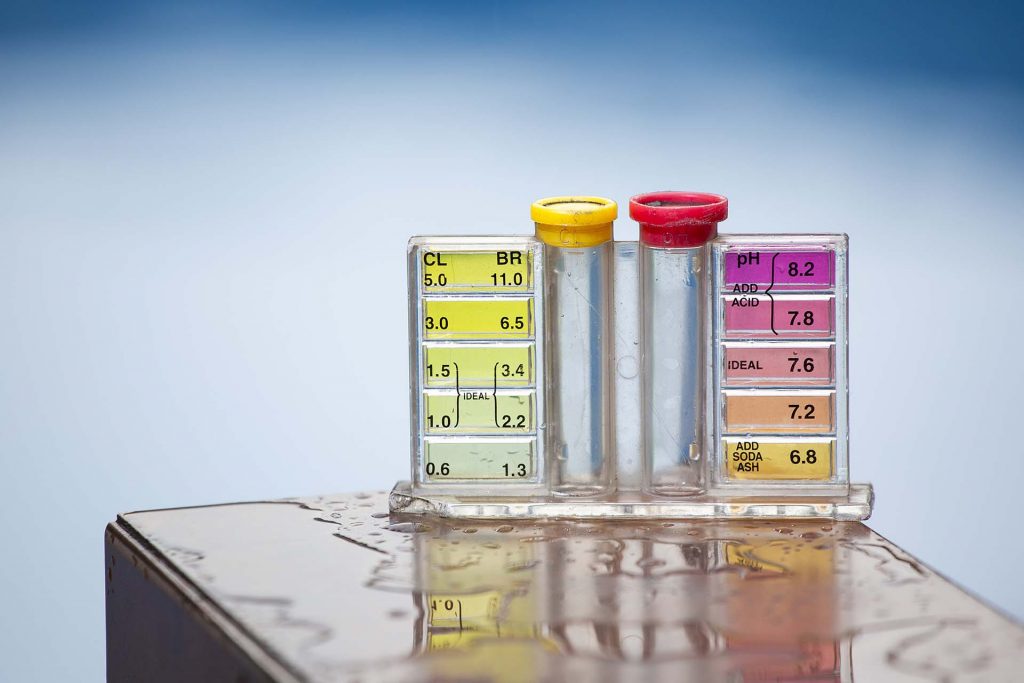
When people ask me for advice on their swimming pools or spas on where they should start at the beginning of the season, I tell them that the most important critical parameter test to run for water treatment is the total alkalinity test because low or high alkalinity can make or break your pool water chemistry. What Causes Low Alkalinity in Pools?
Causes of low alkalinity in pool H2O include:
- Carbon dioxide outgassing(Pool H2O agitation)
- Acidic rainwater or sources(acidic)
- pH imbalance(summer loads,lotions)
- Overuse of acidic chemicals
- Organic matter decomposition(urine)
- High calcium hardness levels
- Incorrect water balance(evaporation)
- Lack of preventive maintenance
Excess urine and perspiration in the pool water can bring the alkaline levels of your pool down. Another common reason is when your pool water gets flooded with rainwater due to a heavy downpour. Using chlorine tablets in excess is also said to cause a drop in the alkalinity levels as they contain a low pH level. The use of too much dry acid can hurt your pool water. The pH and alkalinity of a pool are not the same measurements, but they are closely related. With alkalinity out of proper range, pH will become unstable keeping the disinfection product from doing its job.
What Causes Low Alkalinity in Pools
Proper Alkalinity and pH balance are key to maintaining a healthy pool or spa water. Alkalinity helps to stabilize the pH balance in your pool. The alkalinity range for pools should be between 80 – 120 ppm, ideally at 100 ppm. The pH scale is 1-14, and the pool and spas should be between 7.2 and 7.6, ideally at 7.4.
They are both necessary but if the Alkalinity balance fluctuates too high or low range pH will follow and the pool water won’t be an Acid rain can cause alkalinity levels and pH levels to drop. Sweat and even urine may cause alkalinity levels to lower.
Low Acid pH Levels and Decrease Alkalinity in Pool Water
Causes of Falling Alkalinity
Alkalinity levels can decrease for a wide range of reasons, which extend to:
- A high amount of rainwater enters the pool, which leads to the water’s TA being diluted
- Acid rain can increase acidity levels and cause alkalinity level and pH levels to drop
- Sweat and even urine may cause alkalinity levels to lower (all those hineys can ruin your sparkling pool water)
- If you happen to shock your pool with chlorine tablets, it’s important to understand that these tablets have low pH levels, which means that using too many chlorine tablets can lower alkalinity levels
- High H2O evaporation-losing H2O can dilute alkalinity level
- Pool H2O agitation-H2O agitation from the filtration system increases the loss of CO2 affecting Total Alkalinity
- Lotions & detergents-Keep a pool shower and demand that swimmers use it
Salt Water Pool Alkalinity Levels: Swimming Pool Lower pH Level
Salt chlorine generators are fairly new to the pool industry, and they are very useful and innovative for pool owners. What some pool owners may not be aware of when buying a salt chlorine generator is they increase your pool’s pH and Alkalinity. What exactly are pH and pool Alkalinity are.
How does salt water affect pH and alkalinity? Much the same way it does in a chlorine pool. Anything that enters your pool has a pH. That includes humans, animals, rain, dirt, leaves, bugs, and yes, salt.
Salt itself does not dramatically change the pH or total alkalinity in a swimming pool. However, the liquid form of chlorine generated by the salt cell will cause higher pH swings. This is very common during seasons when the source water is already high in alkalinity.
This poses a unique problem for saltwater pool owners: the challenge of constantly maintaining their pool pH alkalinity your pH levels can swing back and forth between being too high by natural causes such as evaporation or agitation of your pool’s water.
If you allow pH and alkalinity(TA) to rise without any response, it will result in water that could allow staining and scaling. Salt pool owners who choose to perform no maintenance on their pool aside from adding salt usually find out in a couple of years they have to deal with major scaling problems, plaster staining, or unusual watercolors.
One of the simplest ways to avoid all these issues is to wash the generator cell with an acid wash a couple of times per summer season. This, on top of regular maintenance, should keep your pool running smoothly.
Total Alkalinity in Pools
Alkalinity is the buffer or stabilizer some people refer to as the “Muscle” for your pool or spa’s pH. Alkalinity is measured in parts per million (ppm). An ideal alkalinity range is between 80 – 120 ppm. If the Alkalinity is below 80 ppm, we recommend In The Swim Pool Alkalinity Increaser.
If your Alkalinity is above 120 ppm, In The Swim Pool pH reducer will do the trick. Alkalinity over 120 ppm may cause the water to cloud up and cause scale to form. Alkalinity under 80 ppm will cause the pH to move freely on its scale. This can damage the pool or equipment over time with corrosion.
Total alkalinity plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and balance of pool water chemistry. It represents the water’s ability to resist changes in pH levels, acting as a buffer against fluctuations.
Total alkalinity in pools is typically measured in parts per million (ppm) and should ideally fall within the recommended range, usually between 80 to 120 ppm, although specific recommendations may vary based on factors such as pool type and local water conditions.
Maintaining proper total alkalinity levels helps prevent rapid pH swings, which can lead to discomfort for swimmers, corrosion of pool equipment, and reduced effectiveness of sanitizers like chlorine. Low total alkalinity can result in acidic water, causing skin and eye irritation and potentially compromising swimmer safety. On the other hand, high total alkalinity can lead to cloudy water, scale formation on pool surfaces, and difficulty in adjusting pH levels.
Regular testing and adjustment of total alkalinity are essential components of pool maintenance. Adding an alkalinity increaser, typically sodium bicarbonate, can raise total alkalinity levels when they fall below the recommended range. Conversely, lowering total alkalinity levels may require the addition of acid or dilution of the pool water, depending on the specific circumstances.
By carefully monitoring and managing total alkalinity levels, pool owners can help ensure a comfortable, safe, and enjoyable swimming environment while also prolonging the lifespan of pool equipment and surfaces.
Total alkalinity refers to the ability of the pool water to resist a change in pH. The key purpose total alkalinity serves is to help control the pH in the pool. It does this by acting as a buffer so that when materials are added to a pool that would otherwise cause the pH to go up or down, these changes are managed and do not result in severe changes to pool water balance.
Then you get the normal excess urine and perspiration in the pool water can play havoc with the pool water’s balance, swimming pool pH, and the water’s alkalinity, natural causes such as evaporation or agitation of your water pool water chemistry always change.
Warm pool water causes drastic changes in pool water pH especially during heavy loads on a hot day pH levels can drop right away
When a foreign substance is added to the pool water that could affect the pH, total alkalinity will react to neutralize it and help keep the pH in the desired range. Total alkalinity does not determine what the pH will be but rather acts to help keep the pH in the range desired which is a balancing job the most important job in pool water treatment.
Pool spas, cement pools fiberglass pools, and reef pools all work the same with total alkalinity to help keep the pool’s water balance and clear pool clear.
What Are The Adverse Effects Of Low And High Alkalinity
Both low and high alkalinity levels in pool water can lead to various adverse effects:
Adverse Effects of Low Alkalinity: 
- pH Instability: Low alkalinity makes the pool water more susceptible to fluctuations in pH levels. This can result in rapid pH swings, leading to discomfort for swimmers and potential damage to pool equipment and surfaces.
- Corrosion: Acidic water caused by low alkalinity can corrode metal components of pool equipment, such as pumps, heaters, and filters. It can also damage pool surfaces, including plaster, vinyl liners, and tile grout.
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Acidic water can irritate the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes of swimmers, causing redness, itching, and discomfort.
- Reduced Sanitizer Efficiency: Low alkalinity can impair the effectiveness of chlorine and other sanitizers, leading to inadequate sanitation and an increased risk of algae growth and waterborne illnesses.
Adverse Effects of High Alkalinity:
- Cloudy Water: High alkalinity levels can cause the pool water to become cloudy or hazy due to the formation of calcium carbonate (scaling) and other minerals precipitating out of the solution.
- Scaling: Excessive alkalinity can lead to scale formation on pool surfaces, equipment, and plumbing. Scale deposits can be difficult to remove and may require the use of specialized chemicals or mechanical cleaning methods.
- Difficulty Adjusting pH: High alkalinity can make it challenging to adjust pH levels in the pool. This can result in pH levels that are consistently higher than the recommended range, leading to potential discomfort for swimmers and reduced sanitizer effectiveness.
- Staining: Elevated alkalinity levels can contribute to metal staining on pool surfaces, particularly if the water also has high levels of dissolved metals such as iron or copper.
To maintain a safe and comfortable swimming environment, it’s essential to regularly test and balance alkalinity levels in the pool within the recommended range (typically 80 to 120 ppm). This helps ensure water stability, effective sanitation, and the longevity of pool equipment and surfaces.
If you find that the alkalinity in your pool is too low, it’s possible to raise the amount that’s in your pool by placing a simple solution in the water. The main problem with low pool alkalinity is that it can be damaging to the walls and surfaces of your pool.
You may start to notice cracks and pits in these surfaces. Any metallic surfaces will begin to corrode and become discolored until they eventually dissolve entirely. When the pool water has low amounts of alkalinity in it, the chlorine that you use to disinfect the pool will also be less effective. Raising pool alkalinity is beneficial to your pool because it will keep these issues from worsening. As a pool owner, raising the alkalinity will also help reduce expenses for repairing the damage caused by low alkalinity.
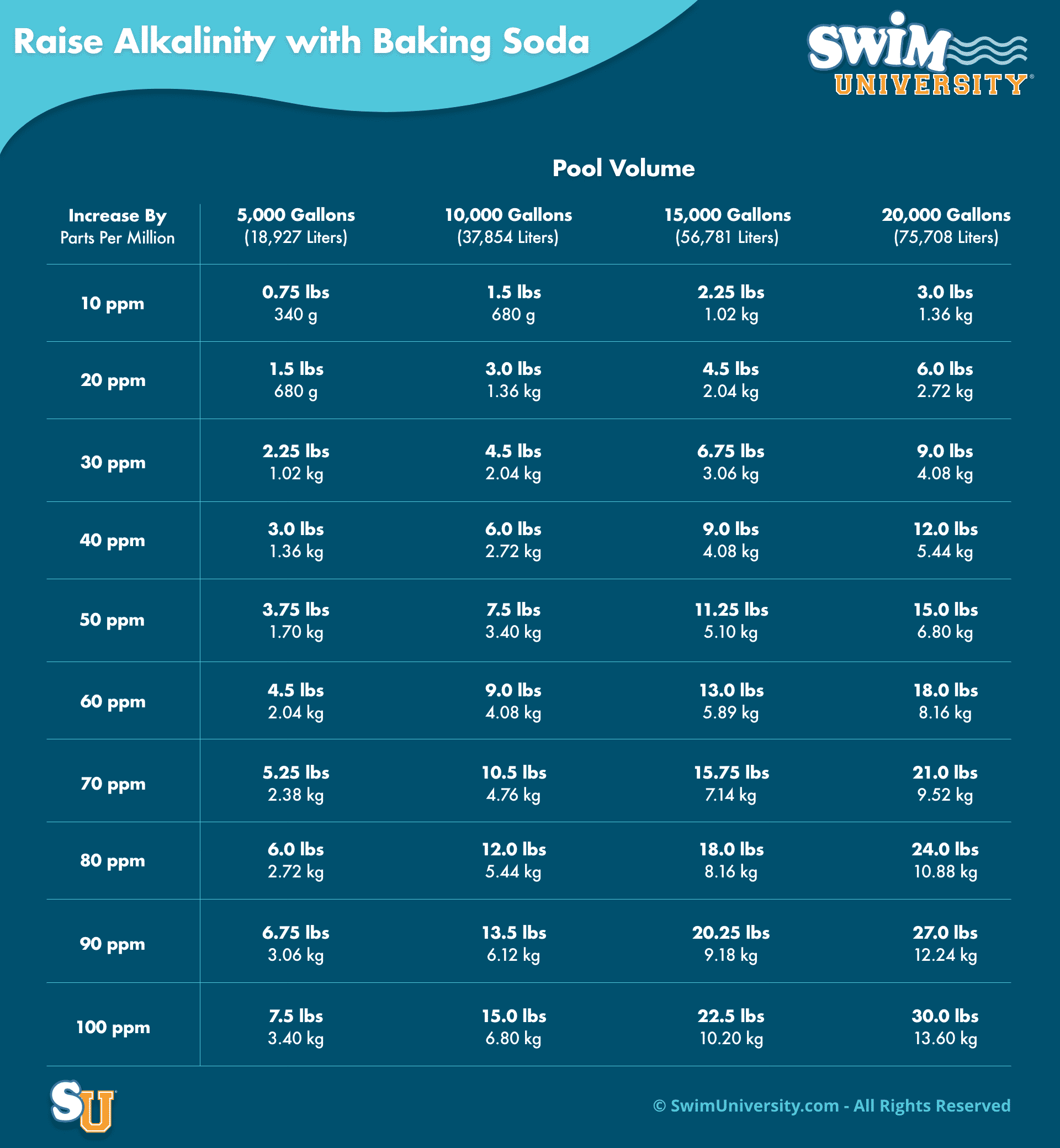
Raise Alkalinity: Low Alkalinity in Your Pool
Do you need to raise pH without affecting alkalinity dropping Total Alkalinity?
You can sometimes raise the pH by aerating the pool water. That’s right just add some air! It’s the same reason hot tubs and spas often suffer from high pH issues. Although this will bump your pH, it’s important to note that this isn’t an exact science, and results can vary by pool.
You can aerate a swimming pool by bubbling air through the pool water, agitating the surface, spraying droplets through the air with a pool fountain, or even get the kids just playing and splashing around in the pool. During the hot summer months, this method also can be used to lower pool water temperature.
Even the slightest alterations in pool water chemical composition can cause severe fluctuations in the pH levels. When the pH level becomes unbalanced, the phenomenon is called pH bounce and can cause low alkalinity in the pool.
With low alkalinity, the standard amount of chlorine added to your pool would be useless. It would only be useful when more than the usual amount is added for standard results. This means you buy more chlorine and waste more time and money trying to get to the right concentration level with the substance. Aside from its effects on your pool, a low-alkalinity swimming pool is unsafe for swimmers as the acidic water can cause nasal, eye, and skin rashes.
Is It Safe to Swim in a Pool with Low Alkalinity
Yes, but at the same time, the pool owner should find out the reason the alkalinity is low and adjust it right away. When the pool’s alkalinity is low, it becomes difficult to maintain the proper pH level for a safe, comfortable swimming environment. Thus, it’s essential to understand the causes of low alkalinity in your pool and how to correct it.
Swimming in a pool with low alkalinity can present certain risks and discomfort for swimmers. Low alkalinity levels can lead to fluctuations in pH, making the water more acidic. This acidic environment can irritate the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes of swimmers, causing discomfort and potential health issues such as redness, itching, and irritation.
Moreover, low alkalinity can also affect the effectiveness of other pool chemicals, such as chlorine, leading to inadequate sanitation and potentially allowing harmful bacteria and pathogens to thrive in the water. Additionally, low alkalinity can contribute to the corrosion of pool equipment and surfaces, leading to costly damage and maintenance issues over time.
While swimming in a pool with slightly low alkalinity levels for a short period may not cause immediate harm, prolonged exposure can increase the risk of discomfort and potential health hazards. Therefore, it’s essential to address low alkalinity levels promptly by adjusting the water chemistry and maintaining proper pool maintenance practices to ensure a safe and enjoyable swimming experience for all users. Regular testing of water parameters and diligent maintenance efforts are key to ensuring that the pool water remains balanced, comfortable, and safe for swimming.
To raise the pool’s alkalinity safely, pool owners can use chemicals like sodium bicarbonate, also known as baking soda. This chemical can help balance the pool water by raising the alkalinity and buffering pH levels.
Pool owners should follow the instructions on the product label and test the pool water regularly to maintain the appropriate pool water balance.
Overall, it’s safe to swim in a pool with low alkalinity in the short term, but it’s essential to address the issue for the long-term health and safety of your pool and swimmers. Regularly testing your pool water and adjusting the alkalinity and pH levels accordingly helps maintain a safe, comfortable, and clean pool environment for swimmers to enjoy.
What causes High alkalinity in a pool?
- Cyanuric acid also called CYA or chlorine stabilizer raises TA
- Liquid chlorine (or ‘sodium hypochlorite) has a high pH
- High Alkaline fill water
- Soda ash-pH control
- Sodium bicarbonate-pH control
- TA rises due to excess hydroxides left behind ………………………………………. Read more

References:
Barrier Reef Pools- Understanding Alkalinity In Your Pool
FAQ’s


