U.S. wild-caught Pacific yellowfin tuna is a smart seafood choice because it is sustainably managed and responsibly harvested under U.S. regulations. What Are Ideal Water Conditions for Yellowfin Tuna?
Ideal Water Conditions for Yellowfin Tuna
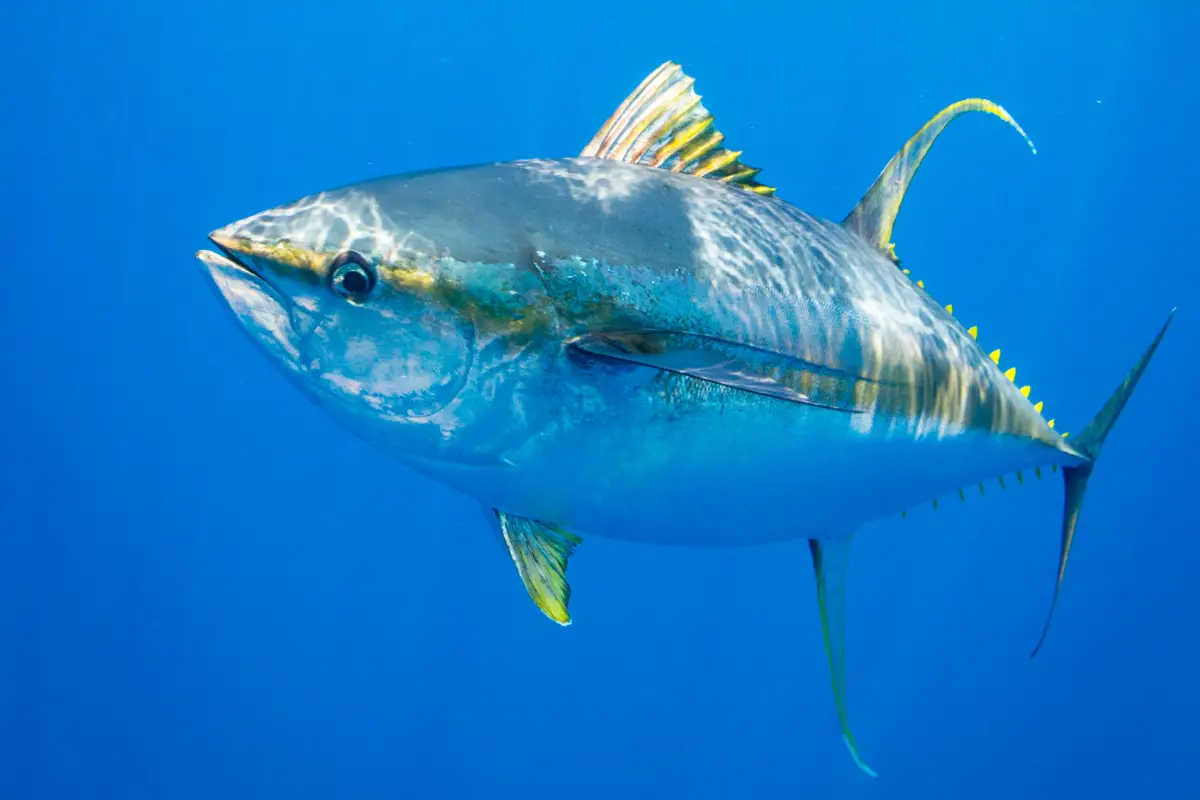
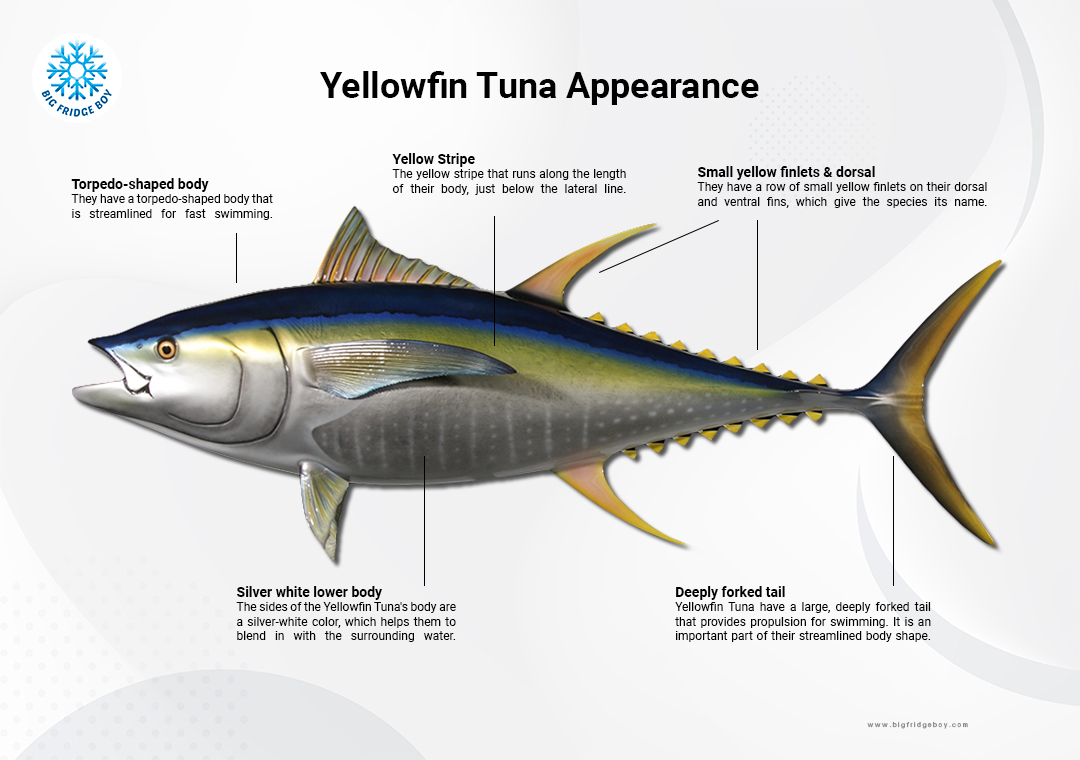
Yellowfin tuna are torpedo-shaped. They are metallic dark blue on the back and upper sides and change from yellow to silver on the belly. True to their name, their dorsal and anal fins and finlets are bright yellow. An adult yellowfin tuna can be distinguished from other tunas by its long, bright-yellow dorsal fin and a yellow stripe down its side. Yellowfin tuna grow fast, up to 6 feet long and 400 pounds, and have a somewhat short life span of 6 to 7 years. Most yellowfin tuna can reproduce when they reach age 2.
Introduction:
Yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) are large, migratory fish found in tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide. They belong to the family Scombridae, which also includes other popular tuna species like bluefin and skipjack. Yellowfin tuna are highly prized for their firm, flavorful flesh and are a staple in seafood markets and restaurants globally.
These sleek, streamlined fish are known for their distinct yellow fins and metallic blue backs, with a silver underside. They have powerful, torpedo-shaped bodies built for speed and endurance, allowing them to travel long distances in search of prey. Yellowfin tuna are voracious predators, feeding primarily on smaller fish, squid, and crustaceans. They are highly migratory, often traveling in large schools across vast stretches of ocean. Their migrations are influenced by various environmental factors, including water temperature, currents, and food availability.
Commercially, yellowfin tuna are harvested for their meat, which is prized for its quality and versatility. However, overfishing and habitat degradation pose significant threats to yellowfin tuna populations, prompting conservation efforts to ensure their sustainable management.
Overall, yellowfin tuna play a crucial ecological and economic role in marine ecosystems, making them a focal species for fisheries management and conservation initiatives worldwide.
What Are Ideal Water Conditions for Yellowfin Tuna
Ideal water conditions for yellowfin tuna include warm temperatures ranging from 20°C to 30°C, stable salinity levels typically between 34 to 36 parts per thousand, and adequate oxygen levels for respiration. Yellowfin tuna prefer depths ranging from the surface to several hundred meters deep, often utilizing nutrient-rich areas and ocean currents for feeding and migration.
Clear, calm weather conditions with stable or rising barometric pressure are conducive to successful yellowfin tuna fishing. While specific tide or moon phase preferences may vary among anglers, yellowfin tuna can be caught throughout the tidal and lunar cycles, with factors like bait availability and fishing techniques also playing significant roles.
Ideal Water Temperature for Yellowfin Tuna
Optimal Temperature Range for Yellowfin Tuna Yellowfin tuna thrives in tropical and subtropical waters where temperatures are relatively warm. The optimal temperature range for yellowfin tuna typically falls between 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F). Within this range, yellowfin tuna exhibit optimal physiological functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Temperatures outside this range can impact their behavior, health, and distribution.
B. Impact of Water Temperature on Yellowfin Tuna Behavior and Distribution
- Migration Patterns: Water temperature influences the seasonal movements and migration patterns of yellowfin tuna. They tend to follow temperature gradients, migrating towards warmer waters during cooler months and moving to cooler waters during warmer months.
- Feeding Behavior: Yellowfin tuna are highly active predators, and water temperature plays a crucial role in determining their feeding behavior. They are more active and feed more vigorously in warmer waters, where their metabolic rates are higher. However, extremely high temperatures can lead to reduced feeding activity due to stress.
- Reproduction: Water temperature also affects the spawning behavior and reproductive success of yellowfin tuna. They typically spawn in warmer waters, with temperature thresholds triggering spawning migrations to specific breeding grounds.
- Vertical Distribution: Yellowfin tuna exhibit vertical movement patterns in response to temperature gradients within the water column. They may adjust their depth to optimize their preferred temperature range for feeding and physiological performance.
- Habitat Selection: Yellowfin tuna prefer areas with stable temperature conditions within their optimal range. They are commonly found near oceanic fronts, where warm and cold water masses converge, providing a dynamic environment rich in prey.
Understanding the impact of water temperature on yellowfin tuna behavior and distribution is crucial for fisheries management and conservation efforts. Monitoring temperature changes and their effects on yellowfin tuna populations can help mitigate the impacts of climate change and ensure the sustainability of tuna fisheries.
Ideal pH Levels For Yellowfin Tuna
Yellowfin tuna, like many marine species, prefers water with stable pH levels within the range of approximately 7.5 to 8.5. These pH levels are characteristic of the marine environment and support the physiological processes necessary for the health and well-being of yellowfin tuna. Deviations from this optimal pH range can disrupt the acid-base balance within the tuna’s body, potentially leading to physiological stress or health issues. Maintaining stable pH levels in the ocean through responsible environmental stewardship is essential for ensuring the continued viability of yellowfin tuna populations.

Ideal Weather Conditions:
- Calm seas reduce boat motion, making it easier to spot and target yellowfin tuna.
- Clear skies provide better visibility, allowing fishermen to locate schools of tuna more easily.
- Moderate winds help maintain stability on the water and improve maneuverability for fishing vessels.
Ideal Barometric Pressure:
- Stable or rising barometric pressure indicates stable weather conditions, which are favorable for fishing.
- Barometric pressure between 29.90 to 30.20 inches of mercury (inHg) is considered optimal for yellowfin tuna fishing.
- Stable pressure often corresponds to calmer seas and increased tuna activity, leading to better fishing success.
Ideal Moon Phase for Yellowfin Tuna Fishing
References:

Pacific Yellowfin Tuna: Seafood
FAQ’s