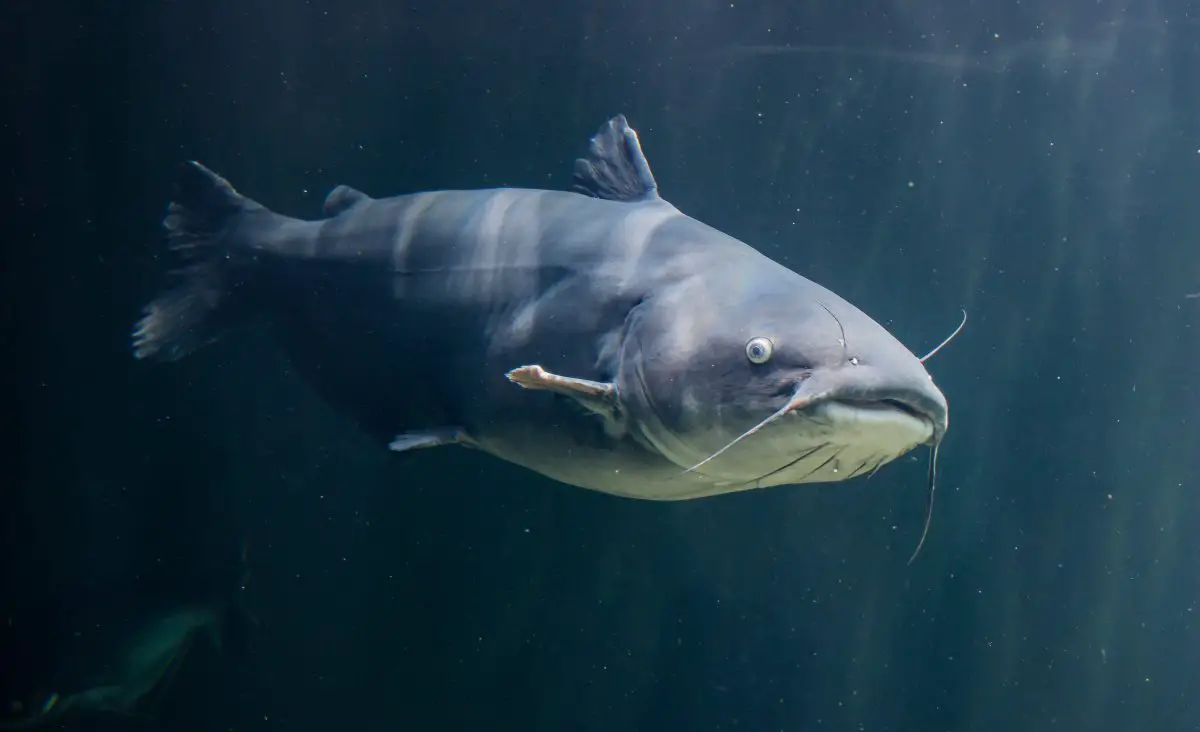
Until you’ve experienced it, nothing can prepare you for experiencing the astonishing power of a big 50-pounder trophy-class fish like a Blue Catfish it can rival any fresh or saltwater game fish you can encounter. What Are Ideal Water Conditions for Blue Catfish?
Ideal Water Conditions for Blue Catfish:
- Temperature: 70-85°F
- pH: 6.5-7.5
- Oxygen: well-oxygenated water
- Water quality: low ammonia, nitrites, nitrates
- Hardness: Moderate
- Substrate: sandy or gravel
- Habitat: ample hiding spots
- Filtration: efficient filtration system
When it comes to fishing for blue cats, it’s important to know where to find them. Blue cats are known to be bottom-dwelling fish that prefer deep, slow-moving waters. In this section, we will explore some of the ideal for blue cats, including river channels, deep holes, and creek junctions.
Introduction:
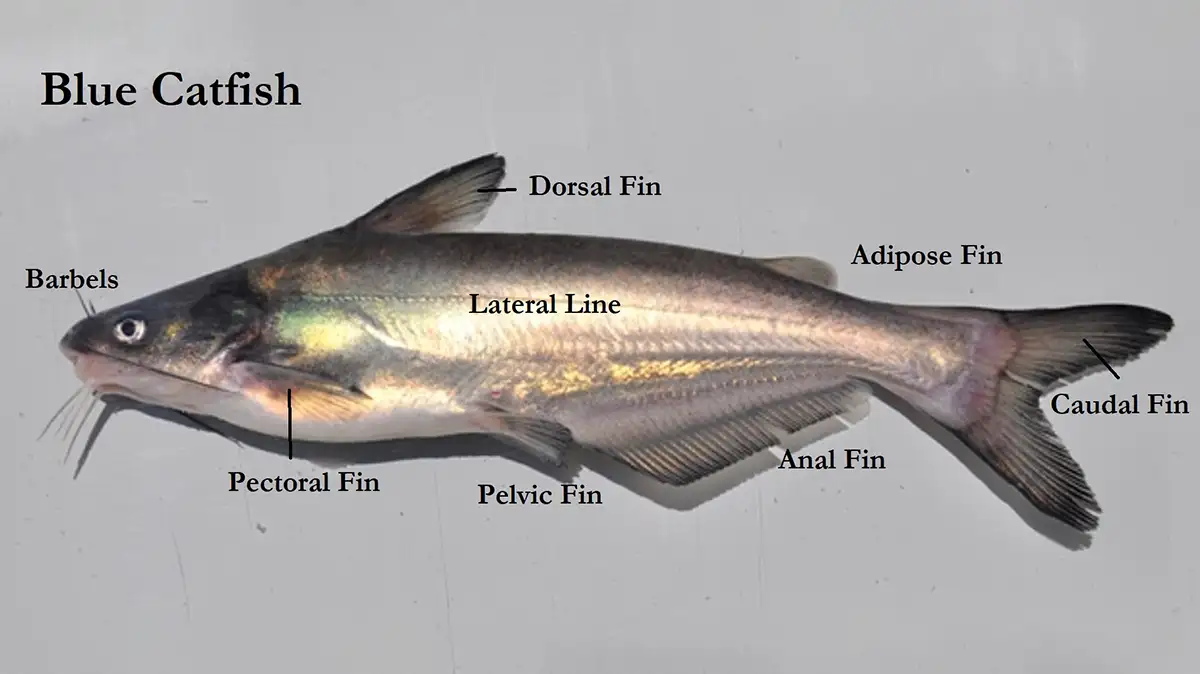
Blue catfish (Ictalurus furcatus) are a prominent species of freshwater fish native to North America, particularly found in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs throughout the Mississippi River basin and its tributaries. Recognized for their striking blue-gray coloration and impressive size, blue catfish are highly sought after by anglers and aquarists alike.
These majestic fish can grow to substantial lengths, with individuals reaching weights exceeding 100 pounds not uncommon in their natural habitat. Their large size, coupled with their voracious appetite and strong fighting ability, make them prized catches among recreational fishermen.
Blue catfish are also valued for their role in aquatic ecosystems, where they serve as apex predators, helping to regulate fish populations and maintain ecological balance. In recent years, blue catfish have gained popularity in aquaculture and aquaponics systems, further highlighting their versatility and adaptability to various aquatic environments.
Throughout this guide, we will delve deeper into the specific water conditions necessary for the health and well-being of blue catfish, ensuring optimal growth and vitality in both natural and artificial habitats
References:
Reel Rapture-FISHING FOR BLUE CATS: TECHNIQUES, BAIT, SPOTS, BEHAVIOR, AND GEAR
FAQ’s
How big do blue catfish grow?
Blue catfish can grow to impressive sizes, with individuals commonly reaching lengths of 24 to 48 inches and weights exceeding 100 pounds in their natural habitat. In optimal conditions, blue catfish have the potential to grow rapidly, particularly in large bodies of water with abundant food sources.
What is the lifespan of blue catfish?
Blue catfish have a relatively long lifespan compared to many other freshwater fish species, with individuals often living for 20 to 30 years in the wild. Factors such as water quality, habitat conditions, and available food resources can influence the lifespan of blue catfish in both natural and artificial environments.
Are blue catfish aggressive?
Blue catfish are generally not considered aggressive towards humans, but they can exhibit territorial behavior and may become defensive if provoked or threatened. In their natural habitat, blue catfish are apex predators and may display aggressive feeding behaviors, especially when competing for food or territory.



