When you own an Inground Pool or any type of swimming pool there is a lot of work that goes along with it, to keep it looking the way it should during those hot summer months when there is no time for closing the pool to fix any issues and problems that are certain to develop. What are common inground swimming pool problems?
- pH problem-high/low
- Alkalinity problem out of range
- Disinfection problem-low/high
- Filtration & Circulation problems-low flow
- Structural Damage problem-cracks/leaks
- Equipment Malfunction problems-electrical/mechanical
- Safety Concern Problems-slipping/chemical/electrical
- Heating Problem-temperature variations
Introduction:
Inground pools are a popular choice for homeowners seeking to enhance their property with a luxurious and functional outdoor oasis. These pools are constructed by excavating the ground and installing a permanent structure below the surface, providing a seamless integration into the landscape. Inground pools come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, offering versatility to accommodate different preferences and space constraints.
While inground pools offer countless hours of enjoyment and relaxation, they also require diligent upkeep to ensure optimal performance and safety. Proper maintenance is essential to preserve water quality, structural integrity, and equipment functionality. Moreover, timely troubleshooting of common issues is crucial to address problems before they escalate, minimizing potential damage and costly repairs. In this guide, we will explore some of the most common inground pool problems and provide practical solutions to keep your pool in pristine condition year-round.
Inground Pool Problems
Inground pool problems encompass a range of challenges that can affect water quality, structural integrity, and overall enjoyment. Common issues include pH imbalance, algae growth, filtration and circulation problems, structural damage like cracks, and equipment malfunctions such as pump or heater issues.
These problems often manifest in symptoms like cloudy water, reduced water flow, or unusual noises from equipment. Addressing these issues requires proactive maintenance, timely repairs, and adherence to proper water chemistry and safety protocols.
Because in-ground pool problems are normally on a larger scale than smaller above-ground pools, seeking professional assistance when needed can help resolve complex problems and ensure the long-term health and functionality of the inground pool. Read this article for a better handle on problems you will face if you invest in an In-ground swimming pool. Before we talk about swimming pool problems and solutions we should look at how the swimming pool works. Take a look at this great video!
Essential Tips to Maintain Your Swimming Pool’s Water Quality
Maintaining the pristine condition of swimming pools requires an understanding of common swimming pool issues and the deployment of diligent maintenance practices. High on the list of priorities is ensuring optimal water quality, which stands as the bulwark against a myriad of potential problems.
The cornerstone of swimming pool maintenance lies in the regular monitoring of chlorine levels; which is instrumental in thwarting bacterial growth and preserving the water’s clarity. A proper balance should be maintained; too little chlorine can invite pathogens, while too much can lead to skin and eye irritation.
Circulation is another vital aspect; water must be circulated to distribute the chlorine evenly and prevent the buildup of algae, which is a problem many pool owners face. Regularly inspecting the pool’s filtration system, and ensuring it is free from debris, optimizes the efficacy of water circulation and maintenance efforts. Additionally, the pool’s pH levels demand attention, as an imbalance can hinder chlorine’s disinfecting properties and exacerbate water problems.
A critical component of pool maintenance is the administration of shock treatments, especially after heavy pool usage or severe weather conditions. This gesture forestalls the emergence of water problems by eradicating organic contaminants that might overcome normal chlorine levels. Lastly, routine inspection and timely rectification of structural issues, such as cracks or worn-out linings, will prevent water leakage—a significant pool problem that undermines water quality and pool integrity. Adherence to these maintenance tips will ensure your swimming pool remains a sparkling oasis for relaxation and enjoyment.
Understanding Chlorine Levels: Solving Two Major Swimming Pools Water Problems
Addressing the intricacies of swimming pool issues, specifically those concerning water quality, requires an in-depth comprehension of chlorine management. The equilibrium of chlorine a pivotal disinfectant is essential in circumventing two prevalent problems plaguing pools.
Proper chlorine levels combat pathogens, thus ensuring safe and hygienic water for swimmers. An excessive quantity of chlorine can lead to skin and eye irritation, while inadequate levels make the water a fertile abode for bacteria and algae. These issues, if not addressed promptly, can exacerbate, making pools unsuitable for use.

There is a balance to strike; too much chlorine can create a problem, yet too little is equally problematic. The challenge lies in maintaining a delicate balance, ensuring the water is neither under-chlorinated which could compromise health nor over-chlorinated, which may deter from the enjoyment of the pools.
Therefore, regular testing and adjustment of water chemistry are paramount. By incorporating a few essential tips to maintain your swimming pool’s water quality, as discussed in previous sections of this article, and understanding common swimming pool issues, owners can navigate the nuances of effective chlorine levels with finesse.
Being mindful of these swimming pool water problems and embracing a proactive stance towards pool maintenance can preserve the integrity of your aquatic oasis. In conclusion, precise management of chlorine levels is the control of an imperative stride towards crystal clear, inviting pools that beckon you to dive into their tranquil depths.
Swimming Pool Problems: 3 Indicators Your Pool Needs Immediate Attention
Swimming pools, while the epicenter of family fun and relaxation, can harbor numerous pool problems that require swift action. The vigilance of the pool owner is paramount in ensuring these swimming pool issues don’t spiral out of control. Among the myriad of potential pool problems, 3 critical indicators signal the immediate need for intervention.
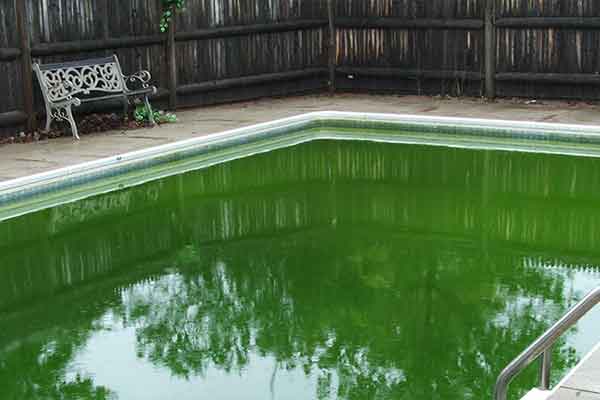
- First and foremost, pool water clarity is non-negotiable; a murky abyss suggests a troubling imbalance that could stem from improper chlorine levels. In this case, solving this swimming pool problem swiftly is crucial to prevent a ripple effect of additional swimming pool issues.
- Secondly, the presence of algae is a telltale sign of swimming pools crying out for help. Not only does this problem compromise aesthetic appeal, but it also indicates a problem within your pool’s maintenance regimen. Algal infestation requires an integrated approach, incorporating rigorous sanitization and often adjusting the pool’s chemistry, highlighting the interconnected nature of swimming pool issues.
- Lastly, an unexplained drop in pool water level suggests a problem that’s more than just evaporation; you could be facing a pool leak. Ignoring such a pool problem can lead to significant structural damage down the line.
In summary, these 3 key indicators—water clarity issues, rampant algae growth, and decreasing water levels—embody the quintessence of pool problems demanding your immediate attention. Address these swimming pool issues proactively to secure the longevity and enjoyment of your swimming pools.
Swimming Pools: Solutions to Recurring Pool Problems
Owners of swimming pools are often met with recurring pool problems that can mar the efficiency of a good working pool is meant to provide. Understanding these swimming pool issues is the first step towards implementing effective solutions.
At the forefront of these pool problems are imbalanced chlorine levels—one of the two major swimming pool water problems that, if not managed properly, can lead to discomfort and health risks for swimmers.
Another prevalent concern is maintaining impeccable water quality; our essential tips to maintain your swimming pool’s water quality serve as a guide to tackle this challenge. Homeowners face myriad pool-related problems, with common swimming pool issues accounting for a notable portion of pool maintenance efforts.
This article addresses the most fundamental problems affecting pools, ranging from water imbalance to structural integrity. Pool owners often encounter the same pool problems repeatedly but understanding the root cause can lead to long-lasting solutions.
It isn’t uncommon for a pool owner to encounter a multitude of problems within their pools over time. Whether it be algae growth, filtration issues, or plumbing defects, identifying the indicators your pool needs immediate attention is crucial to the longevity and enjoyment of your pools. As we dive into these pool conundrums, we ensure each of the problems is met with tailored, actionable solutions, enhancing the overall experience for pool enthusiasts.
Combat Common Problems Pool Owners Encounter With These Effective Strategies
As pool owners, the journey of maintaining a pristine swimming oasis is often dotted with various swimming pool issues. Indeed, common problems that seem as persistent as the ripples on the water’s surface can be daunting.
However, arming oneself with effective strategies is the key to navigating this labyrinth of pool problems. Whether battling against algae invasion, wrestling with imbalanced pH levels, or relentless fighting off of contaminants, these challenges are universal for those who boast an inground pool in their oasis. Addressing these common swimming pool issues requires vigilance and a deep understanding of the nuanced dynamics of pool care. 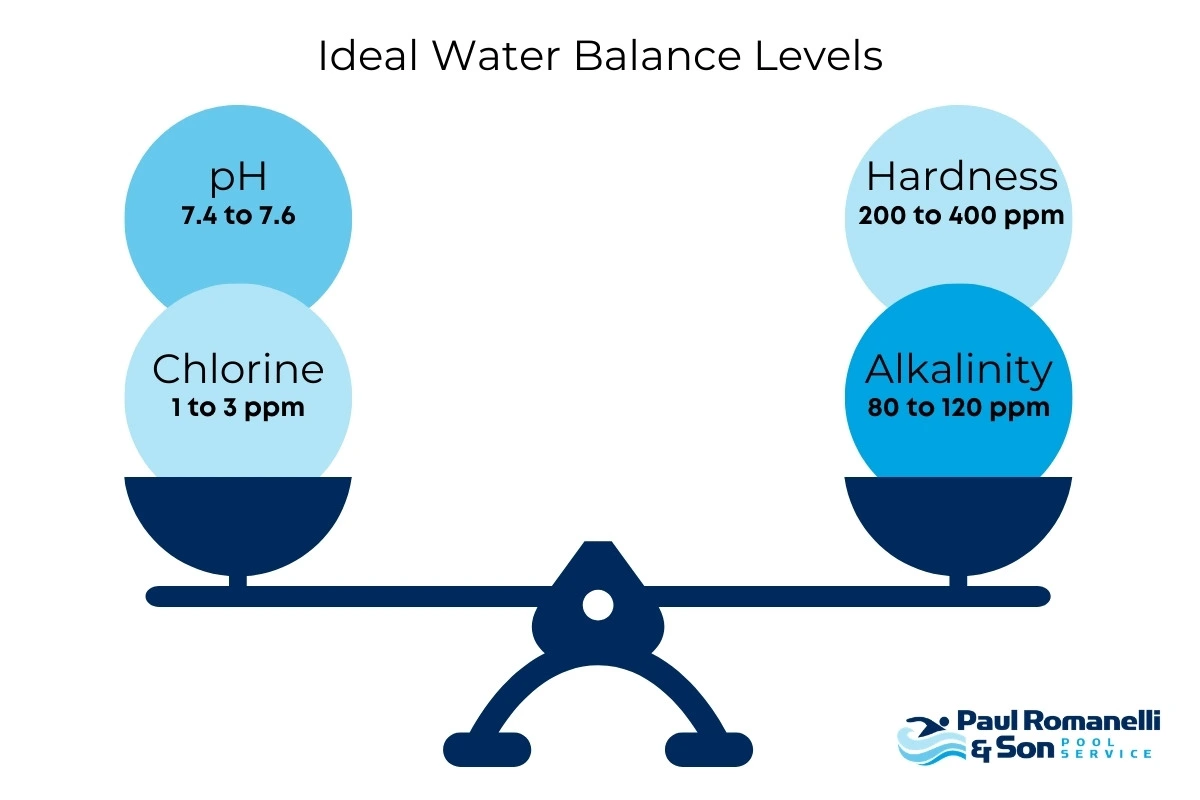
From the egregiously green waters that signal chemical imbalance to the stealthy leaks that threaten the very integrity of your pool, a myriad of pool problems await the unsuspecting owner.
It’s not just about reactionary measures, but preventative ones – understanding that the best defense is a good offense when it comes to pool care. The article discusses essential tips to maintain your swimming pool’s water quality, which is paramount in preventing common problems. Recognizing the two major swimming pool water problems related to chlorine levels and employing tactics to mitigate them are necessary steps discussed herein.
Moreover, we delve into three key pool problems homeowners face, signifying the critical areas requiring undivided attention. Perhaps your pool’s plea for help comes through the indicators your pool needs immediate attention, a section dedicated to timely intervention.
The journey towards crystal clear waters is a meticulous one, embroiled with recurring pool problems, which finds a remedy in solutions tailored for these common recurring pool problems. In culmination, the compendium of knowledge presented offers an indispensable manual for the intrepid pool owner seeking to restore and maintain the allure of their cherished aquatic retreat.
The Ultimate Guide to Addressing Your Pool Problems and Enhancing Water Clarity
Understanding the multifaceted nature of swimming pool issues is paramount for any pool owner seeking to maintain an idyllic backyard oasis. Tackling pool problems effectively requires a comprehensive approach that’s meticulously outlined in this guide—designed to help you resolve the most common issues afflicting inground pools.
At the cornerstone of our discussion are three key pool problems many homeowners face: maintaining optimal chemical balance, addressing filtration deficiencies, and combating the pervasive threat of algae. These pool issues must be met with informed combat strategies outlining effective solutions for enhancing water clarity—a paramount indicator of a well-maintained pool.
Issues like fluctuating chlorine levels, which can lead to two major swimming pool water problems, are scrutinized with expert tips on achieving chemical equilibrium. We delve into common problems pool owners encounter, revealing indicators that your pool needs immediate attention such as murky water, inefficient filtration, or surface stains.
Indeed, swimming pools present a variety of challenges, but through this guide, you’ll acquire the knowledge to effectively combat these issues. Equipped with this information, you’re positioned to ensure that your inground pool remains the pinnacle of enjoyment and relaxation in your personal haven. Your commitment to addressing these issues head-on will inevitably lead to a pristine and inviting aquatic environment that epitomizes clarity and hygiene.

Here’s a troubleshooting table for addressing an imbalance in alkalinity levels in an inground pool:
Imbalance of pH and Alkalinity Level Problems
Imbalance of Disinfectant Level Problems
An imbalance of disinfectant levels in an inground pool can lead to various challenges in maintaining water quality and safety. Insufficient disinfectant levels may result in ineffective sanitization, allowing harmful bacteria and pathogens to proliferate in the pool water.
On the other hand, excessive disinfectant levels can irritate swimmers’ skin, eyes, and respiratory system, as well as damage pool equipment and surfaces. Regular testing and monitoring of disinfectant levels, such as chlorine or bromine, are essential to ensure they remain within the recommended range for optimal sanitization without causing discomfort or harm to swimmers. Adjustments to disinfectant levels should be made carefully and gradually, following manufacturer guidelines and professional advice when needed, to maintain a healthy and balanced pool environment for all users.
Troubleshooting table for addressing an imbalance in disinfectant levels in an inground pool:
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Cloudy or hazy water | Insufficient disinfectant | 1. Test disinfectant levels (chlorine or bromine). 2. Shock the pool with appropriate shock treatment. 3. Adjust the sanitizer levels as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
| Strong chemical smell | Excessive disinfectant | 1. Test disinfectant levels (chlorine or bromine). 2. Allow the pool to aerate by running the pump and opening vents. 3. Dilute the water by adding fresh water if necessary. 4. Adjust the sanitizer levels as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
| Skin and eye irritation | Imbalance in disinfectant or pH levels | 1. Test disinfectant and pH levels. 2. Adjust pH levels to the recommended range (7.2-7.6). 3. Shock the pool with appropriate shock treatment if necessary. 4. Adjust the sanitizer levels as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
| Algae growth | Insufficient disinfectant | 1. Test disinfectant levels (chlorine or bromine). 2. Brush and vacuum the pool thoroughly. 3. Shock the pool with appropriate shock treatment. 4. Adjust the sanitizer levels as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
| Discoloration of pool surfaces or equipment | Excessive disinfectant | 1. Test disinfectant levels (chlorine or bromine). 2. Rinse pool surfaces and equipment with fresh water. 3. Allow the pool to aerate by running the pump and opening vents. 4. Adjust the sanitizer levels as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. |
*This table provides a structured approach to troubleshooting an imbalance in disinfectant levels, along with possible causes and corresponding steps to address each symptom. Adjustments should always be made by manufacturer recommendations and professional advice when necessary.
Effects of Disinfection Imbalance:
Testing and Maintenance:
Testing and maintenance play a crucial role in addressing and preventing disinfection imbalances in an inground pool. Regular testing of disinfectant levels, such as chlorine or bromine, allows pool owners to monitor the effectiveness of sanitation efforts. By detecting any imbalances early on, adjustments can be made promptly to restore proper disinfectant levels and ensure water safety.
Additionally, consistent maintenance practices, including cleaning filters, checking circulation systems, and removing debris, help optimize disinfection efficiency and prevent potential contamination sources. By staying vigilant with testing and maintenance routines, pool owners can effectively manage disinfection imbalances, maintain water quality, and create a safe and enjoyable swimming environment for all users. Overall, maintaining proper disinfectant levels is crucial for preserving water quality, ensuring swimmer safety, and prolonging the lifespan of pool infrastructure in an inground pool. Regular testing, monitoring, and adjustment of disinfectant levels are essential components of effective pool maintenance.
Preventive measures are essential for maintaining optimal water quality and preventing issues in an inground pool. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Regular Testing: Conduct regular testing of water parameters such as pH, alkalinity, chlorine or bromine levels, and calcium hardness to ensure they are within the recommended ranges.
- Proper Chemical Balance: Maintain proper chemical balance by adjusting pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels as needed to prevent imbalances that can lead to water quality problems.
- Routine Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule to clean filters, vacuum debris, skim the surface, and brush pool surfaces to prevent algae growth and maintain water clarity.
- Monitor Water Level: Keep an eye on the water level and ensure it remains within the optimal range to prevent damage to the pool equipment and maintain proper skimming and filtration.
- Regular Inspection: Inspect pool equipment, such as pumps, filters, and heaters, regularly to identify and address any issues promptly before they escalate.
- Safe Chemical Storage: Store pool chemicals in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from sunlight and moisture to prevent degradation and ensure their effectiveness.
- Educate Pool Users: Provide education and guidelines to pool users on proper swimming hygiene, such as showering before entering the pool and avoiding urination, to minimize contaminants in the water.
By implementing these preventive measures consistently, pool owners can proactively maintain water quality, prevent potential problems, and ensure a safe and enjoyable swimming experience for all users.
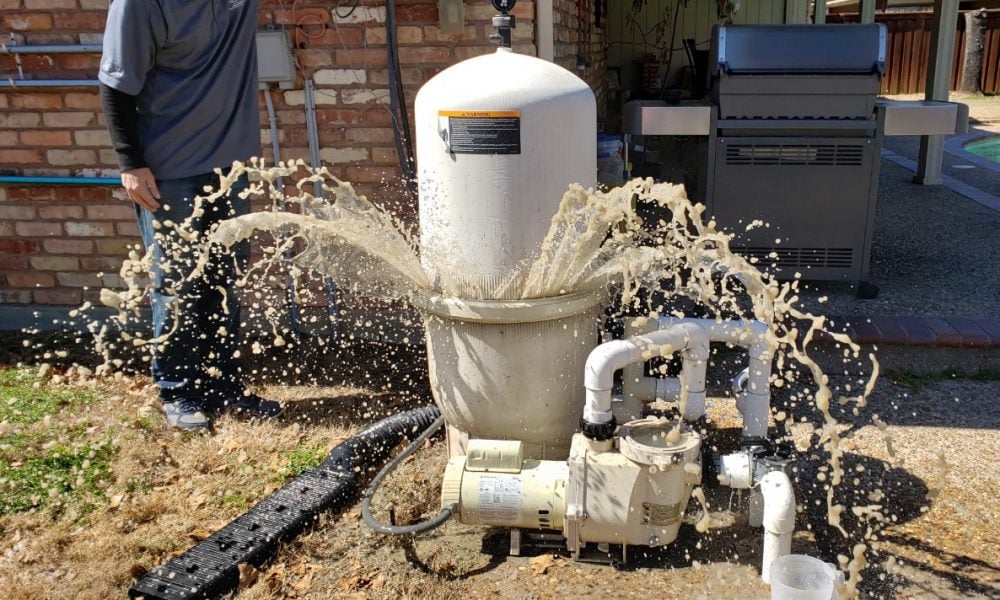
Filtration and Circulation Problems
Filtration and circulation problems are common challenges encountered in maintaining an inground pool. Reduced water flow and cloudy water are telltale signs of clogged or malfunctioning filters, which can compromise water clarity and sanitation. Inadequate circulation can lead to stagnant water pockets, promoting the growth of algae and other contaminants. 
Troubleshooting these issues typically involves inspecting and cleaning filters, adjusting pump settings, and ensuring proper water circulation throughout the pool.
Addressing filtration and circulation problems promptly is essential to maintain optimal water quality and a pleasant swimming environment for pool users. Efficient filtration and circulation are essential for keeping an inground pool clean and clear. When filters become clogged or pumps malfunction, it can lead to poor water quality and potentially harmful bacteria buildup.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning filters and checking pump functionality, is crucial in preventing these issues. Additionally, ensuring proper water circulation helps distribute chemicals evenly and prevents stagnation, reducing the risk of algae growth and other contaminants. By addressing filtration and circulation problems promptly, pool owners can enjoy a safe and inviting swimming experience all season long.
Here’s a troubleshooting table for filtration and circulation problems in an inground pool:
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced water flow | Clogged or dirty filters | 1. Shut off the pump and check the filter for debris. 2. Clean or backwash the filter according to the manufacturer’s instructions. 3. Inspect and replace filter cartridges if necessary. 4. Restart the pump and monitor the water flow. |
| Cloudy or murky water | Inadequate filtration | 1. Check the filter pressure gauge for abnormally high readings. 2. Clean or backwash the filter to improve filtration efficiency. 3. Ensure proper chemical balance and shock the pool if necessary. 4. Monitor water clarity and adjust filtration settings as needed. |
| Air bubbles in the pump basket or return lines | Air leaks in suction lines or pump housing | 1. Inspect suction lines, pump seals, and fittings for leaks. 2. Tighten or replace any loose or damaged connections. 3. Prime the pump to remove airlocks and ensure proper water circulation. 4. Monitor pump operation for any recurrence of air bubbles. |
| Uneven distribution of chemicals | Poor circulation patterns | 1. Adjust pump settings to optimize water circulation. 2. Check the placement and orientation of return jets for proper water dispersion. 3. Consider adding additional return jets or repositioning existing ones. 4. Monitor chemical levels and adjust as necessary to maintain balance. |
This troubleshooting table offers a structured approach to diagnosing and addressing common filtration and circulation problems in an inground pool. It includes possible causes, corresponding symptoms, and step-by-step troubleshooting steps to help pool owners resolve issues effectively.

Preventive Measures:
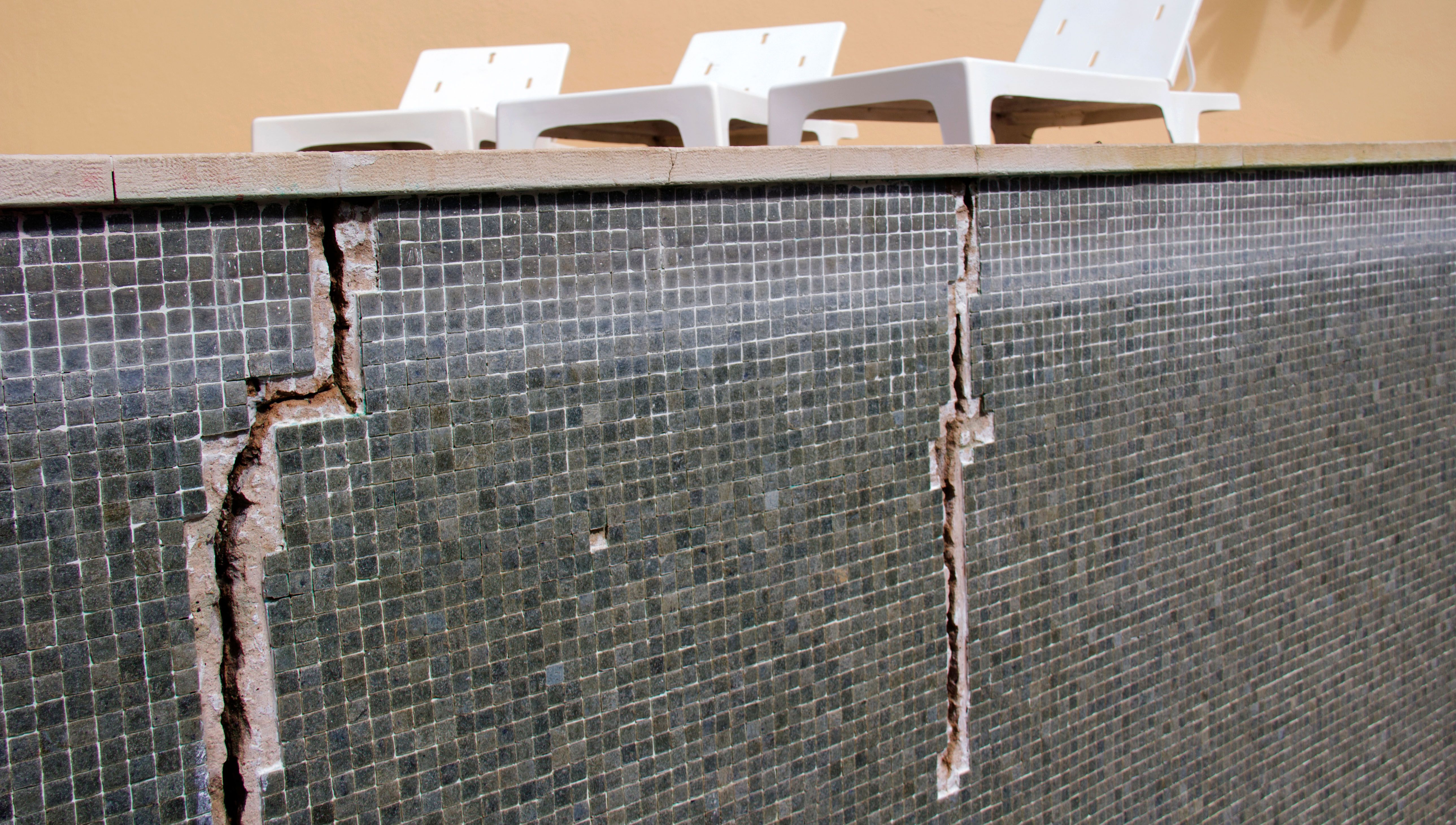
Structural Damage Problems
Structural damage to an inground pool, particularly cracks in the pool shell, can arise from various environmental factors and wear over time. Common causes include ground movement due to soil shifting and the expansion and contraction of materials during freeze-thaw cycles.
Effects of Structural Damage Problem:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of the pool structure, including the pool shell, walls, floors, and surrounding areas, to identify any signs of damage or deterioration. Look for cracks, leaks, bulges, or shifting in the pool structure.
- Proper Installation: Ensure that the pool is installed correctly by experienced professionals following industry standards and guidelines. Proper installation minimizes the risk of structural issues due to poor construction practices.
- Maintain Proper Water Levels: Maintain the proper water level in the pool to prevent undue stress on the pool walls and surrounding soil. Avoid overfilling or allowing the water level to drop too low, as this can affect the structural integrity of the pool.
- Monitor Soil Conditions: Monitor the soil conditions surrounding the pool, especially during periods of heavy rainfall or drought. Excessive moisture or soil movement can exert pressure on the pool structure, leading to cracks or shifting.
- Address Drainage Issues: Ensure proper drainage around the pool area to prevent water accumulation and soil saturation. Poor drainage can exacerbate soil erosion and increase the risk of structural damage to the pool.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a regular maintenance schedule to address minor issues promptly before they escalate into larger problems. This includes repairing any cracks or leaks, maintaining proper water chemistry, and inspecting pool equipment for signs of damage or malfunction.
- Reinforcement and Repairs: If structural issues are identified, take immediate action to reinforce or repair the damaged areas. This may involve patching cracks, sealing leaks, or reinforcing the pool structure as necessary to prevent further deterioration.
By implementing these preventive measures consistently, pool owners can minimize the risk of structural damage and ensure the long-term integrity and safety of their inground pool. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and prompt repairs are essential for preserving the structural integrity of the pool and preventing costly damage.
Safety Concern Problems

Effects of Safety Concerns Problems:
In conclusion, maintaining an inground pool involves navigating various common challenges that can arise. Issues such as pH imbalance, filtration problems, structural damage, equipment malfunctions, and safety concerns like electrical hazards and slippery surfaces are frequently encountered by pool owners. However, proactive maintenance and timely repairs are key to addressing these problems effectively and ensuring the continued functionality and safety of the pool.
It’s crucial to emphasize the importance of regular inspections, preventive measures, and prompt repairs to minimize the risk of more significant issues down the line. Additionally, when faced with complex or challenging problems, seeking professional assistance from qualified technicians or contractors is highly encouraged. By staying proactive and seeking help when needed, pool owners can enjoy their inground pools with confidence and peace of mind.
The management of an inground pool necessitates an understanding of the common challenges it may encounter. From water chemistry issues to structural damage and equipment malfunctions, each problem demands attention and proactive measures for resolution. By highlighting the significance of proactive maintenance and timely repairs, pool owners can ensure the longevity and safety of their investments. Moreover, advocating for the involvement of professionals underscores the importance of expertise in addressing complex issues effectively. Ultimately, a combination of vigilance, maintenance, and professional support fosters a safe and enjoyable environment for all who utilize the inground pool.
References:
Watson’s – Common Pool Problems
FAQ’s
What are the common signs of pH imbalance in an inground pool? Signs of pH imbalance include cloudy water, skin and eye irritation, corrosion of pool surfaces, and reduced effectiveness of sanitizers like chlorine.
How can I prevent algae growth in my inground pool? Regular brushing of pool surfaces, proper filtration and circulation, maintaining balanced water chemistry, and using algaecides as a preventive measure can help prevent algae growth.
What should I do if I notice cracks in my inground pool? If you notice cracks, it’s essential to assess their severity. Minor cracks can often be patched with pool patching materials, while extensive cracking may require professional resurfacing to restore structural integrity.
Why is my pool pump making unusual noises? Unusual noises from the pool pump could indicate issues such as clogged filters, worn-out bearings, or air leaks. It’s crucial to troubleshoot and address these problems promptly to prevent further damage.
How can I troubleshoot heater problems in my inground pool? Check the gas supply to ensure it’s turned on and sufficient. Inspect the gas line for leaks or blockages and examine the pilot light or ignition system for faults. Cleaning or replacing clogged or damaged heating elements may also resolve heater issues.
What are some safety concerns associated with inground pools? Safety concerns include electrical hazards from faulty wiring near the pool, slippery pool decks, drowning risks for unsupervised swimmers, and entrapment hazards from faulty pool drains.




