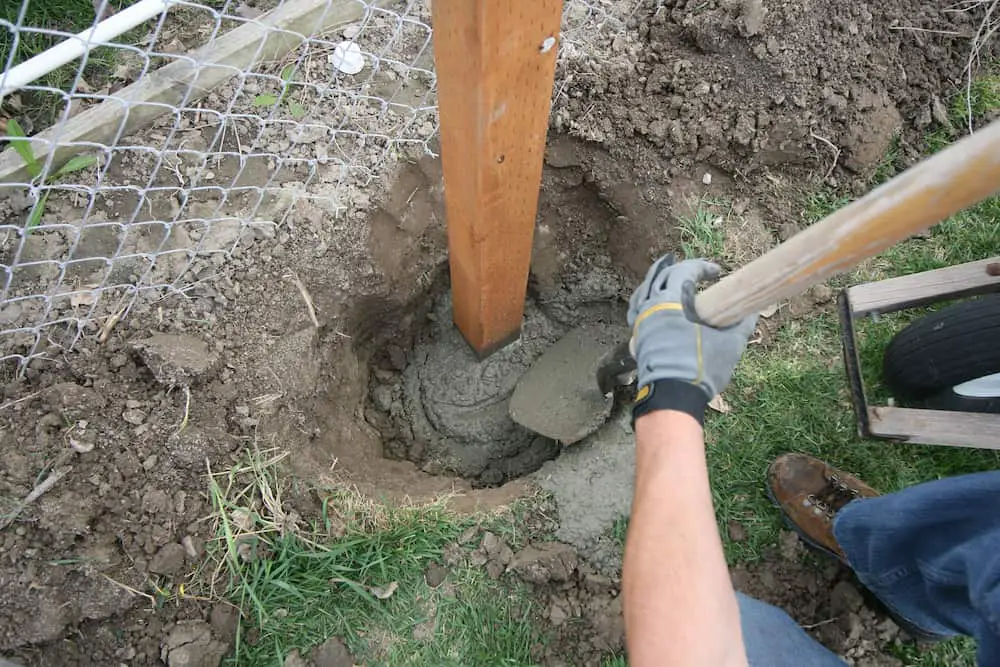
The foundation of any structure is crucial to its longevity. To ensure that it remains in place, you need a deep and strong footing that will resist the weight from above as much as possible without sacrificing stability or mobility when needed, most during times like heavy rainstorms or harsh winters where conditions may be too wet for roadways but not necessarily at your home. How Deep is the Frost Line?
The Frost Line which is the depth where groundwater freezes varies with the maximum frost depth ranging between zero ft. in the warmest regions to eight ft. in the coldest regions of the United States.
The frost line is the freezing depth where the moisture present in the soil is expected to freeze. Once the bottom of a footing is buried below the frost line, the residual heat in the ground below the footing will ensure the soil below the footing will not freeze in the winter.
How Deep is Frost Line Depth
The frost line is the depth at which moisture will freeze in the ground. Due to variations in winter temperatures and soil moisture content, frost lines aren’t the same everywhere. The frost line is much deeper in Minnesota than it is in Florida, for example.

Frost line depth matters in building mainly because of what happens when something freezes and thaws. Expansion and Contraction is a law with changing temperatures. A can of soda explodes when left in the freezer or the trunk of a car in winter. Frozen roads and sidewalks result in cracks, pits, and potholes. The same things happen below ground when the surrounding soil and water freeze.
Homeowners who Build decks, fences, and anything above grade require the use of footings for support. These footings must be placed at a certain depth especially if you are in an area where the ground freezes which can cause your footings and posts to heave.
What depth is determined by frost lines in your area and the map below will show you how deep you need to dig to safely place your footings.
Testing the exact depth relies on instruments known as Frost Tubes which consist of a small hollow tube that is inserted into a drilled hole in the frozen ground. Testers put a bag of water with measurement indicators into the tube and determine the depth based on the line at which the water freezes.
- When frost penetrates the ground and Frost Tube is in the ground, separation occurs between the water solution and blue methylene in a tube.
- The water solution becomes colorless when it is frozen.
- Blue methylene tends to remain in the unfrozen section of the tube because of its low density, where the concentrated solution is.
- This phenomenon is also reversible, which means it can follow the frost and thaw evolution over time. But engineers can not measure exactly each inch of the Earth and find frost depth or the frost line on the field.
Frost Heave Building Codes
Frost heave is when the ground freezes and then thaws. This process causes the ground and anything in it to move upwards. This can be detrimental to the level of any posts or footings.
Just as you don’t want to build on poor soil where the weight of the building will cause unequal downward settling which can destroy the structure, you don’t want the structure or post from your deck to lift up into the air unequally.
Frost heaving can and does lift things up, things that weigh thousands of pounds. Should the soil beneath the footing freeze, the uplift force created by the expanding freezing water can lift the footing and anything on it up into the air. The uplift force is tremendous and can do significant structural damage to your deck.
When posts, foundations, footings, and other supports are installed above the frost line, the structures become vulnerable to significant damage that can be caused by frost heaves. A frost heave occurs when the water in the soil freezes and expands, forming a pocket of ice called a frost lens.
This lens pushes dirt, rocks, and any other objects upwards, as it gradually expands. The result is a chaotic movement of hardened earth that has enough force to bend posts, break rock, and shift entire building foundations.
Frost Lines and Frost Depth by State
When you build any structure, your goal is to ensure the foundation of the structure doesn’t move over time. Builders find the Frost line to ensure this won’t happen. Average frost lines are used in building codes according to a line map.
Frost depth in the north and south reports are commonly from frost tube instruments, visual reports from construction or cemetery sites, or other types of electronic probes. The data shown in this map are queried from the National Weather Service River Forecast Center (RFC) databases late morning each day.
The values shown represent the latest measurement taken within the last seven days. Frost Tubes have many different applications as this video shows for state road maintenance, safety, and declaration
Frost lines vary by latitude and are deeper and closer to the poles. According to the Federal Highway Administration, the maximum frost depth ranges between zero to eight feet north in the contiguous United States. Here are the 10 states with the deepest frost lines:
- Alaska – 100 inches
- Minnesota – 80 inches
- North Dakota – 75 inches
- Maine – 74 inches
- Wisconsin – 65 inches
- South Dakota – 64 inches
- Montana – 61 inches
- New Hampshire – 60 inches
- Vermont – 60 inches
- Iowa – 58 inches
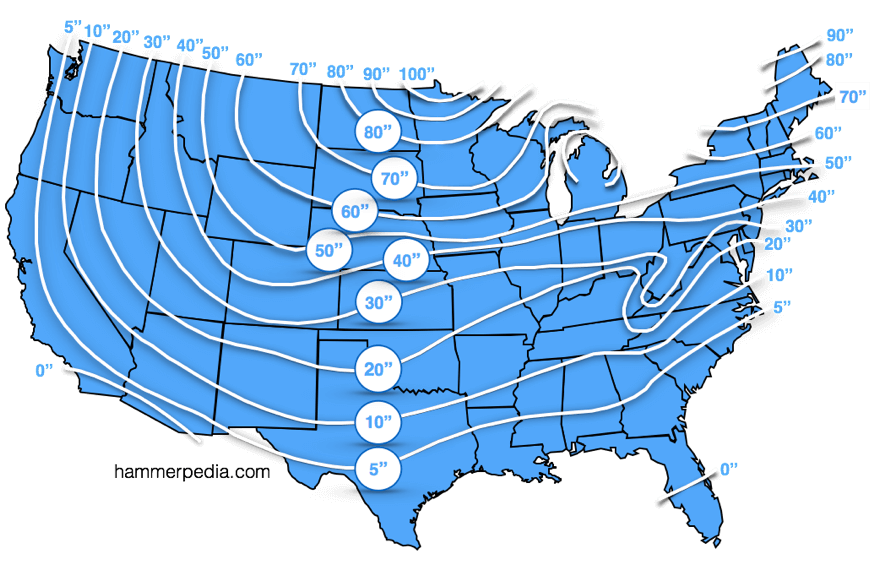
*Always check with your local building inspector to see what is required in your area.
Frost Line Map by Zip Code
If the map isn’t accurate enough for you. It will give you a general idea of where frost lines are at your location for the time of the year. Check your frost line by zip code or address using this NCREC map from the National Weather Service. As we mentioned before, make sure you check with your local building codes before you start digging.
This map displays recent frost depth measurements in terms of inches below the soil surface. To view all frost depth sites in the NCRFC service area, beyond those that were recently reported, turn on the “All NCRFC Frost Depth Sites” layer using the layer list button in the top right of the map.

References:
National Weather Service-Frost Depth
Related Questions:
- Where is the deepest frost line? The maximum frost line depth is 100 inches, as seen near the tip of Minnesota, North Dakota, and Alaska, all the way to zero inches in Florida, southern Arizona, and southern California.
- What happens if you don’t dig below the frost line? A Footing Destined to Fail: Frost Line Depth Chart If the footing does not extend below the frost line, the footing will heave as the ground freezes and thaws.

