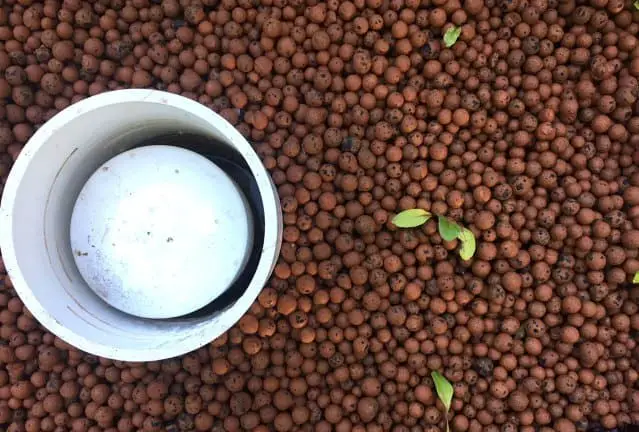
In the wonderful world of Aquaponics, simple mechanical and biological theories are put to the test to create a product from a process of nature. The most important control in Hydroponics or Aquaponics systems for the process to function is called a Bell Siphon. What is a Bell Siphon?
A Bell Siphon is a simple yet effective device used in media-based aquaponics systems to regulate water levels automatically without human intervention and provide a natural filtration system that improves the oxygenation and nutrient delivery to the roots of the hydronic plants.
Using no powers or timers a Bell Siphon controls a necessary function critical for the Hydroponic and Aquaponic systems. A simple function that is genius and effective.
Introduction:
A Bell Siphon is a clever hydraulic device utilized in various hydroponic and aquaponic systems to regulate water flow efficiently. This ingenious mechanism consists of a vertical standpipe known as the “bell” and an outer sleeve or pipe. By harnessing the principles of siphon action, the Bell Siphon enables controlled flooding and draining cycles within grow beds or containers, facilitating optimal nutrient delivery to plants while maintaining proper oxygen levels in the water. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice among growers seeking efficient water management solutions.
What is a Bell Siphon
A Bell Siphon is a device commonly used in aquaponics and hydroponics systems to regulate the flow of water. It consists of a vertical standpipe (the “bell”) and an outer sleeve or pipe. When water fills the standpipe, it creates a siphon effect, causing water to be rapidly drained from the container until air enters the standpipe, breaking the siphon. This cyclic process allows for the periodic flooding and draining of grow beds, facilitating nutrient uptake by plants and oxygenation of the water. Bell siphons are efficient and low-maintenance components in water recirculation systems.
A Bell Siphon is an easy way to drain grow beds in Aquaponics or Hydroponics systems. It can regulate the flow without the need for human or mechanical intervention. The fundamental principles of a Bell Siphon are based on hydrostatics or the relationship between the height of a water column and its pressure. At the highest point in a siphon, the pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure, also known as a vacuum in the aquaponics system. 
This allows the atmospheric pressure to push water up over the peak of the siphon so gravity can carry it the rest of the way. For most situations, that’s enough theory to describe your typical siphon. It’s a very convenient way to drain a reservoir or transfer a liquid without a pump, electric power, or timers. The Bell Syphon is used in different applications but for this article, we show how important it is in the field of Hydroponics and Aquaponics.
A Bell Syphon has three parts:
- Reservoir – A Bell Siphon reservoir is a container or tank used to hold the water supply for hydroponic or aquaponic systems employing Bell Siphons. It serves as the source from which water is periodically pumped or gravity-fed into grow beds, initiating the flooding cycle controlled by the siphon mechanism.
- Bell-siphon bell is a crucial component of the siphon mechanism, typically consisting of a cylindrical or conical structure placed atop the standpipe. Its purpose is to create a seal against the outer sleeve or pipe, allowing water to accumulate inside the bell and initiate the siphon action when the water level reaches a critical point.
- Riser- The riser on a Bell Siphon refers to the vertical standpipe through which water flows into the siphon mechanism. It plays a central role in regulating the water level within the grow bed and initiating the siphon action when the water reaches a predetermined height.
Components of a Bell Siphon
The components of a bell siphon are simple and available at most local hardware stores. The media guard can be drilled or cut, depending on your preference. These are the components of a bell siphon.

1. Bell Cap: When water overflows into the standpipe, low pressure will eventually build up under the bell cap. This will force out the water at a higher rate until the air enters the bell.
2. Reducer: This is placed on top of the standpipe, which helps the siphon discharge pipe create a smooth transition; a 2:1 ratio in a reducer is optimum. (if the standpipe is 1 inch long, a reducer should be 2 inches).
3. Siphon Pipe: The siphon pipe should have a diameter twice as big as the reducer. Bell siphon pipe creates a barrier between the siphon and the atmosphere and prevents air from entering. It also allows the siphon to build up a negative pressure that creates a vacuum that keeps the water flowing in the siphon.
4. Stand Pipe: This is placed inside the siphon pipe and acts as the discharge pipe. The standpipe also regulates the maximum water level in the grow bed. Water flows out through the standpipe once it reaches the top of the standpipe. It also connects the bulkhead to the reducer.
5. Media Guard: The media guard prevents the growing media in the grow bed from clogging the standpipe and bell siphon.
6. Bulkhead: The Bulkhead holds the standpipe in the grow bed and allows the water to drain through the standpipe without leaking back to the siphon.
7. Outlet Pipe: Also called a drainpipe, this extends from the bottom of the bulkhead into the fish tank.
Design Considerations for Bell Siphon
How Does a Bell Siphon Pipe Work in an Aquaponic System
-
- The drained grow bed is first filled with water using a water pump.
- When the water level reaches the top of the standpipe situated inside the siphon pipe, water will start flowing through the reducer placed at the top of the standpipe and out through the standpipe into the fish tank at low pressure.
- As the water slowly drains out of the standpipe, water builds up inside the bell and pushes air out through the standpipe. As a result, the pressure inside the bell eventually falls.
- The resulting low pressure in the bell leads to a pressure difference between the bell and the atmosphere which forces the siphon to fire. Thus, the siphon rapidly pushes out and dumps the water through the standpipe at a much higher pressure until the water level reaches the base of the grow bed.
- As the water level approaches the base of the siphon pipe, air enters the bell through the slits at the bottom of the siphon pipe which relieves the pressure difference between the bell and the atmosphere, causing the siphon to break and halt the drain of water.

A Bell Siphon is a simple device used in Hydroponics that regulates the flow of water in aquaponic and hydroponic systems easily and efficiently, with no need for human intervention.
The siphon first allows the grow bed to flood, then it automatically drains out the water when it reaches a certain level so as not to flood the system. The siphon also maintains a minimum water level as the excess water is drained automatically.

In Hydroponics and Aquaponics flooding and draining the grow beds is a constant operation that keeps the plants in the system healthy during the growth cycle. It keeps them in contact with the right amount of nutrients and water.
It will also provide oxidization which is also important in plant development. It will slowly fill the tanks and provide plenty of time for the plant’s roots have plenty of time to uptake a good amount of nutrients and water.
When it drains it will do so rapidly that it provides a large amount of air that is used up by bacteria in the bed and at the roots for the plants to grow. This keeps the plants and the system aerobic and healthy.
Air is important in the system where bacteria use it for breaking down and processing the fish waste turning it into nutrients that the plant used for food. Without the oxygen in the growth bed, it acts as a filter and can’t operate properly. Soon the system would turn anaerobic and fail.
In an Anaerobic state, bacteria break down organic material, and fish waste, without oxygen. This process gives off methane and hydrogen sulfide, which produces the rotten egg smell of anaerobic digestion.
In its basic function, the bell siphon regulates the health of the bacteria, foremost, and plants in the media bed. This, in turn, regulates the health of the entire system, plants, bacteria, and fish keeping a fine-tuned ecosystem working in tangent with each other naturally.
Does Singing or Talking to Plants help them grow?
Science has proven that plants:
- Detect vibration
- Emit sound waves at levels of 10-240Hz
- Emit ultrasonic acoustics within 20-300Hz
- Grow into the direction of vibration
- That plants make sounds
- Respond to touch, light, scent, wind & gravity
- But talking & singing to help them grow is inconclusive ………………………………………………………………….. Read more
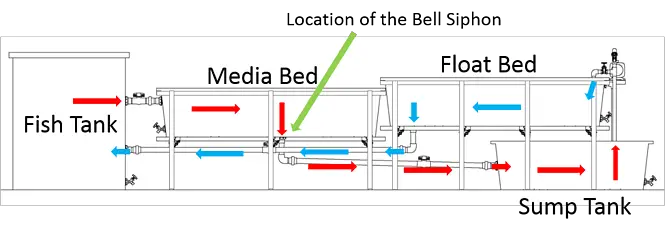
Aquaponics System Water Diagram
The Aquaponic System is a recirculating system, water is continuously running through the system. There are four tanks, a fish tank, a Float Bed, a Sump tank, and a Media bed. Water is pumped from the sump tank into the float bed and then drains to the fish tank. The fish tank drains into the media bed and the bell siphon drains the water to the sump tank.
- As the water fills the Grow Bed

Bell Siphon Setting - the Standpipe limits the maximum fill height of the water.
- When the water rises it pushes air out of the bell housing pipe and down the Standpipe.
- Once the water level reaches the top of the Standpipe it begins to drain down the pipe. This is the beginning stage of the siphon.
How do you Propagate Plants from Cuttings in water?
- Snip cuttings from the plant.
- Cut 1/4″ below the node at a 45° angle with a clean knife or scissors.
- Stick cutting in a clean glass
- Pour tepid room H2O to cover nodes
- Change H2O every 3-5 days
- Wait till the roots grow(this can take weeks to months, depending on the plant)
- Once roots are 2-5″ Pot in soil ………………………………………………………………………………………. Read more
-
-
Why You Should Use a Bell Siphon for Water in Aquaponics
The Bell Siphon does have its limits even though they are far apart. If the water comes into the media bed too fast or too slow the siphon will not be engaged. You need to set the Siphon in place and take it through a few operating times. Make some adjustments to the bell to iron out the pump water levels to the grow bed keeping just the right amount of water and oxygen for plant growth.
The Bell Siphon is not only an integral part of Aquaponics but a fascinating feat of science. The ability to flood and drain a tank in a system with one pump greatly lowers the risks of failure. The siphon runs automatically and consistently giving the plants a stable growing environment. By having even flood drain cycles the plants receive even amounts of air, water, and nutrients in the grow bed.
-

The Bell Siphon in aquaponic systems grow bed does have its limits, even though they are far apart. If the water comes into the media bed too fast or too slow, the siphon will not be engaged. The ebb and water height will be affected.
Adjusting a Bell Siphon in an aquaponics system is a crucial step to ensure proper functioning and water management. Here’s a list of steps to guide you in adjusting the siphon bell pipe:
- Initial Setup:
- Ensure that the bell siphon is correctly installed in the grow bed according to the system design.
- Position the bell siphon so that it allows water to fill the grow bed to the desired level before initiating the draining phase.
- Adjusting Water Inlet Height:
- Modify the water inlet height by adjusting the standpipe connected to the bell siphon. This determines the maximum water level in the grow bed during the flooding phase.
- Testing Water Fill Time:
- Monitor the time it takes for the grow bed to fill with water. Adjust the water inlet height to achieve an appropriate fill time. The goal is to flood the bed efficiently without overfilling.
- Checking Siphon Break:
- Ensure that the siphon break (the opening at the top of the standpipe) is appropriately sized. It should allow air to enter the standpipe, breaking the siphon and initiating the draining phase.
- Adjusting Bell Height:
- Experiment with the height of the bell (outer sleeve) on the standpipe. This can impact the duration of the flooding phase and the speed of the draining phase.
- Fine-Tuning Siphon Break Opening:
- Fine-tune the size of the siphon break opening to control the flow rate during the draining phase. This can be done by adjusting the height of the bell or by altering the size of the opening.
- Ensuring Complete Drainage:
- Verify that the bell siphon allows complete drainage of water from the grow bed during the draining phase. Incomplete drainage may lead to waterlogging and affect plant health.
- Observing Siphon Action:
- Observe the siphon action during both the flooding and draining phases. Adjustments may be needed to achieve a smooth and reliable siphoning process.
- Preventing Air Pockets:
- Ensure that there are no air pockets in the bell siphon. Air pockets can disrupt the siphon action. Adjust the components as needed to eliminate any trapped air.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor the performance of the bell siphon and make adjustments as needed, especially when adding new plants or changing the system configuration.
- Documentation:
- Keep detailed records of adjustments made and their impact on the system. This documentation can be valuable for troubleshooting and optimizing the system over time.
Remember that the adjustment process may require some trial and error to achieve optimal performance. Regular monitoring and fine-tuning will help maintain a well-balanced aquaponics system.
You need to set the Siphon in place and take it through a few operating times in the grow bed. Make some adjustments with the aquaponics bell to iron out the pump levels that control the water level in the grow bed feeding from the fish tank.
Bell Siphons are not only an integral part of the Aquaponic Bell siphon system but a fascinating feat of science. The Aquaponics bell Siphon works to control water height in the grow bed and water level using a siphon bell pipe and aquaponics PVC bell to drain and fill a grow bed that contains grow media and plants.
With the ability to flood with water and drain a tank in a system with one pump greatly lowers the risks of failure. The siphon runs automatically and consistently giving the plants a stable growing environment. By having even flood drain cycles, the plants receive even amounts of air and nutrients necessary for life.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, adjusting the bell siphon in an aquaponics system is a critical step to ensure efficient water management and promote healthy plant growth. Proper adjustment allows for the precise control of flooding and draining phases, optimizing nutrient distribution and preventing waterlogging. By carefully adjusting the bell siphon and maintaining a proactive approach to system monitoring, aquaponics enthusiasts can create a well-balanced and automated water management system that supports thriving plant and fish life.
How to Start a Cheap Hydroponic Indoor Garden:
- Start Seeds
- Seeds Sprout
- Transplant Seedlings to Container holding Water
- Mix the proper amount of Nutrients with water for the Roots of the Plants to Absorb
- Hang a Grow Light Above the Container for Heat & Growth
- Maintain & Monitor your System
- Harvest .…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. Read more

References:
Practical Engineering-Automatic Bell Siphon Explained
Related Questions: