Whenever I’m asked about the most important pool water test that you need to know as a pool owner or operator there is one parameter test that stands out as the most critical fundamental basis in a chemical equation that allows for desired balance for any size swimming pool and that is Alkalinity. What is Pool Alkalinity?
Introduction
Maintaining balanced pool water chemistry is essential for ensuring a safe and enjoyable swimming experience. Just like any body of water, pools require careful monitoring and management to prevent issues such as algae growth, bacterial contamination, and skin irritation. One critical aspect of pool water chemistry that often gets overlooked is alkalinity.
Alkalinity plays a vital role in stabilizing the pH level of pool water, which is a measure of its acidity or basicity. Without proper alkalinity levels, pH fluctuations can occur, leading to discomfort for swimmers and potential damage to pool equipment and surfaces. In this article, we’ll delve into the importance of alkalinity in pool water chemistry and explore how it contributes to overall water balance and quality. Understanding alkalinity is key to maintaining a healthy and inviting swimming environment for everyone to enjoy.
Pool alkalinity describes water’s ability to neutralize acids and bases. Said another way, it denotes how water can hold up against sudden pH changes. Maintaining total alkalinity and pH is crucial for keeping your pool safe for swimmers.
What is Pool Alkalinity
Alkalinity is the measure of the ability of water to resist changes in pH. In other words, adjusting the alkalinity in a pool directly affects the pH balance of the water. When the pH level is low, often, it is alkalinity resulting in more acidic pool water.

We know what you’re thinking: “Acidic pool water?! That doesn’t sound safe at all!” That’s because it’s not. For this reason, it is super important to make sure the total alkalinity (TA) of a pool is at the right level.
In the context of pool water chemistry, alkalinity refers to the water’s capacity to resist changes in pH levels. It represents the concentration of alkaline substances, primarily bicarbonates, carbonates, and hydroxides, dissolved in the water. Alkalinity acts as a buffer, helping to stabilize the pH of the pool water and prevent rapid fluctuations that can occur due to various factors such as environmental conditions, chemical additions, and bather load.
Interaction with Other Chemical Parameters: Alkalinity interacts closely with other chemical parameters in the pool, particularly pH and calcium hardness. Here’s how:
pH Stability: Alkalinity acts as a pH buffer, meaning it helps to maintain the pool water’s pH within the desired range. When alkalinity levels are properly balanced, the water is less prone to sudden pH shifts, which can occur due to the addition of chemicals or organic contaminants. This stability is crucial for ensuring swimmer comfort and preventing corrosion or scaling of pool surfaces and equipment.
Calcium Precipitation: Alkalinity also influences the precipitation of calcium carbonate, a common cause of scale formation in pools. When alkalinity levels are too high, it can lead to calcium carbonate precipitation, resulting in scale buildup on pool surfaces, pipes, and equipment. Conversely, low alkalinity levels can contribute to the erosion of calcium-based materials and the leaching of metals into the water.
Chlorine Efficiency: Proper alkalinity levels optimize the effectiveness of chlorine, the primary sanitizer used in pools. When alkalinity is within the recommended range, chlorine works more efficiently to kill bacteria and other pathogens, helping to maintain clear and hygienic pool water. However, excessive alkalinity can reduce chlorine’s effectiveness, requiring higher doses to achieve the desired sanitization levels.
Overall, maintaining balanced alkalinity levels is essential for ensuring the overall stability and water quality of the pool. It’s a key parameter that pool owners and operators should regularly monitor and adjust as needed to keep the water safe, comfortable, and inviting for swimmers.
Testing Alkalinity
Testing alkalinity in pool water can be done using test strips, liquid test kits, or digital testers, with each method offering varying degrees of accuracy and convenience. Regular testing is essential to monitor alkalinity levels and ensure proper water balance, preventing issues such as pH fluctuations and equipment damage. Pool owners should follow a consistent testing schedule and adjust alkalinity levels as needed to maintain a safe and comfortable swimming environment.
Troubleshooting Alkalinity Issues
When facing alkalinity imbalance in pool water, common issues may include pH fluctuations, scaling on pool surfaces, and diminished effectiveness of sanitizers. To address high alkalinity levels, diluting the pool water or adding an acid like muriatic acid can be an effective solution, while low alkalinity levels can be raised by adding alkalinity increasers like sodium bicarbonate. Regular testing and prompt adjustments are key to maintaining balanced alkalinity levels and ensuring a safe and enjoyable swimming environment
Alkalinity imbalance in pool water can lead to various problems that affect water quality, swimmer comfort, and equipment longevity. Here are common issues associated with alkalinity imbalance and solutions for addressing both high and low alkalinity levels:
1. Problems Associated with High Alkalinity:
- pH Stability Issues: High alkalinity can cause the pH level of pool water to become too stable, making it difficult to adjust. This can lead to persistent high pH levels, resulting in scale formation, cloudiness, and reduced effectiveness of sanitizers.
- Scale Formation: Excessive alkalinity can contribute to scale buildup on pool surfaces, pipes, and equipment. Scale formation not only affects water clarity but also reduces the efficiency of filtration and circulation systems, leading to decreased water flow and potential damage to equipment.

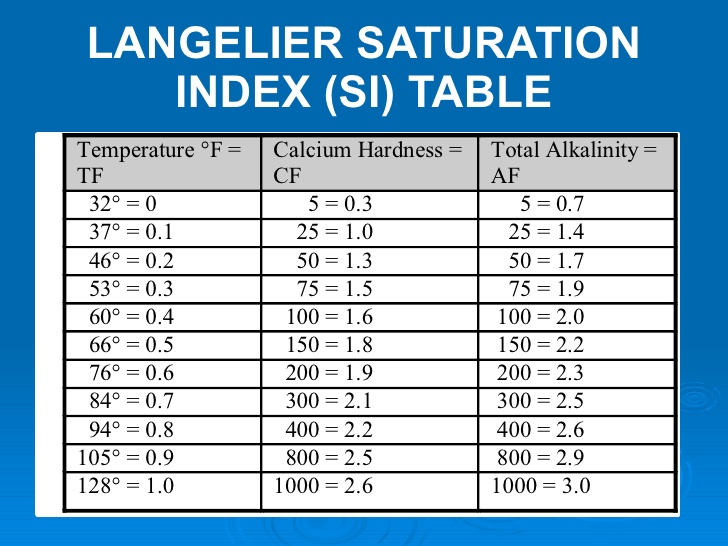
Pool Water Chemical Levels Chart
Solutions for High Alkalinity:
- Acid Addition: Lower alkalinity levels by adding an appropriate amount of acid, such as muriatic acid or sodium bisulfate, to the pool water. Follow manufacturer instructions and dosage recommendations carefully to avoid overcorrection.
- Dilution: If alkalinity levels are extremely high, partial draining and dilution with fresh water may be necessary to bring levels back within the recommended range.
2. Problems Associated with Low Alkalinity:
- pH Fluctuations: Low alkalinity can result in pH fluctuations, making it difficult to maintain a stable pH level in the pool water. This can lead to rapid pH changes, which can cause skin and eye irritation, corrosion of pool surfaces, and reduced effectiveness of sanitizers.
- Corrosion: Insufficient alkalinity can lead to corrosive water conditions, causing damage to pool surfaces, metal fixtures, and equipment. Corrosion can shorten the lifespan of pool components and result in costly repairs.
Solutions for Low Alkalinity:
- Alkalinity Increasers: Raise alkalinity levels by adding an appropriate alkalinity increaser, such as sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), to the pool water. Calculate the amount needed based on the pool’s volume and the current alkalinity reading, and dissolve the product in water before adding it to the pool.
- Buffering Agents: Consider using stabilizers or buffering agents to help maintain stable alkalinity levels over time, especially in pools exposed to environmental factors that may affect water chemistry.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Testing: Implement a regular testing schedule to monitor alkalinity levels and catch any imbalances early on. Test the water at least once a week or as recommended by pool professionals.
- Maintain Water Balance: Properly balance other chemical parameters, such as pH and calcium hardness, to support stable alkalinity levels. Avoid sudden changes in water chemistry by gradually adjusting chemical levels as needed.
By addressing alkalinity issues promptly and implementing preventive measures, pool owners can maintain balanced water chemistry, prolong equipment lifespan, and provide a safe and enjoyable swimming environment for all users.


/how-to-use-a-pool-test-kit-2736561-hero-0439e745c14d41eeade16c3f029279b8.jpg)
