Pool safety laws were designed to protect your family, friends, and neighbors from accidental drowning, injury, or electrocution. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), there are more than 3,000 deaths from drowning each year unrelated to boats as well as many more injuries from near-drowning incidents. What are Residential Swimming Pool Regulations?
- Rules set by local officials for residential pool safety
- Cover design/construction/safety features
- Laws for fencing/alarms/permits
- Aim to prevent accidents/ensure compliance
- Mandate proper upkeep, H2O quality
- Standards for materials/dimensions
- Non-compliance may lead to legality
- The aim is to create safe pools
Swimming Pool Regulations may cover aspects such as pool design, materials used, drainage systems, and filtration equipment to ensure structural integrity and water quality.
Introduction:
Residential swimming pool regulations play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals who enjoy these aquatic amenities. These regulations encompass a wide range of standards and guidelines aimed at mitigating risks and preventing accidents. From safety features to construction requirements, these regulations are designed to safeguard both swimmers and bystanders.
The necessity of adhering to residential swimming pool regulations cannot be overstated. At the heart of these regulations lies the paramount concern for safety. By implementing measures such as fencing, alarms, and proper maintenance protocols, homeowners can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents, particularly drowning incidents which tragically remain one of the leading causes of unintentional death worldwide, especially among children.
Moreover, compliance with local laws and regulations is not just a legal obligation but also a moral imperative. By following these guidelines, homeowners demonstrate their commitment to community safety and responsibility. Additionally, adherence to regulations can help homeowners avoid costly fines, legal liabilities, and potential lawsuits that may arise from non-compliance.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the various aspects of residential swimming pool regulations, exploring the different types of regulations, safety measures, construction requirements, and the importance of compliance with local laws. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, homeowners can create a safer environment for themselves, their families, and their communities to enjoy the benefits of residential swimming pools without unnecessary risks.
Residential Swimming Pool Regulations
Residential swimming pool regulations are a set of rules and standards established by local governments or authorities to ensure the safety, health, and legality of swimming pools installed on residential properties. These regulations typically cover various aspects of swimming pool ownership, including design, construction, safety features, maintenance, and compliance with building codes and zoning laws. The specific requirements may vary depending on factors such as pool size, location, and jurisdiction, but common regulations often include:
- Fencing Requirements: Regulations often mandate the installation of fences or barriers around swimming pools to prevent unauthorized access, especially by children. Requirements may specify fence height, materials, gate mechanisms, and locking mechanisms.
- Safety Features: Mandatory safety features such as pool alarms, safety covers, and rescue equipment may be required to mitigate the risk of drowning incidents and ensure the well-being of pool users.
- Construction Standards: Regulations may outline standards for pool design, materials, drainage systems, and filtration equipment to ensure structural integrity, water quality, and compliance with building codes.
- Maintenance Guidelines: Requirements for regular testing and treatment of pool water, cleaning, equipment upkeep, and inspection schedules may be specified to maintain a safe and hygienic swimming environment.
- Permitting and Compliance: Homeowners typically need to obtain permits from local authorities before constructing or installing a swimming pool on their property. Compliance with regulations is essential to avoid legal liabilities, fines, and enforcement actions.
Overall, residential swimming pool regulations aim to promote responsible pool ownership, protect public health and safety, and prevent accidents and injuries associated with swimming pools. Homeowners are encouraged to familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure compliance to create a safe and enjoyable swimming environment for themselves, their families, and their communities.
Types of Residential Swimming Pool Regulations
Safety Regulations:
Safety regulations encompass a wide range of measures aimed at preventing accidents and ensuring the well-being of pool users. These may include requirements for pool depth, slope, and dimensions to minimize the risk of drowning. Mandatory safety features such as fences, gates, alarms, and pool covers are often stipulated to prevent unauthorized access, especially by children.
Regulations may also mandate the installation of safety equipment such as lifebuoys, rescue poles, and first aid kits to handle emergencies effectively.
Construction Regulations: 
Construction regulations dictate the standards and procedures for building or renovating residential swimming pools. This includes obtaining permits, adhering to specific building codes, and following safety protocols during construction.
Requirements may cover aspects such as pool design, materials used, drainage systems, and filtration equipment to ensure structural integrity and water quality.
Environmental considerations, such as water conservation measures and energy-efficient pool equipment, may also be addressed in construction regulations.
Maintenance Regulations:
Maintenance regulations outline the responsibilities of pool owners in maintaining a safe and hygienic swimming environment. This includes regular testing and treatment of water to maintain proper chemical balance and prevent the spread of waterborne illnesses.
Guidelines for cleaning, servicing, and inspecting pool equipment such as pumps, filters, and heaters are often specified to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Regulations may also include requirements for maintaining surrounding areas, such as removing debris, repairing damaged surfaces, and ensuring adequate lighting for nighttime use.
Fencing Regulations:
Fencing regulations are aimed at preventing unauthorized access to swimming pools, especially by young children who may be at risk of drowning.
Requirements for fence height, materials, gate latches, and self-closing mechanisms are commonly specified to enhance security and compliance with safety standards.
Exemptions or variations in fencing requirements may exist for certain types of pools, such as indoor pools or those located within enclosed areas.
Variations by Region and Jurisdiction
Residential swimming pool regulations can vary significantly from one region to another and even within different jurisdictions within the same country. Differences may arise due to varying climatic conditions, cultural norms, population density, and legal frameworks. Some regions may have stricter regulations regarding safety features and construction standards, while others may have more lenient requirements based on local priorities and considerations. It’s essential for homeowners to familiarize themselves with the specific regulations applicable to their location and ensure compliance to avoid potential penalties or legal consequences. Consulting local authorities or professional experts can help clarify any uncertainties and ensure that residential swimming pools meet all necessary requirements for safety and legality.

Construction Regulations for Residential Swimming Pools
Construction regulations for residential swimming pools govern the process of building or renovating pools on residential properties. These regulations typically require homeowners to obtain permits from local authorities before commencing construction.
Standards for materials, drainage, and filtration systems are specified to ensure structural integrity, water quality, and compliance with building codes. Additionally, environmental considerations and energy efficiency requirements may be addressed in construction regulations to promote sustainability. Adherence to construction regulations is essential for creating safe and compliant swimming environments for homeowners and their communities.
- Construction Process and Required Permits:
- Before commencing construction, homeowners typically need to obtain permits from local authorities or building departments. Permit requirements vary by jurisdiction but generally involve submitting detailed plans and specifications for the proposed pool construction.
- The construction process typically involves excavation, installation of pool shell or structure, plumbing and electrical work, decking, and finishing touches such as tiling or plastering. Compliance with building codes and safety standards is essential at every stage of construction.
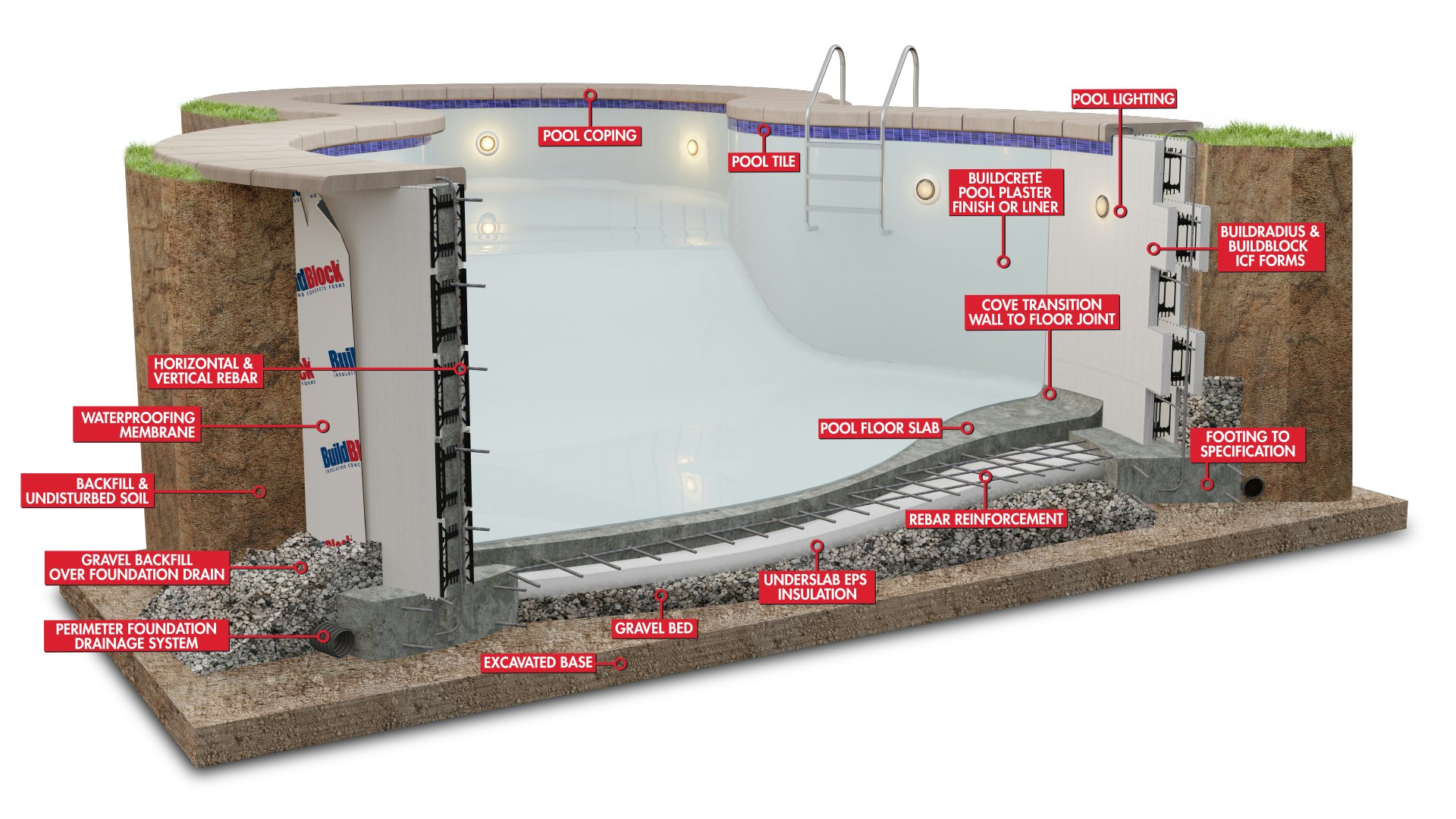
- Standards for Materials, Drainage, and Filtration Systems:
- Materials: Regulations may specify requirements for pool construction materials to ensure durability, safety, and water quality. Common materials include reinforced concrete, fiberglass, or vinyl for pool shells, while decking materials may include concrete, stone, or wood.
- Drainage: Proper drainage is essential to prevent water accumulation around the pool area, which can lead to safety hazards and structural damage. Regulations may dictate the installation of drainage systems, such as French drains or surface drains, to manage runoff effectively.
- Filtration Systems: Regulations often require the installation of filtration and circulation systems to maintain water clarity and hygiene. These systems typically include pumps, filters, skimmers, and chemical treatment equipment to remove impurities and maintain balanced water chemistry.
- Environmental Considerations and Energy Efficiency Requirements:
- Water Conservation: With growing concerns about water scarcity, some jurisdictions may have regulations or guidelines promoting water conservation measures for swimming pools. These measures may include the use of water-saving technologies such as variable-speed pumps, water-efficient filtration systems, and covers to minimize evaporation.
- Energy Efficiency: Regulations may also address energy efficiency considerations for pool equipment and operation. This may involve requirements or incentives for using energy-efficient pumps, heaters, and lighting fixtures, as well as promoting solar or other renewable energy sources for pool heating.
- Safety Considerations During Construction:
- During construction, safety measures should be implemented to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with regulations. This includes securing the construction site, providing adequate barriers and signage, and adhering to safety protocols for excavation, electrical work, and equipment installation.
- Construction activities should be supervised by qualified professionals, such as licensed contractors or pool builders, to ensure that work is performed according to industry standards and regulatory requirements.
By adhering to construction regulations, homeowners can ensure that their residential swimming pools are built safely, comply with legal requirements, and contribute to environmental sustainability. Consulting with experienced professionals and familiarizing oneself with local building codes and regulations are essential steps in the pool construction process to ensure successful completion and compliance.
1. What are the requirements for fencing around a residential swimming pool? Fencing requirements vary by jurisdiction but typically include specifications for fence height, materials, gates, and locks. Fences must be tall enough to prevent unauthorized access, constructed from durable and non-climbable materials, and equipped with self-closing and self-latching gates.
2. Do I need a permit to build a swimming pool in my backyard? Yes, in most cases, you will need a permit from your local building department or authority before constructing a swimming pool in your backyard. Permit requirements may vary depending on factors such as pool size, location, and local regulations.
3. What safety features are mandatory for residential swimming pools? Mandatory safety features typically include fences, gates, alarms, and pool covers. These features are designed to prevent unauthorized access, especially by children, and mitigate the risk of drowning incidents.
4. How often should I test and treat the water in my swimming pool? It’s recommended to test the water in your swimming pool at least once a week during the swimming season and adjust chemical levels as needed to maintain proper balance. Additionally, regular monitoring of water clarity and appearance can help identify issues that require attention.
5. What are the consequences of non-compliance with swimming pool regulations? Non-compliance with swimming pool regulations can result in legal liabilities, fines, and safety hazards. Homeowners may be held responsible for accidents or injuries resulting from failure to comply with safety regulations, leading to potential lawsuits and financial penalties.



