Largemouth Bass fishing provides an exciting season all year round, and that’s largely due to not only the viciousness that bass exhibit when they’re caught, but also because of how their behaviors change frequently in their environment. What are Ideal Water Conditions for Largemouth Bass?
Ideal water conditions for Largemouth Bass:
H2O Temperature: 65-85°F
Oxygen: Adequate dissolved oxygen levels
pH: 6.5-8.5
Clarity: Moderate to clear
Cover: Vegetation, woody debris
Structure: Submerged rocks, docks
Nutrients: Balanced levels
Human Impact: Reduced pollution, habitat preservation
While there are a lot of different factors that go into when the best time to fish is, from water temperature to barometric pressure and water clarity, there’s one surefire period when the bass are ready to nab just about anything that comes into sight: Spawning season.
Introduction:
Largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) is an iconic freshwater fish species renowned for its popularity among anglers and its role in ecosystem dynamics. Recognizable by its distinctive largemouth, sleek body, and characteristic greenish coloration, the largemouth bass is native to North America but has been introduced to various other regions worldwide due to its recreational value. With a voracious appetite and impressive growth potential, largemouth bass often occupy the top of the food chain in freshwater ecosystems, exerting significant influence on prey populations and overall ecosystem balance.
The habitat requirements of largemouth bass extend beyond mere availability of water; rather, they are intricately linked to specific water conditions vital for their survival and well-being. Optimal water conditions encompass a delicate balance of factors such as temperature, dissolved oxygen levels, pH balance, water clarity, and habitat structure.
These factors collectively influence the distribution, behavior, and reproductive success of largemouth bass. Any deviations from the ideal conditions can have profound impacts on bass populations, affecting growth rates, spawning success, and overall ecosystem health. Consequently, understanding and managing water conditions is paramount for ensuring the sustainability of largemouth bass populations and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Ideal Water Conditions for Largemouth Bass
Ideal water conditions for largemouth bass include temperatures ranging from 65°F to 85°F, ensuring optimal metabolic rates and activity levels. Adequate dissolved oxygen levels are crucial for bass survival, with concentrations above 5 parts per million (ppm) generally preferred.
Bass thrive in waters with a pH range of 6.5 to 8.5, maintaining physiological balance. Clear to moderately clear water allows bass to effectively locate prey and navigate their environment, while abundant cover such as submerged vegetation and woody debris provides essential shelter and spawning sites for bass populations. Overall, maintaining these key water conditions is vital for supporting healthy largemouth bass populations and sustaining productive fisheries.

Ideal H2O Temperature Range for Largemouth Bass
Largemouth bass thrive within a relatively narrow water temperature range, typically between 65°F to 85°F (18°C to 29°C). Within this range, bass exhibits optimal metabolic rates, feeding activity, and growth potential. Temperatures towards the upper end of this range are generally preferred during the warmer months when bass are more active and undergo spawning activities.
Effects of Temperature Extremes
Temperature extremes, whether excessively high or low, can have detrimental effects on largemouth bass populations.
- High Temperatures: Excessive heat can lead to reduced dissolved oxygen levels in water, causing stress and potentially suffocating bass. It can also increase bass metabolism, leading to greater energy expenditure and potential heat stress.
- Low Temperatures: Extremely cold temperatures can slow down bass metabolism, reducing their activity levels and feeding behavior. Prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can even result in mortality, especially if ice cover prevents access to oxygen.
Seasonal Variations in Water Temperature
Seasonal fluctuations in water temperature significantly influence largemouth bass behavior and habitat utilization.
- Spring: Water temperatures rise, triggering increased bass activity, feeding, and spawning. Bass move to shallower areas to seek out warmer water and suitable spawning sites.
- Summer: Water temperatures peak, with bass often seeking cooler, deeper waters or shaded areas during the hottest parts of the day.
- Fall: As temperatures begin to cool, bass becomes more active again, feeding voraciously to store energy for the upcoming winter months.
- Winter: Water temperatures drop, leading bass to adopt slower metabolic rates and reduced activity levels. Bass may seek out deeper, warmer waters or areas with minimal temperature fluctuations to conserve energy and survive the colder temperatures.
Understanding these seasonal temperature variations is crucial for anglers and fisheries managers in predicting bass behavior and optimizing management strategies throughout the year.
Ideal Water Clarity for Largemouth Bass
Effects of Water Clarity on Bass Feeding and Spawning Behavior
Water clarity significantly influences largemouth bass behavior, particularly regarding feeding and spawning:
- Feeding Behavior: Bass relies heavily on sight to locate and ambush prey. In clear water, bass have better visibility, allowing them to effectively hunt for prey such as smaller fish, insects, and crustaceans. However, in turbid or murky water, visibility is reduced, making it more challenging for bass to locate prey.
- Spawning Behavior: Water clarity also affects bass spawning behavior. Bass typically prefers clear water with adequate vegetation or structure for nesting. Clear water allows bass to defend their nests more effectively and enhances the survival rate of their offspring by providing better visibility and protection.
Optimal Clarity Conditions for Largemouth Bass
The optimal clarity conditions for largemouth bass vary depending on factors such as habitat structure and prey availability. However, in general:
- Moderate Clarity: Bass often thrive in water with moderate clarity, where visibility is sufficient for effective hunting and nest defense, but not so clear that bass are easily spooked by predators.
- Clear Water: Clear water conditions are preferred for bass spawning activities, as they provide better visibility for nest construction and guarding.
Factors Influencing Water Clarity
Several factors can influence water clarity in freshwater environments:
- Sedimentation: Runoff from land, erosion, and sedimentation can cloud water, reducing clarity. Construction activities, deforestation, and agriculture can increase sedimentation rates.
- Algal Blooms: Excessive nutrient input can lead to algal blooms, which can reduce water clarity by imparting a greenish tint or forming surface scums.
- Turbulence: Wave action, wind, and boat traffic can stir up sediment and decrease water clarity, especially in shallow areas.
- Aquatic Vegetation: Under certain conditions, aquatic vegetation can improve water clarity by stabilizing sediments and absorbing nutrients. However, excessive vegetation growth can also reduce clarity if it becomes too dense.
Understanding the factors influencing water clarity and its effects on bass behavior is crucial for fisheries management and habitat conservation efforts. Monitoring water clarity and implementing measures to mitigate factors that degrade water clarity can help maintain suitable habitat conditions for largemouth bass and other aquatic species.
Ideal Cover and Structure for Largemouth Bass
Nutrient levels in freshwater ecosystems can significantly impact largemouth bass growth and reproduction:
- Growth: Excessive nutrient levels, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, can stimulate primary productivity, leading to increased availability of food resources for bass. This can result in enhanced growth rates and larger individual bass within the population.
- Reproduction: Adequate nutrient levels are essential for supporting the growth and survival of planktonic organisms, which serve as food sources for larval bass. Insufficient nutrients can lead to reduced prey availability, impacting larval bass growth and survival rates. Conversely, excessive nutrient levels can lead to algal blooms and hypoxic conditions, which may negatively affect bass spawning success and offspring survival.

Sources of Nutrients in Freshwater Ecosystems
Nutrients enter freshwater ecosystems from various sources, including:
- Agricultural Runoff: Fertilizers and manure applied to agricultural fields can wash into nearby water bodies, contributing excess nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Urban Runoff: Stormwater runoff from urban areas can carry pollutants, including nutrients from lawns, gardens, and impervious surfaces, into streams, rivers, and lakes.
- Wastewater Discharge: Sewage treatment plants and septic systems release nutrients into water bodies through effluent discharge.
- Atmospheric Deposition: Airborne pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides from vehicle emissions and industrial activities, can deposit into water bodies via rainfall and atmospheric deposition.
Balancing Nutrient Levels for Healthy Bass Populations
Achieving a balance in nutrient levels is crucial for maintaining healthy bass populations and overall ecosystem health:
- Nutrient Management: Implementing nutrient management strategies, such as agricultural best management practices (BMPs), to reduce nutrient runoff from agricultural lands can help mitigate nutrient pollution in freshwater ecosystems.
- Stormwater Management: Implementing green infrastructure practices, such as rain gardens and vegetated buffers, can help capture and filter nutrients from urban runoff before they reach water bodies.
- Wastewater Treatment: Upgrading wastewater treatment facilities and implementing advanced treatment technologies can help reduce nutrient loads in effluent discharge.
- Eutrophication Control: Managing excessive nutrient inputs to prevent eutrophication, such as through the reduction of nutrient runoff and the implementation of nutrient trading programs, can help maintain balanced nutrient levels in freshwater ecosystems.
By managing nutrient levels effectively, fisheries managers and conservationists can help ensure suitable habitat conditions for largemouth bass and other aquatic species, ultimately supporting healthy and resilient freshwater ecosystems.
Ideal Moon Phase for Largemouth Bass Fishing
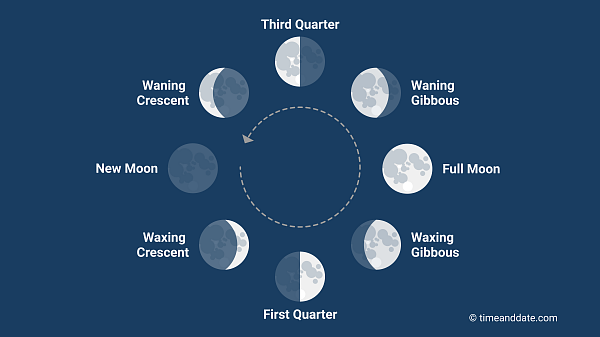
The ideal moon phase for largemouth bass fishing is typically associated with the periods leading up to the full moon and new moon. During these phases, bass tend to be more active and feed more aggressively, making them more susceptible to angler presentations. However, it’s important to note that factors such as weather conditions, water temperature, and time of day also play significant roles in bass behavior. Anglers should adapt their strategies based on a combination of factors rather than relying solely on the moon phase.
During the period leading up to the full moon, largemouth bass tend to feed actively both during the day and night, as the increased moonlight provides better visibility for hunting prey. This can result in heightened feeding activity and more opportunities for anglers to catch bass.
Similarly, the new moon phase, when the moon is not visible in the sky, can also be productive for bass fishing. Bass may take advantage of the darkness to move into shallower waters to hunt for prey under the cover of darkness.
However, it’s essential to consider other factors such as water temperature, weather conditions, and the presence of natural or artificial cover when planning a bass fishing trip. While moon phases can influence bass behavior, they are just one piece of the puzzle in successful fishing strategies.
Ideal Weather and Barometer Pressure for Largemouth Bass Fishing
Ideal weather conditions for largemouth bass fishing typically involve stable atmospheric conditions and moderate temperatures. A mild, partly cloudy day with light winds is often preferred, as it allows the bass to remain active without being overly affected by harsh weather.
In terms of barometric pressure, a steady or rising barometer reading is generally associated with improved fishing success, as it indicates stable weather conditions. However, some anglers also find success during periods of falling barometric pressure, particularly if accompanied by slight cloud cover or light rain. Overall, a barometer reading in the range of 29.80 to 30.30 inches of mercury (Hg) is considered favorable for largemouth bass fishing, but adaptability to changing conditions and understanding local weather patterns are key for successful angling.
Ideal Water Depth for Largemouth Bass Fishing
Human Activities Affecting Water Quality for Largemouth Bass Habitat
Human activities have a significant impact on water quality and largemouth bass habitat, including:
- Pollution: Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and urban stormwater runoff introduce pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, fertilizers, and organic contaminants into water bodies. These pollutants can degrade water quality, disrupt aquatic ecosystems, and harm largemouth bass and other aquatic organisms.
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, urbanization, and land development lead to habitat loss and fragmentation, reducing the availability of suitable habitat for largemouth bass. Wetland drainage and shoreline alteration also contribute to habitat degradation, diminishing bass spawning areas and foraging grounds.
- Overfishing: Overfishing and unsustainable harvesting practices can deplete largemouth bass populations, leading to declines in abundance and genetic diversity. Illegal fishing methods, such as dynamite fishing and electrofishing, further exacerbate the problem by indiscriminately killing bass and other non-target species.
- Introduction of Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native invasive species, such as exotic plants and predatory fish, can disrupt native ecosystems and outcompete native species like largemouth bass for food and habitat resources.
- Climate Change: Climate change impacts, including rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events, can exacerbate existing stressors on largemouth bass populations and their habitats. Changes in water temperature and flow regimes, as well as increased frequency of droughts and floods, can negatively affect bass survival, reproduction, and distribution.
Effective management and conservation efforts are essential for mitigating the adverse effects of these human activities on water quality and largemouth bass habitat. Implementing measures such as pollution control, habitat restoration, sustainable fisheries management, invasive species control, and climate adaptation strategies can help protect and preserve largemouth bass populations and their ecosystems for future generations.
Conclusion:
References:
Bass Forecast-When Do Bass Spawn?
FAQ’s
What should I look for when selecting a fishing spot for largemouth bass?
- Look for areas with suitable habitat features such as cover, structure, and depth changes. Also, pay attention to water temperature, current flow, and the presence of baitfish, as these factors can influence bass behavior and feeding patterns.
What is the best rod and reel setup for bass fishing?
- The best rod and reel setup for bass fishing depends on personal preference, fishing style, and budget. However, a medium to medium-heavy spinning or baitcasting rod paired with a quality reel and suitable line (such as monofilament, fluorocarbon, or braided line) is often recommended for bass fishing.
What fishing regulations should I be aware of when targeting largemouth bass?
- It’s essential to familiarize yourself with local fishing regulations, including size limits, bag limits, and seasonal closures for largemouth bass. Additionally, practicing catch-and-release fishing can help conserve bass populations for future generations.
How do I handle and release largemouth bass properly to ensure their survival?
- When handling largemouth bass, wet your hands before touching them to minimize damage to their protective slime coat. Support the fish horizontally, avoid squeezing or dropping them, and release them gently back into the water as soon as possible to minimize stress and increase their chances of survival.
How do I locate largemouth bass in a lake or pond?
- Bass can be found near various types of cover and structures, such as submerged vegetation, docks, fallen trees, and rocky areas. Additionally, bass often relate to changes in depth, including points, drop-offs, and humps. Using a fish finder or paying attention to water temperature and seasonal patterns can also help locate bass.



