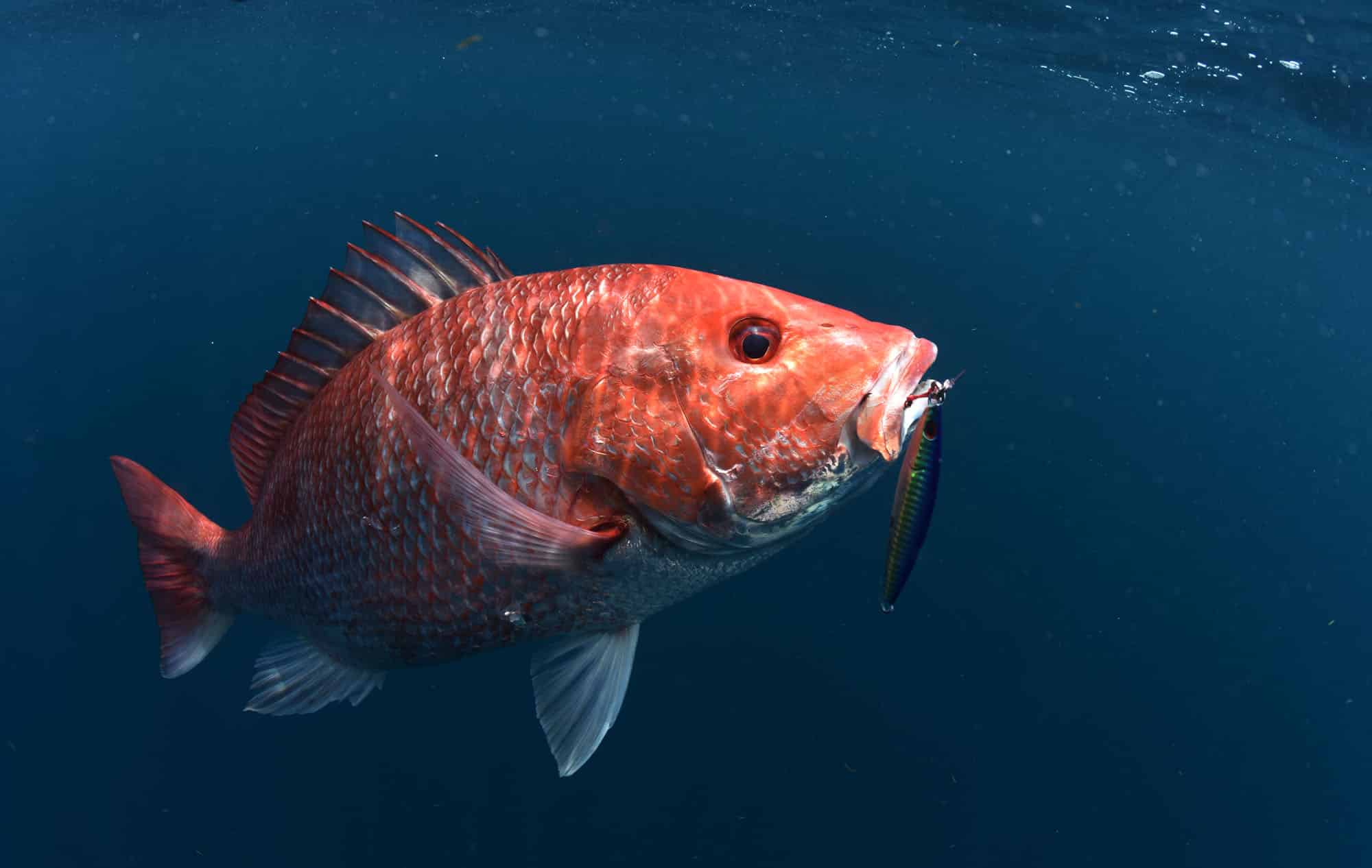
Red Snapper can grow very large and they are popular with recreational fishermen as well as commercial seafood markets and restaurants. Snappers are bottom dwellers that are a trophy catch for anglers. What are Ideal Water Conditions for Snapper?
Introduction:
Ideal water conditions for snapper fishing typically include clear water with good visibility, moderate currents, and water temperatures ranging from 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C). Snappers are often found in areas with ample structure such as reefs, wrecks, and underwater ledges, providing them with shelter and opportunities to ambush prey. Additionally, areas with a variety of baitfish and crustaceans, which snapper feed on, are prime locations for finding these fish.
While Snapper can be caught in different water depths, they often prefer depths ranging from 30 to 100 feet (9 to 30 meters), depending on the species and environmental conditions. Lastly, water clarity and conditions can vary depending on location and season, so adapting to local conditions and using techniques suited to the prevailing environment can enhance your chances of success when targeting snapper.
Characteristics of Snapper
Snapper fish are a diverse group of marine fish belonging to the family Lutjanidae, which encompasses over 100 species worldwide. They are primarily found in tropical and subtropical waters, inhabiting coastal areas, reefs, and offshore structures. Snapper are characterized by their sleek, elongated bodies, powerful jaws equipped with sharp teeth, and vibrant coloration ranging from red and pink to yellow and silver.
Common characteristics of Snapper fish include a streamlined body shape, typically ranging from cylindrical to slightly compressed. They have large, prominent eyes positioned high on their heads, allowing for excellent vision in dimly lit environments. Snapper possess well-defined fins, including a dorsal fin with sharp spines, an anal fin, and a caudal fin, which aid in maneuverability and propulsion.
Their scales are often small and cycloid, providing them with a smooth, reflective surface. Additionally, snappers exhibit various color patterns and markings, often featuring stripes, spots, or mottled patterns, which can serve as camouflage or visual signals within their habitats. Overall, these physical features contribute to the adaptability and predatory prowess of snapper fish in their marine ecosystems.
Ideal Water pH for Snapper
The ideal water pH for Snapper fish typically ranges between 7.5 and 8.5. Snapper fish are adaptable to a variety of water conditions, but they tend to thrive in slightly alkaline environments. A pH within this range provides a stable and suitable pH level for the physiological processes of snapper, including respiration, digestion, and osmoregulation.
However, it’s essential to note that water pH is just one factor among many that can influence snapper behavior and health. Other factors such as water temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen levels, and habitat characteristics also play significant roles in determining the overall suitability of an environment for Snapper fish.
Ideal Oxygen Rate for Snapper
Ideal H2O Nutrients for Snapper
While water nutrient levels are not typically a direct consideration for snapper fishing, healthy marine ecosystems with balanced nutrient levels can indirectly benefit snapper populations. Nutrient levels in the water, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, play a vital role in supporting primary productivity, which forms the base of the marine food chain. Adequate nutrient availability can lead to the growth of phytoplankton and algae, which in turn provide food for zooplankton, small fish, and crustaceans that snapper feed on.
In general, nutrient-rich coastal areas, estuaries, and upwelling zones tend to support robust marine ecosystems with abundant prey resources for snapper. However, excessive nutrient runoff from human activities such as agriculture, urban development, and sewage discharge can lead to eutrophication, algal blooms, and degraded water quality, which may negatively impact snapper habitats and prey availability.
Therefore, while there is no specific “ideal” nutrient level for snapper fishing, maintaining balanced nutrient levels and healthy marine ecosystems is essential for supporting sustainable snapper populations and productive fishing grounds. Conservation efforts aimed at reducing nutrient pollution and preserving critical habitats can help ensure the long-term health and viability of snapper fisheries.
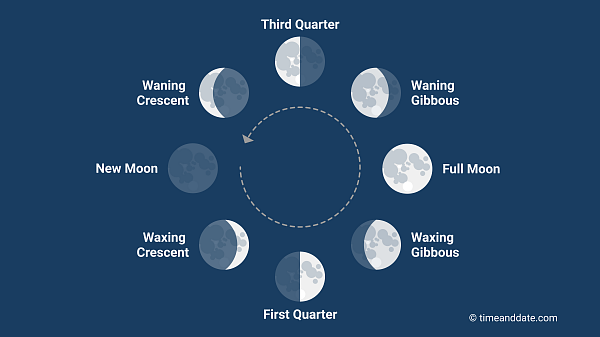
Ideal Moon Phase for Snapper Fishing
References:
HookinMouth Tackle- What Optimal Conditions for Snapper Fishing
FAQ’s
- How can I ensure I’m fishing for snapper sustainably?
Know and Follow Regulations- Familiarize yourself with local fishing regulations, including size limits, bag limits, and closed seasons. Adhere to these regulations to prevent overfishing and help maintain healthy snapper populations.
- What types of snapper are commonly targeted by anglers?
Anglers commonly target several species of snapper, prized for their delicious taste and sporting challenge. Some of the most commonly targeted snapper species include:
- Red Snapper (Lutjanus campechanus): A highly sought-after species known for its firm texture and sweet flavor. Red snappers are found in the Gulf of Mexico and along the southeastern coast of the United States.
- Yellowtail Snapper (Ocyurus chrysurus): Recognized by their vibrant yellow tail, yellowtail snapper inhabit the warm waters of the Caribbean Sea and western Atlantic Ocean. They are prized for their delicate flesh and are popular among anglers.
- Mangrove Snapper (Lutjanus griseus): Found in coastal mangrove habitats throughout the western Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico, mangrove snapper are known for their reddish-orange coloration and delicious taste.
- Lane Snapper (Lutjanus synagris): Characterized by their pale pink or reddish bodies adorned with yellow stripes, Lane Snapper are commonly found in the western Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico. They are abundant and cooperative targets for anglers.
- Mutton Snapper (Lutjanus analis): Revered for their large size and succulent, white meat, mutton snapper inhabit the coral reefs and rocky bottoms of the Caribbean Sea and western Atlantic Ocean.