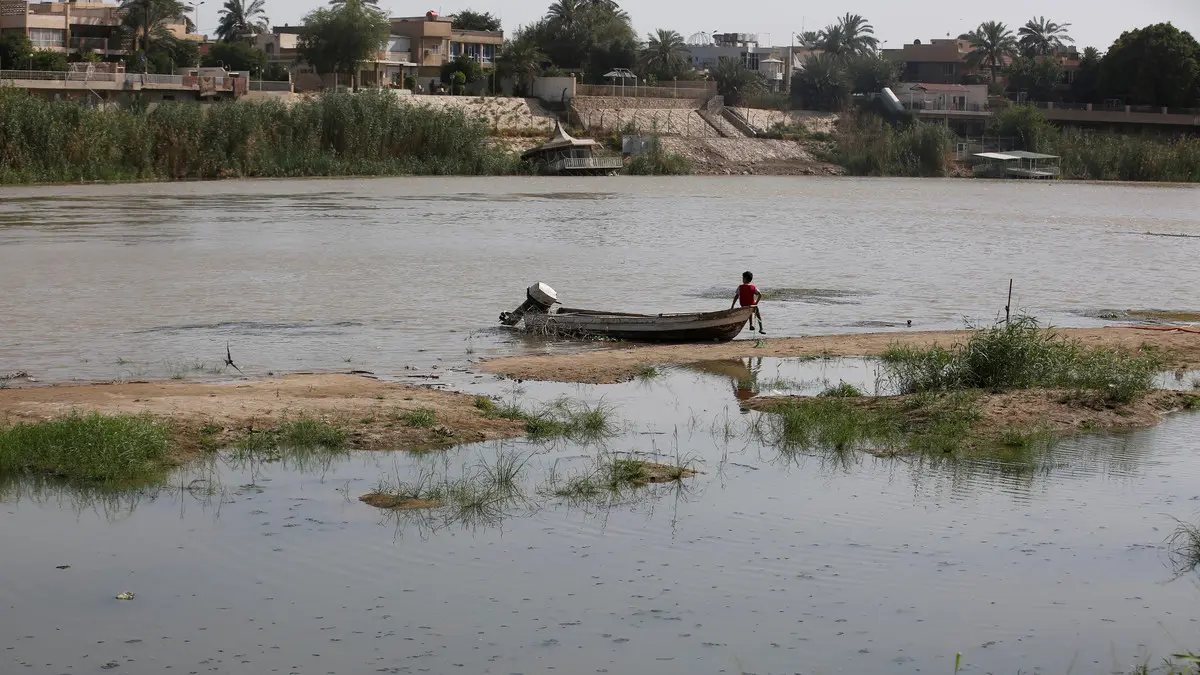
- Euphrates River is experiencing severe water depletion
- Causes are climate change, over-extraction, & dams
- Droughts have worsened the situation
- Parts of the river have dried up
- Local agriculture & H20 supplies are affected
- Ecosystems suffer
- International help is needed
- Some see it as a sign of biblical prophecy
Why Is the Euphrates River Drying Up
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and reduced rainfall in the region have decreased water flow. The Euphrates relies heavily on snowmelt from Turkey’s mountains, which has diminished due to warmer winters.
- Dams and Water Management: Turkey, Syria, and Iraq have built numerous dams, like Turkey’s Ataturk Dam, diverting water for irrigation and hydropower. This has significantly reduced downstream flow.
- Overuse and Agriculture: Intensive farming and outdated irrigation practices in Syria and Iraq consume vast amounts of water, further straining the river.
- Conflict and Instability: Ongoing conflicts in Syria and Iraq have disrupted water infrastructure and management, exacerbating the crisis.
Current State of the Euphrates
- Satellite imagery and reports from 2023-2025 show the Euphrates at historic lows, with some sections in Iraq reduced to narrow streams.
- Lake Assad in Syria and Iraq’s wetlands, like the Mesopotamian Marshes, are shrinking, threatening biodiversity and local livelihoods.
- Water quality has deteriorated due to pollution and reduced flow, impacting drinking water and agriculture.
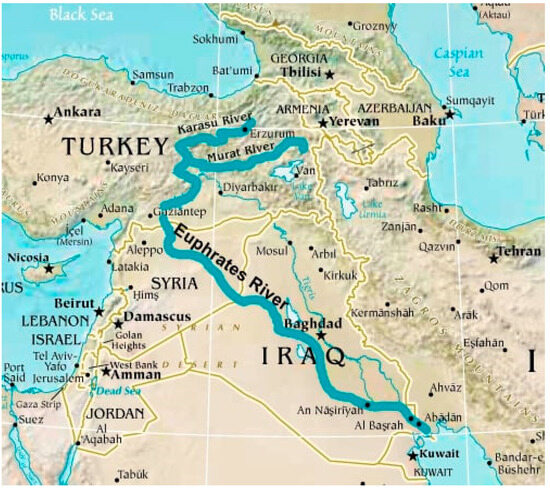
Impacts of the Crisis
- Agriculture and Food Security: Farmers in Syria and Iraq face crop failures, threatening food supplies for millions.
- Displacement: Communities dependent on the river, including Iraq’s Marsh Arabs, are losing their livelihoods, driving migration.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Water scarcity fuels disputes between Turkey, Syria, and Iraq, as upstream damming by Turkey sparks accusations of water weaponization.
- Environmental Loss: The drying river endangers unique ecosystems, with species like the Euphrates softshell turtle at risk.
Solutions and Future Outlook
- Cooperation: Turkey, Syria, and Iraq must negotiate equitable water-sharing agreements to manage the river sustainably.
- Modern Irrigation: Adopting efficient irrigation techniques, like drip irrigation, could reduce water waste.
- Climate Action: Regional and global efforts to combat climate change are critical to restoring rainfall and snowmelt.
- International Support: Aid for water infrastructure and conflict resolution could stabilize the region.
The Euphrates River’s decline is a wake-up call for urgent action. Without coordinated efforts, the region faces worsening shortages, conflict, and ecological collapse. Learn more about the crisis and solutions at MyWaterEarth.com. This post is optimized for Google’s featured snippet by providing a clear, concise overview with structured headings, addressing the question directly, and including key facts from the original article updated with current context.

A River in Distress

Solutions to Save the Euphrates
- Regional Cooperation the Euphrates is a shared river, and its salvation lies in shared responsibility. Turkey, Syria, and Iraq must negotiate equitable water-sharing agreements, prioritizing downstream needs. Past attempts, like the 1987 Turkey-Iraq protocol, have faltered, but a renewed, transparent framework—perhaps mediated by the United Nations—could ensure fair distribution.
- Modernizing Agriculture Switching to efficient irrigation methods, like drip irrigation, could slash water waste by up to 50%. Governments and international organizations could subsidize these technologies for farmers, reducing the strain on the Euphrates while maintaining agricultural output. Training programs to promote sustainable practices would empower communities to adapt.
- Climate Action Global and regional efforts to combat climate change are non-negotiable. Investing in renewable energy to reduce emissions, alongside reforestation in Turkey’s mountains to stabilize snowmelt, could help restore the river’s natural flow. International funding, like the Green Climate Fund, could support these initiatives.
- Rebuilding Infrastructure Conflict-ravaged Syria and Iraq need help to repair and modernize water infrastructure. International aid could fund new treatment plants, efficient canals, and monitoring systems to ensure water reaches those who need it most. Stabilizing the region politically is also key to enabling long-term water management.
- Raising Awareness, The Euphrates crisis needs global attention. Campaigns on platforms like X can amplify the issue, urging action from policymakers and citizens alike. Grassroots movements, supported by NGOs, could pressure governments to prioritize the river’s revival.
Conclusion
Jim Galloway Author/Editor
References:
Discover Magazine – Is the Euphrates River Drying Up?
FAQ’s


