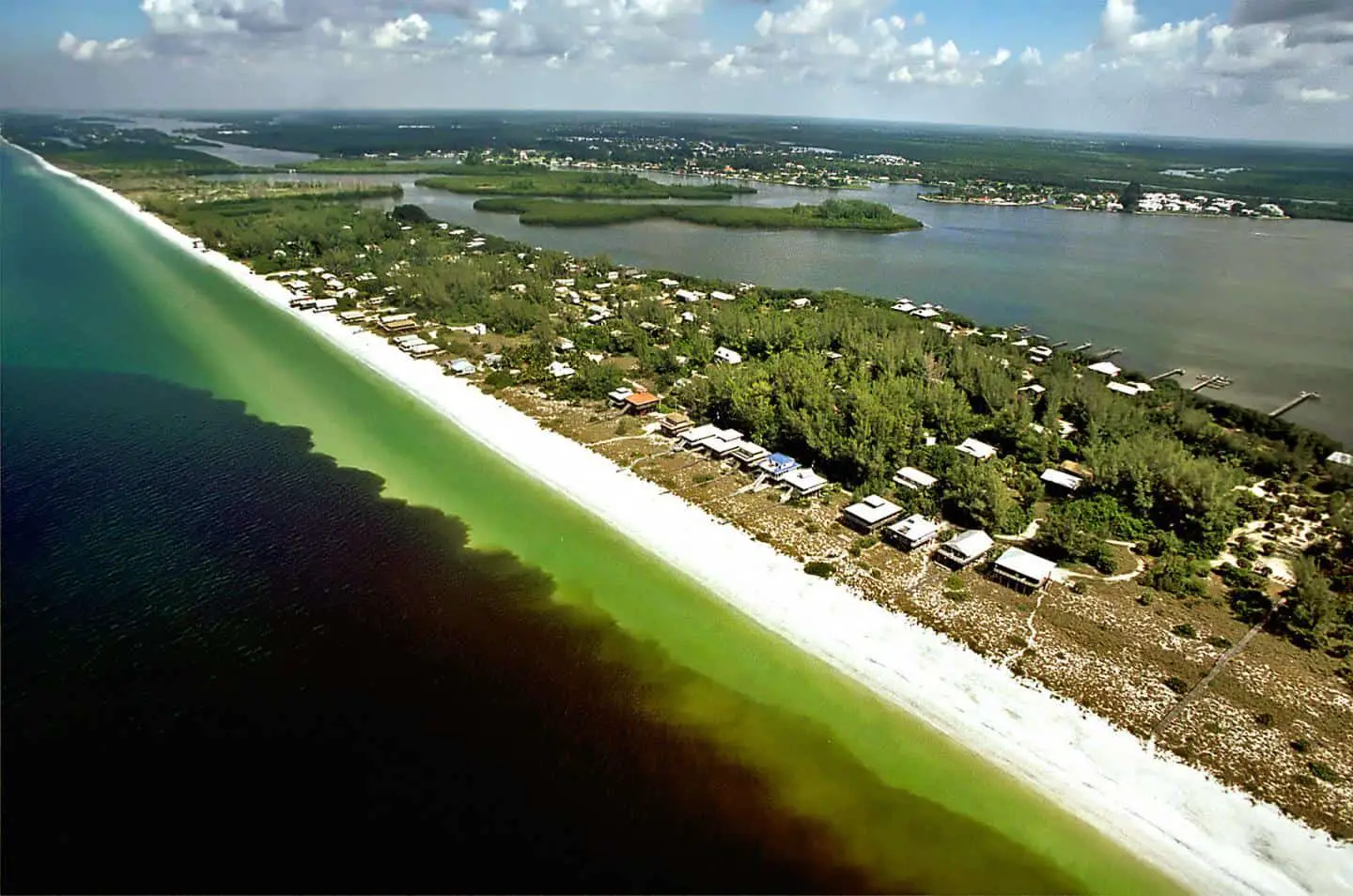
Thousands of dead fish, numerous turtles, manatees, and even sea birds have been washing up on the beach in Southern Florida where Karenia Brevis, microscopic toxic algae that make up the Harmful Algal Blooms (HAB) turning the water off the coast of Florida Red. The Red Tide causes toxins called Brevotoxins that leave the ocean depleted of Oxygen and poisoned also creating airborne toxins that can hurt humans and marine life. How long does the Red Tide Last in Florida?
Normally, Florida’s naturally occurring Red Tides called Karenia brevis last 5-6 months beginning in the late summer/early fall & lasting through winter until February/March, where it normally dissipates because of sustained winds or lack of nutrients to feed on.
Red Tides have been around for hundreds of years and are a typical sight every year in this area of Florida. But for the last 20 years, the massive Algal Blooms have dissipated slower, especially since the 2018 season, according to the NOAA forecast and Update the movement of the Red Tides and monitors daily on their Website called Red Tide In Florida and Texas.
Introduction:
Hello eager learners! Today, we’re diving into an intriguing topic that often mystifies many: the Red Tide. This natural phenomenon can be quite puzzling due to its sudden appearance and disappearance. But, for just how long does the Red Tide last? Read on, as we investigate this topic, unraveling its mystery, and learning about the various factors that determine the duration of Red Tide events in Florida and the Gulf affecting wildlife like shellfish, fish, and even local beach-goers who enjoy the beach.
How Long Does Red Tide Last in Florida
The duration of a red tide can vary based on several factors, including environmental conditions and the specific species of algae causing the bloom. Red tides are typically temporary events, but their duration can range from weeks to months. Some red tides may dissipate relatively quickly, while others persist for a more extended period.
Factors influencing the duration of red tides include nutrient levels, water temperature, salinity, and currents. In some cases, human activities such as nutrient runoff from agricultural areas can contribute to the formation and persistence of red tide events.
If you’re specifically concerned about a current red tide event in a particular location, it’s advisable to check with local environmental agencies or authorities for the most up-to-date and accurate information.
There are early reports of this natural phenomenon called Red Tide in the Gulf Of Mexico region of Florida waters, documented years ago as early as the 1500s in Captains’ logs from Spanish explorers that described the same kind of symptoms of their crew, as people describe today from the coastal areas section of Florida.
Sneezing, coughing, and watery eyes along with red color and dead fish. The first sample was taken from the Gulf in 1844 but the organism that causes the algae wasn’t discovered and named Karenia brevis until 1944. Florida’s Gulf Red Tide was around long previous to humans and industry populated the coast.
Karenia brevis blooms causing Red Tide that occurs in the Gulf of Mexico almost every year, generally in late summer or early fall. They are most common on the central and southwestern coasts of Florida between Clearwater and Sanibel Island but may occur anywhere in the Gulf.
Red Tides show up in the Fall around September but are normally at their peak in November. The Harmful Algae bloom can last anywhere from a few days to three to five months and sometimes longer in Florida waters once a year.
Red tide, caused by an overgrowth of algae, can vary in duration. The duration depends on several factors, including the type of algae, environmental conditions, and nutrient availability. Red tide events can last anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
In some cases, they may persist for a more extended period. Monitoring agencies typically track and provide updates on red tide conditions in affected areas. If you have a specific location in mind, you may want to check with local environmental agencies for more accurate and up-to-date information on the duration of red tide in that area.
Impacts of Red Tide Blooms: Health Concerns and Respiratory Irritations
Red tide blooms, caused by the proliferation of harmful algal species, can have significant health impacts. One of the primary concerns is the release of toxins known as brevetoxins, which can contaminate shellfish and finfish. Consuming contaminated seafood can lead to neurotoxic shellfish poisoning in humans.
Additionally, red tide blooms can release aerosolized toxins into the air, leading to respiratory irritations when inhaled. This can cause symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, throat irritation, and in severe cases, difficulty breathing. People with pre-existing respiratory conditions may be particularly vulnerable to these effects, necessitating caution and public health advisories during red tide events.
Red tide blooms can have various impacts on both marine life and human health. Here are some of the health concerns and respiratory irritations associated with red tide:
- Toxins in the Air: The algae responsible for red tide, such as Karenia brevis, can release toxins into the air. These toxins become aerosolized and can be carried by the wind. When people breathe in these aerosols, it can lead to respiratory irritation.
- Respiratory Irritations: Exposure to red tide toxins can cause respiratory symptoms in humans, particularly in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic bronchitis. Symptoms may include coughing, sneezing, throat irritation, and difficulty breathing.
- Eye Irritation: Contact with red tide toxins, either through direct exposure to the water or inhalation of aerosolized toxins, can cause eye irritation. This may include redness, tearing, and a burning sensation.
- Skin Irritation: Some individuals may experience skin irritation after contact with water affected by red tide. This can manifest as redness, itching, or a rash.
- Fish and Shellfish Toxin Accumulation: Seafood, such as shellfish and certain types of fish, can accumulate red tide toxins. Consumption of contaminated seafood can lead to various health issues, including neurotoxic shellfish poisoning (NSP) and paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP).
It’s essential for individuals in areas affected by red tide to stay informed about the current conditions and follow any advisories issued by local health authorities. If you experience symptoms related to red tide exposure, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. Additionally, individuals with respiratory conditions should take extra precautions, such as staying indoors during red tide events and using air purifiers to reduce exposure to airborne toxins.
Some Officials believe the many estuaries around the Gulf in Florida mainland are the source of nutrients that are feeding the Algae blooms, but those same nutrients are feeding the fish in the ecosystem around Florida waters.
The red tide blooms start too far offshore for anything onshore to determine their size and longevity. Other reasons have been looked at like runoff from Lake Okeechobee and worldwide Climate Change.

Researchers have studied nutrients that have been dragged miles away offshore to feed the harmful algal blooms by hurricanes that have developed in the area in the last few years.
The only thing they are sure of is that the Karenia brevis algal blooms are getting worse and the Brevotoxins that come with them are doing increasing damage. This alga can feed off of other algal blooms. There could be a huge different type of algal bloom in the Gulf water and Florida waters and the Red Tide could be using that as a food source.
It can inhibit the growth of other (blue-green) algal blooms until everything dies. Eat all the food that other species need to survive, Karenia algal bloom can use numerous types of nitrogen and other nutrients according to research, so if you take one source away it will find another way to eat.
Red Tide Blooms can kill fish even though the fish don’t use them as a food source if there is a lack of phosphorus in the water, harmful Red tide algae can turn on or turn off their toxins emitters.
So when it runs out of food namely phosphorus it can turn its toxins emitters on, and kill marine fish that will eventually provide plenty of the new food source, creating their own source of nutrients if necessary.
This makes them a pretty powerful self-sustaining entity in the ecosystem. They could be dangerous aquatic organisms. Very hard to get rid of in the right circumstances.
There is some scientific proof that the Karenia brevis algae learned to feed off other bacteria.
With a density in population and constant nutrients being washed out to the shore, along with southwest Florida water being a perfect haven for these algae to grow numerous and free, this makes many people believe the Red Tide season is increasing from past years in frequency size, and duration, the event more dangerous from the past here in Florida’s waters and will be a danger around the globe in the future.
Unpacking Red Tide Health Risks: Is Red Tide Harmful to Pets
Yes, red tide can be harmful to pets. The toxins produced by certain harmful algal blooms, including red tide organisms like Karenia brevis, can affect marine life, including fish and shellfish. When pets consume contaminated seafood or come into contact with water affected by red tide, they may experience adverse health effects.
Here are some potential risks and precautions for pets during red tide events:
-
How Long Does Red Tide Last in Florida? Toxin Ingestion: If pets ingest seafood, such as fish or shellfish, that has accumulated red tide toxins, it can lead to poisoning. Symptoms may include vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, difficulty breathing, and in severe cases, it can be fatal.
- Contact Irritation: Pets that come into direct contact with water affected by red tide may experience skin irritation. This can manifest as redness, itching, and discomfort.
- Respiratory Issues: Like humans, pets can experience respiratory issues if they inhale aerosolized red tide toxins. This can lead to coughing, sneezing, and difficulty breathing.
To protect pets during red tide events, consider the following precautions:
- Avoid Allowing Pets to Swim in Affected Areas: Keep pets away from waters experiencing red tide blooms to minimize the risk of skin contact and ingestion.
- Do Not Feed Pets Seafood from Affected Areas: Avoid giving pets seafood caught in areas affected by red tide, as it may contain harmful toxins.
- Monitor for Symptoms: Be vigilant for any signs of illness in pets, especially if they have been in or around waters affected by red tide. If you notice symptoms, consult with a veterinarian promptly.
- Follow Local Advisories: Stay informed about red tide conditions in your area through local environmental agencies or health departments. Follow any advisories or guidelines provided for pet safety.
If you suspect that your pet has been exposed to red tide toxins or is showing symptoms of illness, seek veterinary care promptly. Veterinarians can provide appropriate treatment and guidance based on the specific situation.
Red and Blue-Green Algae Blooms: A Comparison
Red and blue-green algae blooms, also known as cyanobacteria blooms, are two distinct types of algal proliferation with different characteristics. Red tide blooms are caused by certain species of dinoflagellates, leading to the discoloration of water and the release of harmful toxins.
These toxins can affect marine life and pose health risks to humans. On the other hand, blue-green algae blooms are caused by cyanobacteria, and they often produce toxins called cyanotoxins. Unlike red tide blooms, blue-green algae blooms are commonly found in freshwater bodies such as lakes and ponds. Both types of blooms can have detrimental environmental impacts, affecting aquatic ecosystems and posing challenges for water quality management.
The dinoflagellate Karenia brevis, or K. brevis, is the alga responsible for red tide, while blue-green algae are caused by different types of cyanobacteria, namely Microcystis aeruginosa, which is believed to be blamed for the massive bloom in Lake Okeechobee, according to researchers from the University of Florida.
Blooms in freshwater lakes and reservoirs are most commonly caused by blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Several different kinds of blue-green algae can cause algal blooms including Microcystis, Anabaena, and Cylindrospermopsis. Water samples suggest that the dominant species affecting the 2018 Lake Okeechobee bloom is Microcystis aeruginosa.
Lake Okeechobee is most prone to having large cyanobacteria blooms when the weather is warm and sunny (spring through early fall). Periods of high rainfall and tropical storms can increase the potential for blooms by stirring up nutrients in the lake bed and increasing the flow of nutrient-rich water into the lake from upstream watersheds.
Like the red tide, blue-green algae can also be harmful to humans and wildlife. Some, but not all, blue-green algae types release toxins that can kill fish and wildlife. These toxins can also have negative human health impacts. Microcystis aeruginosa is known to release a toxin called microcystin, which can result in gastrointestinal problems and possibly liver damage if contaminated water is ingested.
Red tide and blue-green algae blooms are two distinct phenomena, and they differ in their causes, characteristics, and impacts. Here are the primary differences between red tide and blue-green algae blooms:
1. Causing Organisms:
- Red Tide: Red tide is caused by certain species of marine dinoflagellates, such as Karenia brevis. These algae produce toxins that can harm marine life and, in some cases, pose health risks to humans and animals.
- Blue-Green Algae Blooms: Blue-green algae, technically known as cyanobacteria, are responsible for blue-green algae blooms. Unlike true algae, cyanobacteria are bacteria that can
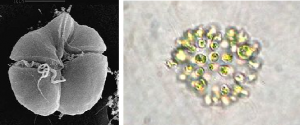
Left: K. brevis, the species that causes red tide and associated fish kills. Right: The dominant cyanobacteria (Microcystis aeruginosa) responsible for the blue-green algal bloom in Lake Okeechobee, 2018. photosynthesize. Some species can produce toxins, which can have adverse effects on aquatic ecosystems and may pose health risks.
2. Color:
- Red Tide: The name “red tide” comes from the coloration of the water during blooms, which can range from red to brown. However, not all red tide blooms necessarily cause the water to turn red.
- Blue-Green Algae Blooms: The water affected by blue-green algae blooms can appear green, blue-green, or even brown.
3. Toxin Production:
- Red Tide: The toxins produced by red tide organisms can have harmful effects on marine life and can lead to respiratory and other health issues in humans and animals.
- Blue-Green Algae Blooms: Some species of blue-green algae can produce toxins called cyanotoxins. These toxins can pose risks to both aquatic life and human health, causing issues such as skin irritation, gastrointestinal problems, and liver damage.
4. Habitats:
- Red Tide: Red tide primarily occurs in marine environments, affecting coastal waters and estuaries.
- Blue-Green Algae Blooms: Blue-green algae blooms can occur in various water bodies, including freshwater lakes, ponds, and slow-moving rivers.
5. Nutrient Sources:
- Red Tide: Red tide blooms are often associated with nutrient-rich waters, and their occurrence can be influenced by factors such as nutrient runoff from coastal areas.
- Blue-Green Algae Blooms: Nutrient pollution, especially from sources like agricultural runoff and wastewater near beaches, can contribute to the development of blue-green algae blooms.
It’s important to note that both red tide and blue-green algae blooms can have ecological and public health implications, and monitoring and management efforts are crucial to mitigate their impacts. Local environmental agencies and health departments typically provide information and advisories related to these events.
Red Tide Triggers: What Causes Harmful Red Tide Algal Blooms
Harmful red tide algal blooms are triggered by various environmental factors. One key factor is nutrient availability, particularly high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus, which promote the rapid growth of the algae responsible for red tide.

Warm water temperatures are also conducive to the development and intensification of red tide blooms, as many of the responsible dinoflagellates thrive in warmer conditions. Coastal nutrient runoff from agricultural activities and urban areas can exacerbate nutrient levels, contributing to red tide formation.
Additionally, certain oceanographic conditions, such as upwelling events, can transport nutrient-rich waters to the surface, fostering the growth of red tide algae. Understanding these triggers is crucial for monitoring and managing red tide events and their potential impacts on marine ecosystems and human health.
Several noteworthy red tide events have occurred globally, leading to recurring respiratory irritation cases in affected areas. Here are a few examples:
- Florida Red Tide Events:
- The Gulf of Mexico, particularly the coast and beaches of Florida, experiences red tide events caused by the dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. These events can lead to significant fish kills and respiratory issues for humans. Notable occurrences include the prolonged red tide event in 2017-2019, which had severe impacts on marine life and local communities.
- California Red Tides:
- The California coast and beaches have also experienced red tide events. In some cases, blooms of the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum have caused bioluminescent displays along the coastline. While these events are visually stunning, they can also contribute to respiratory irritation.
- Chesapeake Bay Red Tides:
- The Chesapeake Bay on the United States East Coast has had red tide events caused by dinoflagellates such as Alexandrium monilatum. These events can lead to harmful effects on fish and shellfish populations, impacting local ecosystems and fisheries.
- Australian Red Tide Events:
- Australia has seen red tide events, including those caused by dinoflagellates such as Gymnodinium catenatum. These events have been associated with paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) and respiratory issues in humans.
- Asia-Pacific Region:
- Red tide events on beaches have been reported in various locations across the Asia-Pacific region, affecting countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea. These events have led to economic losses in fisheries and aquaculture and have posed health risks to local communities.
- Global Impact of Harmful Algal Blooms (HABs):
- Harmful algal blooms, including red tide events, are a global phenomenon. They can occur in freshwater and marine environments. HABs have been associated with respiratory irritation, shellfish poisoning, and other health concerns in different regions worldwide.
The recurrence of respiratory irritation cases is a common feature of red tide events, especially in areas where the responsible algae release toxins into the air. Monitoring agencies and health authorities typically issue advisories to inform the public about the risks and recommend precautions during red tide events, such as avoiding contact with affected waters and using respiratory protection when necessary.
Connection between Red Tides and People: Managing and Understanding Risks
The connection between red tides and people is quite significant. These naturally occurring phenomena, primarily caused by the algal bloom known as Karenia brevis, present considerable risks, especially to folks living in beachside communities. Often found in beach water, Karenia brevis is the main culprit behind red tides. As soon as these tides roll in, people start facing several health-related risks, underscoring the importance of managing and understanding these risks.

Stats suggest that a spike in respiratory issues is one of the major causes of concern during red tide occurrence. These health issues are largely due to the tide toxin released by the Karenia brevis algal blooms. The frequency and impact of red tides seem to be escalating, posing multiple problems for people living near the oceans. We’ve noticed a steady rise in both the occurrence and effect of these red tides in recent years.
When it comes to red tide, what many people don’t often know is that it doesn’t just affect the water or the marine creatures residing in it. The risk extends to humans and our pets too. Red tide’s influence is far-reaching beyond the beach and water, having substantial, and sometimes, devastating effects on people’s health and livelihood.
Over a while, more and more people have experienced the undesirable effects of tide toxin, particularly during a red tide outbreak. Red tide’s tide toxin can sometimes become airborne, impacting air quality and causing respiratory difficulties. Karenia brevis, with repeated introductions, continues to be a significant concern for a majority of the beach communities.
Despite the gravity of the situation, there’s no need to panic. Being aware of the relationship between red tides and people can help in managing these risks more efficiently. Stats show that many people, when informed and aware, tend to evade high-risk areas during a red tide. While complete prevention of contact with Karenia brevis during red tides isn’t always possible, reducing exposure largely helps in mitigating the risk.
Red tide also called harmful algal blooms (HABs), occur when microscopic algae (the best-known association-Karenia brevis), occur in the H20 & multiply to higher-than-normal concentrations because of certain correct environmental, chemical, & physical conditions .………………………………………………………………………… Read more
Understanding and managing the risks associated with red tides involves a combination of monitoring, research, and public education. Here is a list of key considerations for managing and understanding the connection between red tides and people:
- Monitoring Programs:
- Establish and maintain robust monitoring programs to track the occurrence and intensity of red tide events. Regular monitoring helps authorities assess potential risks to human health and the environment.
- Early Warning Systems:
- Develop and implement early warning systems to notify the public and relevant authorities about the presence of red tide blooms. Timely information can allow for the implementation of precautionary measures.
- Public Education:
- Conduct public education campaigns to raise awareness about red tide events, associated health risks, and appropriate precautions. Inform the public about the importance of avoiding contact with affected waters and seafood during red tide events.
- Respiratory Protection:
- Guide respiratory protection for individuals in areas affected by red tide events. This may include recommendations to use masks or avoid outdoor activities during periods of high aerosol concentrations.
- Shellfish Monitoring:
- Implement monitoring programs for shellfish to detect the presence of red tide toxins. This is crucial for protecting public health, as consuming contaminated shellfish can lead to poisoning.
- Fisheries Management:
- Develop strategies for managing fisheries during red tide events to minimize economic impacts. Implement temporary closures or restrictions on harvesting and consuming seafood from affected areas.
- Collaboration with Health Authorities:
- Foster collaboration between environmental agencies, researchers, and health authorities to assess the health risks associated with red tide toxins. Share information to facilitate coordinated responses.
- Research on Toxin Effects:
- Research to better understand the specific toxins produced by red tide organisms and their effects on human health. This information can inform risk assessments and public health guidelines.
- Climate Change Considerations:
- Consider the potential influence of climate change on red tide dynamics. Changes in temperature, ocean currents, and nutrient availability may impact the frequency and intensity of red tide events.
- Adaptive Management Strategies:
- Implement adaptive management strategies that can be adjusted based on the evolving understanding of red tide dynamics and their impacts. Flexibility in response strategies is essential for addressing changing conditions.
- International Collaboration:
- Engage in international collaboration to share knowledge and best practices for managing red tide events. Red tides can occur in various regions globally, and collaborative efforts can enhance the collective ability to respond effectively.
- Community Engagement:
- Involve local communities in monitoring efforts and decision-making processes. Engaged communities are more likely to adhere to advisories and take necessary precautions during red tide events.
By addressing these considerations, authorities can work towards minimizing the health risks associated with red tides and promoting the well-being of both coastal ecosystems and communities. In conclusion, it’s quite evident that the red tide, primarily caused by Karenia brevis, poses potential risks.
However, understanding these risks and making informed choices can make a huge difference for folks dwelling in beach areas. People must stay informed about the red tides, to ensure adequate preventive actions are taken, and to stay connected to this environmental phenomenon. Remember, it’s not just about the red in the water. It’s also about the well-being of the people.
A red tide is an event that occurs on the coastline when algae a plant-like organism grows out of control. The name “red tide” comes from the fact that overgrown algae can cause the water to change color. ……………………………………………………………Read more
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the duration of a Red Tide can vary significantly depending on the conditions that support it. It may last a few weeks, months, or even over a year in some extreme cases. Despite the latest challenges that Red Tides pose to beaches and fish and wildlife, scientists work relentlessly to understand and predict these episodes, in hopes of mitigating their effects on marine life and humans. Continued research and vigilance are of utmost importance in our ongoing battle against Red Tides. Remember, knowledge is power, and in this case, it can also be a lifesaver. There have been many studies over the years concerning Red Tide Events, especially in Florida and the Gulf region of the US.
*Latest Report-Last week there was no red tide anywhere in Southwest Florida.
- No respiratory irritation due to red tide.
- No smelly dead fish carcasses washed up on the beach en masse.
- Just clean, clear, Gulf of Mexico water. .……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………Read More

References:
Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission –Fish and Wildlife Research Institute Harmful Algal Bloom Database,
When will the Red Tide Go Away- Tampa Bay Times Sept 2018
The University of Florida- Harmful Algal Blooms: Red Tide vs. Blue-green Algae
FAQ’s
Q: What exactly is a red tide?
A: A red tide is a natural phenomenon involving harmful algal blooms, often caused by microscopic algae like Karenia brevis. These blooms can turn seawater a reddish-brown color and are known for their potential to release toxins that can harm marine life and even affect human health.
Q: How long does a red tide last?
A: The duration of red tide varies and depends on environmental factors such as temperature, salinity, and nutrient availability, as well as human interventions and weather events. A red tide can last from a few weeks to over a year.
Q: Are red tide events harmful to pets as well as humans?
A: Yes, pets can be affected by red tides. They may suffer from illnesses after coming into contact with affected seawater or marine life. If you suspect your pet has been exposed to red tide, it’s important to consult a veterinarian.
Q: Can red tides cause health issues for people?
A: Yes, red tides can cause respiratory irritation, especially when the toxins become airborne and are inhaled. Symptoms may include coughing, watery eyes, and skin irritation. People with pre-existing conditions may be more susceptible to these effects.
Q: What’s the difference between red tides and blue-green algae blooms?
A: While both are algal blooms, red tides are usually caused by dinoflagellates and can produce toxins harmful to marine life and humans. Blue-green algae blooms, caused by cyanobacteria, can also produce toxins but often affect freshwater environments and can harm the liver and nervous system if ingested.


