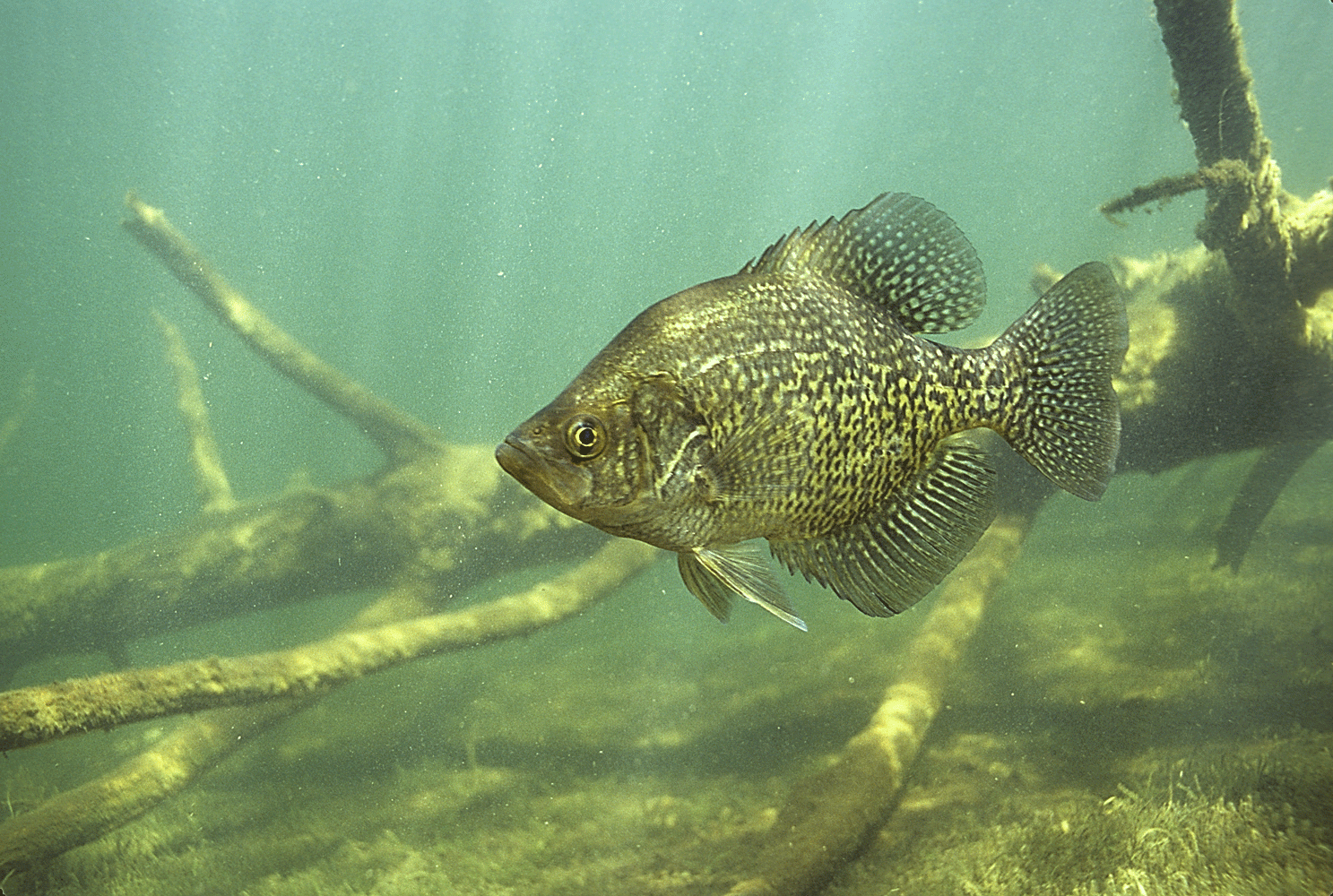
Crappie can be easy to catch when you find them schooled up, particularly in the spring when they go shallow, and then sometimes very tough to find and catch during other parts of the year such as the winter when they congregate in deeper areas where water is a bigger part of trying to catch this fun fish. What are Ideal Water Conditions for Crappie?
Crappie known for great taste & aggressive nature demands H2O quality:
Introduction:
Crappie fishing is a popular recreational activity enjoyed by anglers across the globe. Crappies, a species of freshwater fish belonging to the sunfish family, are renowned for their delicious taste and challenging nature, making them a prized catch among fishing enthusiasts. These fish are known for their distinctive appearance, with large mouths and slender bodies. They typically inhabit freshwater lakes, ponds, rivers, and reservoirs, where they can be found near submerged structures such as fallen trees, weed beds, and underwater brush piles.
Anglers employ various techniques to catch crappie, including using live bait such as minnows or artificial lures like jigs and spinners. Crappie fishing can be pursued year-round, but the best times often coincide with their spawning seasons in the spring and fall. Successful crappie fishing requires knowledge of their behavior, habitat preferences, and the environmental factors that influence their movements. Understanding water conditions, such as temperature, oxygen levels, water clarity, and structure, is crucial for locating and enticing these elusive fish.
Understanding water conditions is essential for successful crappie fishing as it directly impacts the behavior and habitat preferences of these elusive fish. Factors such as temperature, oxygen levels, water clarity, and structure significantly influence where crappie congregate and how they respond to bait. By analyzing and adapting to these conditions, anglers can increase their chances of locating and catching crappie effectively.

What are Ideal Water Conditions for Crappies
The ideal water conditions for crappie fishing typically include:
- Temperature: Crappies thrive in water temperatures ranging from 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C). Warmer temperatures in this range tend to increase their activity and feeding behavior.
- Oxygen Levels: Adequate oxygen levels, ideally between 5 to 7 milligrams per liter (mg/L) of water, are crucial for crappie survival and activity. Oxygen-rich areas, such as near submerged structures or in well-oxygenated waters, attract more crappie.
- Water Clarity: While crappie can adapt to various water clarity conditions, they often prefer clear to slightly stained water. Clearer water allows them to detect prey more easily, although they may adjust their behavior in response to stained or murky conditions.
- Structure and Cover: Crappies are commonly found near submerged structures like fallen trees, brush piles, weed beds, and docks, which provide shelter and ambush points for feeding.
- pH Levels: Crappie habitats typically have pH levels within the range of 6.5 to 8.0. Extremes outside this range can stress crappie and affect their health and behavior.
Understanding and monitoring these water conditions can significantly increase the chances of locating and catching crappie effectively. Anglers often use various techniques and adapt their strategies based on the prevailing water conditions to maximize their success in catching crappie.
Ideal Oxygen Level for Crappie
Oxygen is vital for crappie survival as it is essential for their respiration process. Adequate oxygen levels ensure that crappie can maintain their metabolic functions, including growth, reproduction, and overall health.
Ideal Oxygen Levels for Crappie and How They Vary with Temperature and Depth: The ideal oxygen levels for crappie typically range between 5 to 7 milligrams per liter (mg/L) of water. However, these levels can vary depending on factors such as temperature and depth. Warmer water holds less oxygen than cooler water, so during hot summer months, oxygen levels may decrease, leading crappie to seek out cooler, oxygen-rich areas. Additionally, oxygen levels tend to decrease with depth due to reduced surface agitation and plant photosynthesis, further influencing crappie behavior and distribution.
Factors Influencing Oxygen Levels in Water Bodies: Several factors can influence oxygen levels in water bodies, including temperature, aquatic plant growth, weather conditions, pollution, and nutrient levels. For example, excessive nutrient runoff from agricultural or urban areas can lead to algal blooms, which consume oxygen during decomposition, causing oxygen depletion in the water. Understanding these factors and their impacts on oxygen levels is crucial for managing crappie habitats and ensuring their long-term survival.

Ideal Water Clarity for Crappie
Impact of Water Clarity on Crappie Behavior: Water clarity significantly influences crappie behavior. In clear water, crappie may be more cautious and easily spooked by anglers, requiring stealthier fishing approaches. Conversely, in murky or stained water, crappie may rely more on their lateral line to detect prey, leading to different feeding behaviors and preferences for bait presentation.
Techniques for Fishing in Different Water Clarity Conditions: In clear water, finesse techniques such as using smaller baits, light lines, and subtle presentations like drop-shotting or wacky rigging can be effective for targeting wary crappie. In murky or stained water, anglers may opt for more aggressive tactics such as using larger baits with contrasting colors or noisy lures to attract crappie’s attention.
How Weather and Environmental Factors Affect Water Clarity: Weather and environmental factors can significantly impact water clarity. Heavy rainfall can cause sediment runoff, resulting in muddy or turbid water conditions that reduce visibility. Conversely, periods of drought or low water flow may lead to clearer water as sediment settles. Wind can also stir up sediment and affect water clarity, while aquatic plant growth can either improve clarity by stabilizing sediment or degrade it by releasing organic matter. Understanding these factors allows anglers to adapt their fishing strategies accordingly and maximize their success in varying water clarity conditions.
Ideal Water pH Level for Crappie
Effects of pH Levels on Crappie Health and Behavior:
pH levels can have significant effects on crappie health and behavior. Extreme pH levels outside the optimal range can stress crappie, affecting their immune system, growth rates, and reproductive success. Additionally, pH levels can influence the availability of essential nutrients and toxic substances in the water, further impacting crappie populations.
Optimal pH Range for Crappie Habitats:
The optimal pH range for crappie habitats typically falls between 6.5 to 8.0. Within this range, crappie are better able to maintain physiological functions and thrive. However, it’s essential to note that some local populations may have adapted to slightly different pH ranges based on their specific habitat conditions.
How to Measure and Adjust pH Levels in Fishing Areas:
pH levels can be measured using pH testing kits or meters, which are readily available at fishing supply stores or online. I prefer reliable digital meters. If pH levels are outside the optimal range for crappie, adjustments may be necessary. Adding materials such as agricultural lime to raise pH levels or sulfur to lower them can help bring water conditions closer to the desired range. However, it’s crucial to proceed with caution and consult with local authorities or fisheries experts to ensure any adjustments are done safely and effectively, as excessive pH manipulation can have unintended consequences on aquatic ecosystems.
Ideal Moon Phase for Crappie Fishing
Ideal Water Structure and Covers for Crappie Habitat
Understanding the key factors that influence crappie behavior and habitat preferences is essential for anglers seeking success on the water. Factors such as water temperature, oxygen levels, water clarity, structure, and pH levels play a significant role in determining where crappie congregate and how they respond to bait.
By monitoring and comprehending these water conditions, anglers can pinpoint optimal fishing spots and tailor their techniques accordingly, increasing their chances of catching crappie. Whether it’s adjusting bait presentations based on water clarity or targeting specific structures favored by crappie, adaptability is crucial.
Additionally, staying informed about local weather forecasts and water conditions allows anglers to plan their fishing trips strategically. By remaining patient, flexible, and willing to experiment with different approaches, anglers can maximize their chances of a successful crappie fishing outing, regardless of the prevailing water conditions.
*Portable Dissolved Oxygen Meter Kit, DO Meter Dissolved Oxygen Detector Water Tester, DO Range: 0-20mg/L, DO Sensor Tester with Cable Probe, for Aquaculture and Waterway Testing.
References:
Midwest Outdoors- Water Temperature for Crappie Sucess
Outdoor Life- Crappie by Degrees
FAQ’s
Crappies can be found at various depths depending on the time of year and water conditions. In general, they tend to inhabit shallower waters during spawning seasons in spring and fall, while they may move deeper in the summer and winter months, often suspending at different depths based on factors like temperature and available food sources.
How do I clean and prepare crappie for cooking?
Black and white crappie can be distinguished by several key features:
- Body Coloration: Black crappie tend to have a more uniform dark coloration, while white crappie have a lighter background with distinct vertical bars or stripes.
- Dorsal Fin: The dorsal fin of black crappie has 7 to 8 spines, while white crappie typically has 5 to 6 spines.
- Body Shape: Black crappie has a deeper body compared to white crappie, which are more elongated.
- Distribution: Black crappie is more commonly found in clear, vegetated waters, while white crappie is often found in a wider range of habitats, including lakes, rivers, and reservoirs.