Sturgeon inhabit rivers and coastal waters from Canada to Florida and can live for 30-60 years. The sturgeon family is the most primitive of all bony fish, with ancestors dating back to the Cretaceous period more than 120 million years ago. What are Ideal Water Conditions for Sturgeon?
Ideal water conditions for sturgeon include:
- Cool to moderate temperatures (50-68°F)
- Adequate oxygen levels (>5 mg/L)
- Clear water for visibility
- Moderate to slow currents
- Diverse habitat structures,
- Suitable spawning grounds
- Balanced salinity for anadromous species
- Clean substrate
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction:
Sturgeon, ancient and majestic, represents a family of fish that has remained relatively unchanged for millions of years. These prehistoric giants are known for their large size, long lifespan, and distinctive appearance, characterized by their elongated bodies and rows of bony plates called scutes. Sturgeon are primarily freshwater fish, although some species may venture into brackish or saltwater environments during certain stages of their life cycle.
Popular regions for sturgeon fishing include freshwater bodies such as rivers, lakes, and estuaries, where sturgeon populations thrive. Some of the most renowned sturgeon fishing destinations include the Fraser River in British Columbia, the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States, and the Danube River in Europe. These regions offer ample habitat for sturgeon and attract anglers seeking the thrill of landing these ancient behemoths.
Common techniques used in sturgeon fishing vary depending on the location and regulations governing the fishery. In many cases, anglers employ bottom fishing rigs with heavy sinkers and sturdy tackle to target sturgeon, which are often found near the riverbed or lake bottom. Baits such as nightcrawlers, squid, shrimp, and fish roe are commonly used to entice sturgeon to bite. Additionally, specialized techniques such as drift fishing, anchor fishing, and even kayak fishing are popular among sturgeon anglers seeking to explore different strategies for success.
Despite their allure as a sportfish, sturgeon populations face numerous threats, including habitat loss, overfishing, and pollution. As such, the importance of sturgeon conservation and responsible angling practices cannot be overstated. Many regions have implemented strict regulations governing sturgeon fishing, including catch-and-release policies, size limits, and seasonal closures to protect vulnerable populations and ensure their long-term survival. Anglers play a crucial role in sturgeon conservation efforts by adhering to these regulations, practicing ethical angling practices, and supporting conservation initiatives aimed at preserving sturgeon habitats and populations for future generations to enjoy.

What are Ideal Water Conditions for Sturgeon
The ideal water conditions for sturgeon vary depending on the species and their habitat, but generally include:
- Temperature: Sturgeon prefer cool to moderate water temperatures, typically between 50°F to 68°F (10°C to 20°C). However, specific temperature preferences may vary among sturgeon species.
- Oxygen Levels: Adequate dissolved oxygen levels are crucial for sturgeon survival. They require well-oxygenated water, typically with levels above 5 mg/L, to support their metabolism and activity.
- Water Clarity: Sturgeon are often found in areas with good water clarity, where they can effectively detect prey and navigate their surroundings. While they can adapt to varying levels of water clarity, they may prefer clearer waters for feeding and spawning activities.
- Flow and Current: Sturgeons are adapted to living in riverine environments with varying flow rates and currents. They may prefer areas with moderate to slow currents, such as deep pools and backwaters, where they can conserve energy and access food resources.
- Habitat Structure: Sturgeon are associated with complex habitat structures, such as deep holes, submerged logs, rocky bottoms, and underwater vegetation. These habitats provide shelter, cover, and feeding opportunities for sturgeon throughout their life stages.
- Spawning Habitat: A suitable spawning habitat is critical for sturgeon reproduction. They typically spawn in areas with clean substrate, moderate flow rates, and suitable water depths, such as gravel bars, sandbanks, and riffle areas.
- Salinity: Some sturgeon species, such as the Atlantic sturgeon and the beluga sturgeon, are anadromous and may inhabit estuarine or brackish waters during certain stages of their life cycle. These species may require specific salinity levels for optimal growth and survival.
Overall, maintaining suitable water conditions is essential for the conservation and management of sturgeon populations.
Understanding and protecting these key habitat attributes can help ensure the long-term sustainability of sturgeon fisheries and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Ideal Current and Flow Conditions for Sturgeon Fishing
Sturgeon Preferences for Current and Flow Conditions: Sturgeons are highly adapted to living in rivers and other freshwater environments with varying current and flow conditions. While preferences may vary among species and individuals, sturgeon generally exhibit certain behaviors in response to current and flow dynamics.
How Current Affects Sturgeon Feeding and Positioning:
- Feeding Behavior: Sturgeon are often opportunistic feeders, taking advantage of currents to detect and capture prey more effectively. Strong currents can dislodge bottom-dwelling organisms, such as crustaceans and small fish, making them more accessible to sturgeon foraging along the riverbed.
- Positioning: Sturgeon may utilize currents to conserve energy or maintain their position within a river system. They may seek out areas with slower currents, such as eddies or slack water behind obstacles like boulders or bridge pilings, where they can rest while still maintaining access to food.
Tips for Fishing in Varying Current Strengths:
- Adjust Weights and Rigs: When fishing in strong currents, anglers may need to increase the weight of their rigs to keep bait or lures near the riverbed, where sturgeon are more likely to feed. Using heavier sinkers or sinker rigs can help maintain bottom contact and prevent baits from being swept away by the current.
- Target Structure: Focus on fishing near natural or man-made structures that disrupt current flow, such as bridge abutments, submerged logs, or deep pools. These areas provide shelter from strong currents and may attract sturgeon seeking refuge or feeding opportunities.
- Drift Fishing: Drift fishing techniques, such as drift rigs or drift boats, can be effective in rivers with moderate to strong currents. Anglers can allow their baits to drift naturally with the current while covering a wide area of the river, increasing the chances of encountering actively feeding sturgeon.
- Anchor Strategically: In areas with variable current speeds, anglers can anchor their boats strategically to position themselves within the sturgeon’s feeding zone. Experiment with different anchor placements to find the optimal position relative to current flow and structure.
- Be Patient: Fishing in strong currents can be challenging, requiring patience and persistence. Be prepared to adjust your tactics and adapt to changing conditions throughout the day. Sturgeon may be more active during periods of reduced current flow or tidal changes, so timing your fishing trips accordingly can improve your chances of success.

Ideal Water Oxygen Levels for Sturgeon
Impact of Low Oxygen Levels on Sturgeon Behavior: Low oxygen levels can have significant impacts on sturgeon behavior and overall habitat suitability. Sturgeons are highly sensitive to changes in dissolved oxygen levels due to their large size and metabolic requirements. When oxygen levels in the water decrease below certain thresholds, sturgeon may exhibit the following behaviors:
- Reduced Activity: Sturgeon may become lethargic or less active in response to low oxygen levels, conserving energy to cope with stressful conditions.
- Altered Feeding Patterns: Low oxygen levels can suppress sturgeon’s appetite and feeding behavior, making them less likely to actively pursue prey or take bait.
- Vertical Movement: Sturgeon may move vertically within the water column to access areas with higher oxygen concentrations, such as near the surface or in areas with upwelling currents.
- Increased Vulnerability to Predation: Sturgeon weakened by low oxygen levels may become more susceptible to predation by opportunistic predators, further impacting population dynamics.
Techniques for Identifying Areas with Adequate Oxygen Levels:
Water Quality Monitoring: Regular monitoring of water quality parameters, including dissolved oxygen levels, can provide valuable insights into habitat conditions for sturgeon. Anglers can access real-time or historical data from government agencies, environmental organizations, or research institutions.
Oxygen Sensors: Portable oxygen sensors or meters can be used to measure dissolved oxygen levels directly in the water at various depths and locations. These devices provide on-the-spot data to assess oxygen concentrations and identify areas with adequate oxygen levels for sturgeon.
Visual Observations: Certain visual cues can indicate areas with potential oxygenation, such as surface turbulence, bubbling, or the presence of aquatic vegetation. Sturgeon may congregate in these areas to access higher oxygen concentrations.
Temperature and Flow Patterns: Factors such as water temperature and flow dynamics can influence oxygen levels in aquatic environments. Areas with cooler temperatures or increased water movement, such as riffles or rapids, may have higher oxygen levels due to increased oxygenation and mixing.
Habitat Characteristics: Sturgeon tend to prefer habitats with specific characteristics, including deep pools, well-oxygenated riffles, and areas with abundant aquatic vegetation. Identifying and targeting these habitat types can increase the likelihood of encountering sturgeon in areas with adequate oxygen levels.
Ideal Moon Phase for Sturgeon Fishing
Sturgeon fishing, like many other types of fishing, can be influenced by various factors, including the moon phase. While there’s no definitive answer as to which moon phase is the absolute best for catching sturgeon, certain phases may offer favorable conditions for anglers. Here are some considerations regarding the moon phase and sturgeon fishing:
- New Moon and Full Moon: Some anglers believe that both the new moon and full moon phases can be productive for sturgeon fishing. During these phases, there can be stronger tidal movements, which may trigger sturgeon to feed more actively as they take advantage of the increased water flow to find food.
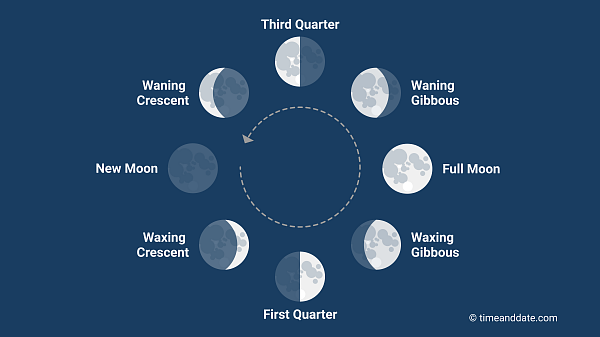
Moon Phases - Incoming Tide: Regardless of the moon phase, many anglers prefer to fish for sturgeon during incoming tides, which typically occur around the time of the new moon and full moon. During incoming tides, water and food are carried into areas where sturgeon feed, increasing the likelihood of encountering feeding fish.
- Low Light Conditions: Sturgeons are known to be more active during periods of low light, such as early morning, late evening, and nighttime. Therefore, fishing during dawn, dusk, or overnight, especially around the new moon and full moon phases when natural light is limited, can be advantageous.
- Solunar Periods: Some anglers also pay attention to major and minor solunar periods, which are believed to coincide with increased fish activity due to the gravitational forces of the moon and sun. Fishing during these periods, which occur multiple times throughout each day, may improve the chances of catching sturgeon.
- Personal Experience: As with any type of fishing, anglers’ personal experiences and observations play a crucial role. Keeping a fishing journal and noting the moon phase during successful fishing trips can help anglers identify patterns over time and develop effective strategies for targeting sturgeon.
While the moon phase can be a factor to consider, other factors such as water temperature, depth, current flow, and the presence of baitfish will also influence sturgeon behavior and fishing success. Experimenting with different techniques and adjusting tactics based on changing conditions can help anglers maximize their chances of catching sturgeon regardless of the moon phase.
Ideal Weather Conditions for Sturgeon Fishing
Influence of Weather on Water Conditions and Sturgeon Behavior:
- Temperature: Weather conditions such as air temperature can directly impact water temperature, influencing sturgeon behavior. Warmer weather may increase water temperatures, leading to heightened sturgeon activity and feeding, while colder weather can have the opposite effect.
- Barometric Pressure: Changes in barometric pressure associated with weather systems can affect sturgeon feeding behavior. Falling barometric pressure, often preceding stormy weather, may trigger increased feeding activity in the sturgeon, while rising pressure may cause them to become less active.
- Precipitation: Rainfall and runoff can impact water clarity, flow rates, and oxygen levels in rivers and lakes, all of which can influence sturgeon behavior. Heavy rainfall can lead to increased turbidity and higher flow rates, potentially dispersing sturgeon or altering their feeding patterns.
How to Adapt Fishing Strategies Based on Weather Forecasts:
- Monitor Weather Forecasts: Stay informed about upcoming weather conditions, including temperature fluctuations, barometric pressure changes, and precipitation forecasts. Online weather services, mobile apps, and marine forecasts are valuable resources for anglers planning fishing trips.
- Adjust Timing: Plan fishing outings during periods of favorable weather conditions, such as stable barometric pressure and moderate temperatures. Consider scheduling fishing trips during early morning or late evening hours when sturgeon may be more active.
- Experiment with Baits and Presentation: Adapt bait selection and presentation techniques based on weather conditions and sturgeon behavior. For example, during periods of falling barometric pressure, try using scent-enhanced baits or varying retrieval speeds to entice feeding sturgeon.
- Target Sheltered Areas: Seek out sheltered areas or structures, such as deep pools, submerged logs, or protected coves, where sturgeon may seek refuge from adverse weather conditions. These areas provide opportunities to continue fishing comfortably and safely.
- Stay Flexible: Be prepared to adjust fishing strategies in response to changing weather conditions and sturgeon behavior. Remain adaptable and open to trying different techniques or locations to maximize success on the water.
Safety Considerations When Fishing in Adverse Weather Conditions:
- Monitor Weather Alerts: Stay informed about weather warnings, including severe storms, high winds, or lightning advisories. Heed weather alerts and took appropriate precautions to ensure personal safety.
- Use Proper Safety Equipment: Wear appropriate safety gear, such as life jackets, rain gear, and non-slip footwear, to protect against adverse weather conditions and potential hazards on the water.
- Seek Shelter: In the event of inclement weather, seek shelter in a sturdy structure or return to shore if conditions become unsafe for fishing. Avoid exposure to lightning, strong winds, or rough seas.
- Notify Others: Inform friends, family members, or fellow anglers about your fishing plans, including your location and expected return time. Establish a communication plan in case of emergencies.
- Exercise Caution: Practice caution when navigating waterways and operating watercraft in adverse weather conditions. Be aware of changing conditions and exercise good judgment to avoid accidents or mishaps.
Conclusion:
Understanding the ideal water conditions for sturgeon fishing is paramount to angling success. These conditions encompass factors such as water temperature, clarity, flow, and oxygen levels, all of which profoundly influence sturgeon behavior and feeding patterns. However, merely knowing the optimal conditions is not enough; anglers must engage in continuous observation and adaptation while on the water.
Weather, time of day, and seasonal variations can all affect water conditions and sturgeon activity, necessitating flexibility in fishing strategies. By continuously monitoring and adjusting to changing conditions, anglers can maximize their chances of success. This requires leveraging technology, such as depth sounders and water temperature sensors, to gather real-time data and make informed decisions. Applying knowledge of water conditions is not just about catching fish; it’s also about responsible angling practices and conservation efforts. By understanding and respecting the environment in which sturgeon thrive, anglers can contribute to the long-term sustainability of sturgeon populations for future generations to enjoy.

Atlantic Sturgeon and Climate Change: Warming Water Impacts Spawning and Development
FAQ’s
- Where are the best locations for sturgeon fishing?
The best locations for sturgeon fishing are often found in large rivers, deep lakes, and estuarine areas with suitable habitat and water conditions. Popular sturgeon fishing destinations include the Fraser River in British Columbia, the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States, and the Danube River in Europe.
- What are the differences between various species of sturgeon?
The differences between various species of sturgeon can include:
- Size: Sturgeon species vary greatly in size, with some reaching lengths of over 20 feet (6 meters) and weighing hundreds of pounds, while others are much smaller.
- Range: Different sturgeon species inhabit distinct geographic regions, including rivers, lakes, and coastal areas around the world.
- Habitat: Sturgeon species have specific habitat preferences, ranging from freshwater rivers and lakes to estuarine and marine environments.
- Appearance: Sturgeon species may differ in their physical characteristics, including body shape, coloration, and the presence of features such as barbels and scutes.
- Behavior: Sturgeon species exhibit various behaviors related to feeding, migration, and spawning, influenced by factors such as habitat, water conditions, and life stage.
- Life Cycle: Sturgeon species have unique life cycles, including spawning behaviors, larval development, and age at maturity, which can vary among species.
- Conservation Status: Sturgeon species face different conservation challenges, with some listed as endangered or threatened due to factors such as overfishing, habitat loss, and pollution.
Examples of sturgeon species include the Atlantic sturgeon, beluga sturgeon, white sturgeon, lake sturgeon, and green sturgeon, each with its own characteristics and ecological importance.
- How do I locate a sturgeon in a river or lake?
To locate a sturgeon in a river or lake, focus on deep pools, submerged structures like logs or boulders, and areas with moderate to slow currents. Using fish finders or depth sounders can help identify potential sturgeon habitat features while observing surface activity such as rolling or jumping sturgeon may indicate their presence in the area.


