One of the most frequent events that happen when you own any size swimming pool is when the pH of the pool water slips down and is out of range where it needs to be to keep the water properly sanitized by chlorine and snowballs out of control. This can happen fast, especially in those hot summer months. What are the signs of Low pH in a Pool?
- Cause Chlorine By-Products(Chloramine)
- Impact chlorine effectiveness
- Eye irritation
- Cause etching of plaster, grout, stone, concrete, & tiling in concrete pools
- Vinyl surfaces will also become brittle, risk of cracks & tares
- This can result in staining & cloudy pool H2O
- Cause Irritated skin
- Affect Breathing
When organic compounds are mixed with chlorine-treated water, by-products are created. These are gases called Chloramines. Chloramines lead to that unusual chlorine smell that we might think is a sign of a clean pool. This sign is of low pH and low total alkalinity in a pool and the beginning of bad things happening to your pool.
Introduction:
Low pH in Swimming Pools
The most immediate signs of low pH in a swimming pool are on swimmers’ skin and eye irritation in swimmers, then eventually etching of the plaster grout and concrete, and the corrosion of pool equipment and accessories.
Long before you see the effects of low pH in your pool you should pick it up when you test your pool water. If the pH level is below 7.2, you should raise it. If you miss this event it’s already too late.
A good pH level in the pool is essential for a pleasant swimming experience. Too low a pH level makes the water acidic and will have negative consequences on water chemistry. To illustrate the importance of regular water checks, the potential consequences of too low a pH level. The pH level is too low when it falls below 7.0 pH.
Too low a pH has a significant influence on the effect of the chlorine. If the pH level is too low, you will have to add a large amount of shock chlorine to ensure proper disinfection of the water. You will end up at the Pool Supply Store. Open your wallet. By the time you figure it out, it will cost you.
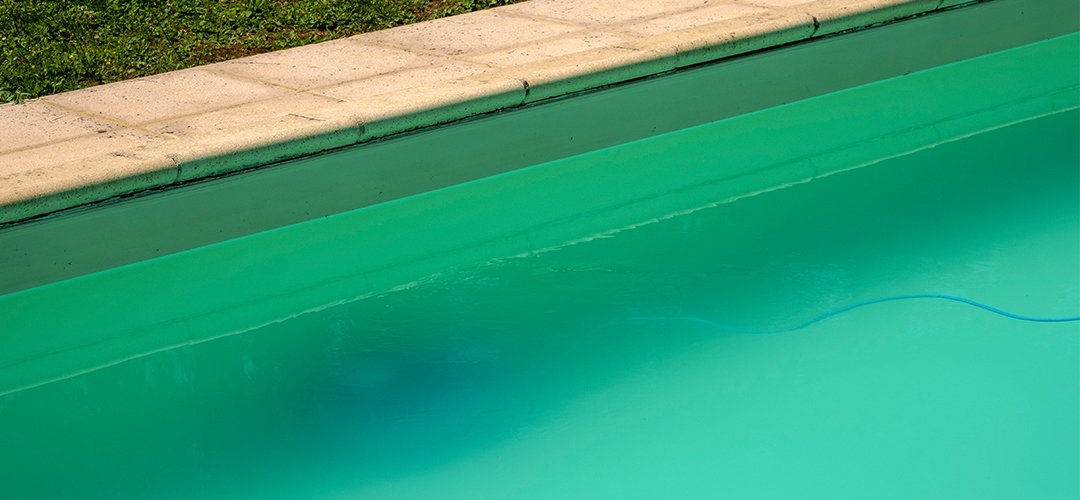
If the pH level becomes too low, it may also cause the water to turn cloudy which is not desirable for family and friends to swim in. Pool water will start to smell sour especially when the surface of the water is disturbed.
Too low a pH level in the pool may cause those typical red eyes and even itching from low pH and large amounts of Chlorine called Chloramines. You will compensate for bad Chlorine readings by adding more chlorine. It makes for a less pleasant swimming experience.
Softer water, with a higher pH level, is much more pleasant! The acid water will also adversely affect your swimming gear, pool floaters, and items in and close to the pool water. Swimwear will wear faster and, over time, become subject to bleaching.
If the pH level is too low, the water becomes acidic. This acid water can cause corrosion on the heat pump, thereby reducing its service life. More money More problems.
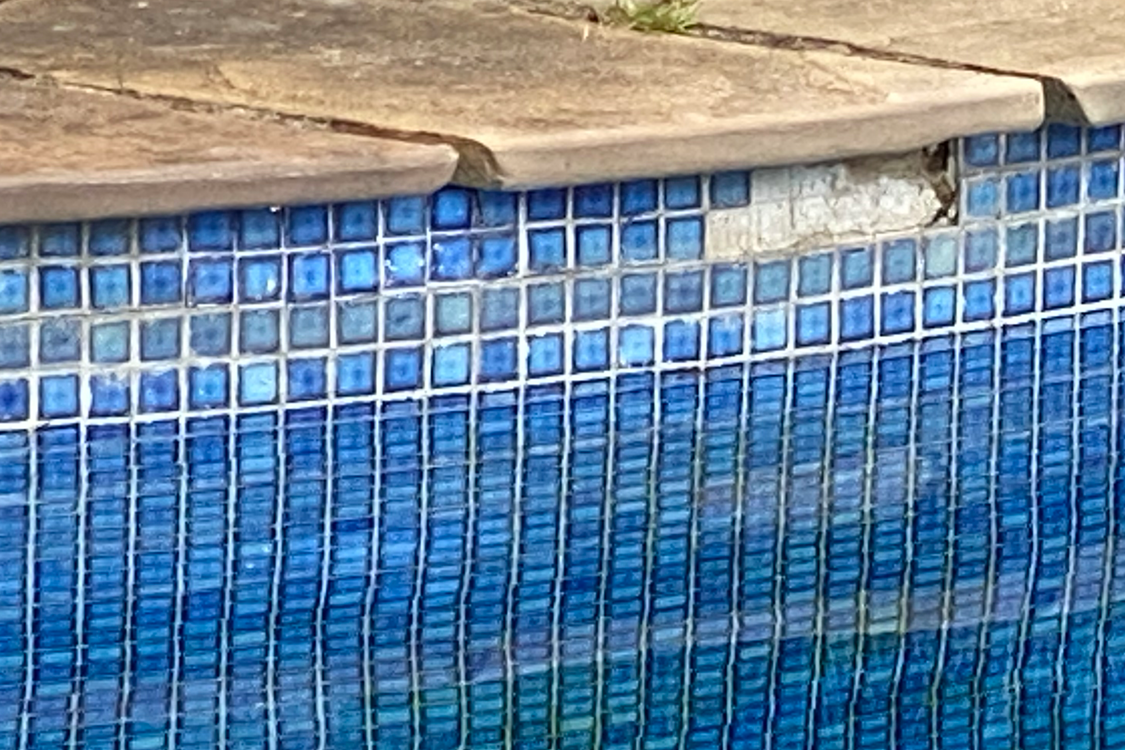
The pH level of the water will also loosen the mosaic tiles in an inground pool in the long term. This will put a great strain on your beautiful tiles. As the mosaic tiles become rougher they will also promote algae growth, especially in the grout holding them together, which should be prevented at all costs.
- Sudden rise in water temperature
- Water features that take water out of the pool aerating it
- Release of Carbon Dioxide(CO2)
- Swimmers using sunblock or lotions
- Liquid bleach, such as Clorox has a pH level of around 11-13
- New pool surface and walls leaching in H2O
- Off-gassing ………………………………………………………………………………. Read more
The main culprits are:
- Chlorine tablets with stabilizer (CYA)-2.9 pH
- Rain 5–5.5 pH
- Children’s urine 6.0 pH
- Shampoos 4.5-6.0.pH
- Beer 4.00–5.00.& Ales 3.00–6.00 pH
- Coffee 4.85-5.1 pH & Soda 2.5 to 3.5 pH
- Leaves that fall are below 6 pH .………………………………………………… Read more

References:
Pool Smith Technologies- The pH Level in Your Pool Dropped
FAQ’s
What are the signs of low pH levels in a pool?
Answer: Signs of low pH levels in a pool include skin and eye irritation, itchy or dry skin, red eyes, corrosion of metal components, deterioration of pool surfaces, reduced effectiveness of chlorine, increased risk of algae growth, and potential bacterial contamination.
How can I test the pH level of my pool water?
Answer: You can test the pH level of your pool water using test strips, liquid test kits, or digital pH testers. Follow the instructions provided with the testing method you choose to obtain accurate results.
How do I adjust pH levels in my pool?
Answer: You can adjust pH levels in your pool using a pH increaser to raise pH levels or a pH decrease to lower pH levels. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and test the water frequently to achieve and maintain the desired pH level.
How often should I test the pH level of my pool water?
Answer: It’s recommended to test the pH level of your pool water at least once a week, especially during the swimming season when pH levels can fluctuate more frequently due to increased use and environmental factors.
What should I do if I have trouble maintaining proper pH levels in my pool?
Answer: If you have trouble maintaining proper pH levels in your pool despite your best efforts, consider seeking professional help from a pool service technician. They can assess your pool’s specific needs and provide expert guidance on how to address pH issues effectively.