- Periods when fish are more active due to the moon’s position
- Major Times: Occur when the moon is overhead or underfoot
- Duration: 2 hrs.
- Minor Times: Occurs during moonrise/moonset
- Duration: 1 hr.
- Theory: Solunar theory
- Impact: Increases chances of catching fish
- Tools: Solunar calendars/fishing apps
What Are Moon Phases for Fishing
-
Major Moon Phases: These are peak activity periods when fish are most likely to feed aggressively, typically lasting 2-3 hours.
-
Minor Moon Phases: Shorter windows of moderate fish activity, usually lasting 1-2 hours.
Understanding Major and Minor Moon Phases
-
Moonrise and Moonset: When the moon rises or sets, fish often become more active.
-
Moon Overhead and Underfoot: These are the peak times for fishing, as the moon’s gravitational pull is strongest.
-
Secondary Moonrise and Moonset: Shorter bursts of fish activity.
-
Transitional Periods: Times when the moon is not at its peak influence but still affects fish behavior.
How Moon Phases Influence Fish Behavior
-
Tidal Movements: Coastal fish species, such as snook or tarpon, are highly responsive to tidal changes driven by the moon. During major moon phases, stronger tides can push baitfish into feeding zones, attracting predatory fish.
-
Light Levels: The brightness of the moon, especially during a full moon, can make fish more active at night, particularly in clear waters.
-
Barometric Pressure: Moon phases often coincide with changes in barometric pressure, which can stimulate fish feeding.
How Moon Phases Influence Fish Behavior
-
Tidal Movements: Coastal fish species, such as snook or tarpon, are highly responsive to tidal changes driven by the moon. During major moon phases, stronger tides can push baitfish into feeding zones, attracting predatory fish.
-
Light Levels: The brightness of the moon, especially during a full moon, can make fish more active at night, particularly in clear waters.
-
Barometric Pressure: Moon phases often coincide with changes in barometric pressure, which can stimulate fish feeding.
Using Solunar Tables for Fishing Success
-
Find Your Location: Solunar tables are location-specific, so input your fishing spot’s coordinates or nearest city.
-
Identify Major and Minor Periods: Look for the time windows labeled as major (peak activity) and minor (moderate activity).
-
Plan Around Weather and Tides: Combine solunar data with weather forecasts and tide charts for coastal fishing to maximize accuracy.
By understanding and utilizing the Solunar Theory, anglers can optimize their fishing strategies. Paying attention to major and minor periods, moon phases, and seasonal patterns can significantly increase your chances of a successful fishing trip.
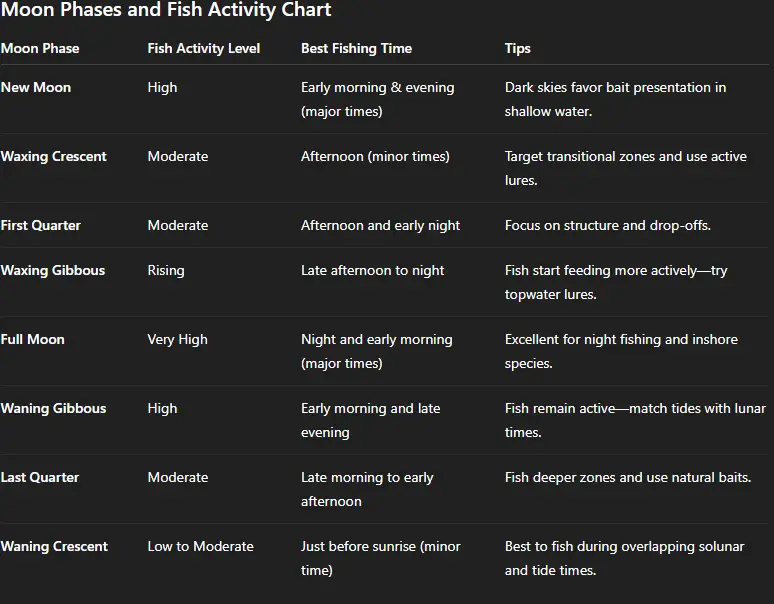
Best Moon Phases for Fishing
While major and minor moon phases are key, certain lunar phases stand out for fishing:
Full Moon: Bright nights increase fish activity, especially for nocturnal feeders like catfish. However, some species may feed less during the day due to high light levels.
New Moon: Darker nights make daytime fishing more productive, as fish are less cautious.
First and Last Quarter: These transitional phases often align with balanced tidal movements, creating ideal conditions for coastal and freshwater fishing.
For example, a major moon phase during a new moon at dawn could be the perfect time to target largemouth bass in a lake or redfish in a coastal estuary.

Tips for Fishing During Major and Minor Moon Phases
-
Time Your Trips: Arrive at your fishing spot 30 minutes before a major or minor phase to set up and capitalize on peak activity.
-
Match Bait to Conditions: Use live bait or lures that mimic local prey during major phases, as fish are more aggressive.
-
Focus on Structure: During minor phases, target fish near cover like docks, weed beds, or drop-offs where they may be resting.
-
Monitor Weather: Overcast skies or light rain can enhance fishing during moon phases by reducing light penetration.
-
Keep a Log: Record your catches with details about moon phases, weather, and location to identify patterns over time.