Angling for snook is always challenging and many times frustrating and they readily take both artificial and live bait. Generally, it is best to fish with artificial lures in the winter and to fish with live bait in the spring and summer. What are Ideal Water Conditions for Snook?
Introduction:
Water conditions are paramount for the well-being of snook, a species highly regarded for its significance in both ecological and recreational contexts. These conditions encompass a range of environmental factors that directly influence the physiological processes, behavior, and overall health of snook populations.
Among the key factors contributing to ideal water conditions are temperature, pH levels, salinity levels, oxygen levels, water quality parameters, and habitat considerations. Each of these factors plays a crucial role in sustaining optimal conditions for snook, ensuring their survival, growth, and reproductive success.
From maintaining stable temperatures to regulating pH levels and monitoring water quality parameters, proactive management of these factors is essential for promoting the thriving existence of snook populations in both natural and captive environments. Understanding and addressing these factors contribute not only to the welfare of snook but also to the preservation of the delicate aquatic ecosystems they inhabit.
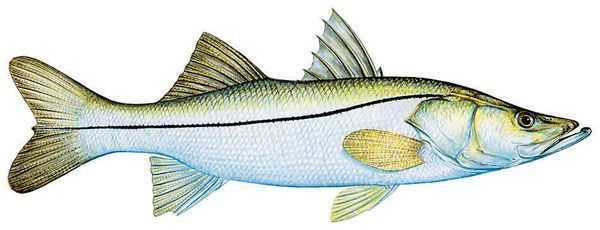
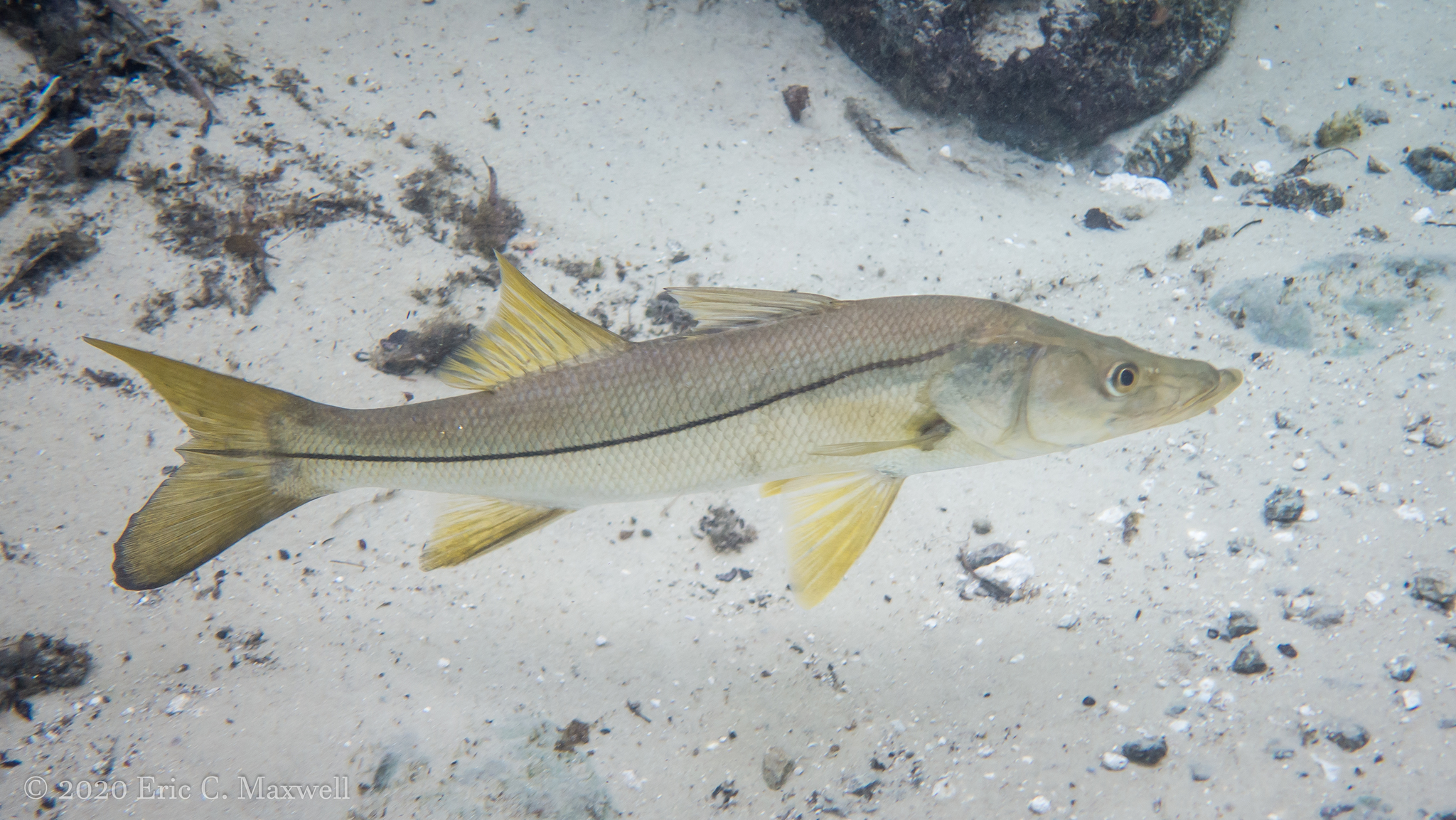
Snook have long, concave snouts with jutting underjaws. The lateral line is pigmented and distinct, extending well into the tail. Coloration ranges from dark brown on the back to silvery on the sides and white below. The two dorsal fins are well separated. Snook is a fine food fish and can be cooked as other bony fish.
What are Ideal Water Conditions for Snook
The ideal water conditions for snook involve maintaining a temperature range between 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C), suitable pH levels around 7.0 to 8.5, and salinity levels typically between 10 to 35 parts per thousand (ppt). Adequate oxygen levels should be ensured, preferably above 5 parts per million (ppm), to support respiration. Additionally, water quality parameters such as ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates should be kept at low levels to prevent stress and maintain overall health. Creating a habitat that mimics their natural environment with appropriate substrate, vegetation, and structural complexity further enhances the well-being of snook populations.
Ideal water conditions for snook in the wild include:
- Temperature: 70-78°F (21-26°C)
- Salinity: 20-35 parts per thousand (ppt)
- pH: 7.2-8.2
- Dissolved oxygen: >5 milligrams per liter (mg/L)
- Clear water with moderate flow
- Presence of habitat structures for shelter and feeding
- Adequate depth for foraging and spawning
- Low turbidity for visibility
Ideal Water Temperature for Snook
Snook thrive within a specific temperature range, typically between 75°F to 85°F (24°C to 29°C), depending on their developmental stage and environmental conditions.
Within this range, snook exhibit optimal metabolic rates, growth, and reproductive activity, essential for maintaining healthy populations.
Effects of Temperature Fluctuations on Snook:
Stress: Rapid or extreme fluctuations in temperature can induce stress responses in snook, compromising their immune function and increasing susceptibility to diseases.
Behavioral Changes: Temperature variations outside the optimal range may alter snook behavior, leading to reduced feeding activity, altered swimming patterns, and increased aggression.
Reproductive Success: Inconsistent temperatures can disrupt spawning behaviors and the development of eggs and larvae, impacting the reproductive success of snook populations.
Strategies for Maintaining Consistent Water Temperatures: The ideal water temperature for snook in the wild typically ranges from 21 to 26°C. Within this temperature range, snook are most active and exhibit optimal physiological functions, including feeding, growth, and reproduction.
Snook thrive in warmer water temperatures, ideally between 70 to 78°F as it supports their metabolism and overall health. In colder waters, their activity may decrease, and they might seek out warmer areas or estuaries for refuge. Conversely, excessively high temperatures can stress snook and lead to reduced feeding activity or even mortality, emphasizing the importance of suitable temperature ranges for their survival and well-being in the wild.

Ideal Water pH for Snook
Ideal Water Salinity for Snook
Ideal Dissolved Oxygen for Snook
Ideal Water Quality Parameters Affecting Snook
In the wild, several water quality parameters significantly affect snook. Optimal conditions include water temperatures ranging from 70 to 78°F (21 to 26°C) and salinity levels between 20 to 35 parts per thousand (ppt). Snook also prefers pH levels within the range of 7.2 to 8.2 and dissolved oxygen concentrations exceeding 5 milligrams per liter (mg/L). Additionally, clear water with moderate flow and the presence of suitable habitat structures for shelter and feeding contribute to ideal conditions for snook in their natural habitat.
References:
Texas Parks & Recreation-Common Snook
Florida Fish & Wildlife-Common Snook in Florida
FAQ’s
To catch snook, use live bait such as mullet, pinfish, or shrimp, and fish near mangroves, bridges, or docks where snook like to hide. Cast your bait along the edges of structure and retrieve slowly, as snook are ambush predators that often strike when prey passes by.
Are Snook good to eat?
Snook are considered excellent table fare by many anglers, with firm, white flesh and a mild, sweet flavor. However, due to conservation concerns and regulations in certain areas, it’s important to check local fishing regulations regarding size limits, catch seasons, and consumption advisories before harvesting snook for consumption.
When is Snook season?
Snook season varies depending on location, but it typically coincides with their spawning season and migratory patterns. In Florida, for example, snook season opens in the spring and closes in the winter to protect spawning populations during their peak reproductive periods.