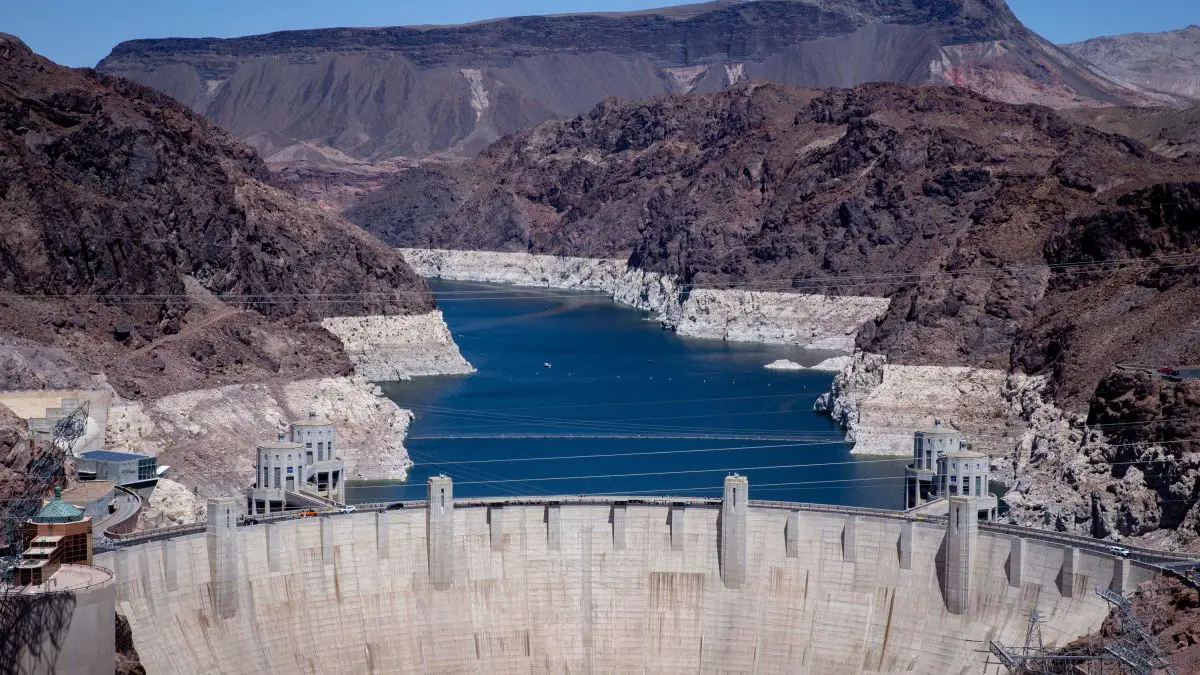
The largest reservoir in the United States Lake Mead was formed when the Hoover Dam was built in the 1930s providing water and power to the Southwestern states of California, Nevada, and Arizona but in the last 2 decades have struggled to keep the water levels from falling recently up to 143 ft. that is 35% of normal capacity. Why is Lake Mead So Low?
Lake Meade part of the Colorado River Basin is undergoing “aridification”, a 21-year mega-drought that’s ravishing Western USA, worsened by higher temperatures, growing population, shrinking flows from tributaries in the northern Colorado River watershed-lowering levels of Lake Powell that feed Lake Mead upriver.
The demand for water has led to problems at Lake Mead for years but this time coupled with Global Warming it could keep the capacity of the country’s largest man-made Reservoir lower for a longer period of time.
Why are Lake Mead Water Levels So Low
 Lake Meade is the Water Reservoir formed by the Hoover Dan it has sunk to all-new low levels in the past 20 years. The lowest levels are seen since the 1930s.
Lake Meade is the Water Reservoir formed by the Hoover Dan it has sunk to all-new low levels in the past 20 years. The lowest levels are seen since the 1930s.
The Southwestern United States has been under a 21-year drought creating massive problems in this huge Reservoir that feeds California, Nevada, and Arizona filling almost 95% from the year 2ooo to only 35% today. Mead Lake is the largest water reservoir in the country.
These decreases in water levels at Lake Mead cause Drought, water shortages for consumption, agriculture, and energy shortages that the Hoover Dam site provides.
These shortages have been created by drought and human consumption in the arid regions of the Southwest US. Basically, there is more water going out of Lake Mead than there is going in.
The dam provides energy for over 1.3 million people in this area of the country. There are estimates of a 25% decrease in power available that normally is made at Hoover Dam directly because of the lower water levels at Lake Mead.
The Electrical energy of Hoover Dam in Nevada provides California with nearly 50% of its energy. Now dwindling to record lows as Lake Mead’s water level decrease lower and lower the turbines at the Hoover Dam spin slower and slower, reducing Hydroelectric power.
At full levels in the reservoir, the Hoover Dam can generate enough hydropower to accommodate 1 million people.
What really worries the people that operate and depend on this water system is the fact of warmer temperatures add more of a factor to drought and the usage of this huge reservoir. Which evaporates more water creating more demand for the crippling system.
A lot of people see Lake Mead as a microcosm of the problem of Water Scarcity in the world happening before their eyes.
Ninety-six percent of the water flowing into Lake Mead comes from snowmelt that drains into the Colorado River. Early spring melt sends water surging through the river and into Lake Powell a man-made reservoir on the Colorado River in Utah and Arizona, United States.
It is a major vacation spot visited by approximately two million people every year. It is the second-largest man-made reservoir by maximum water capacity in the United States behind its southern partner on the Colorado River, Lake Mead. Water from this man-made reservoir, Lake Powell then spills back over into the Colorado River running Southwest through the Grand Canyon feeding Lake Mead and Hoover Dam.
Colorado River Basin Map


Lake Powell is a reservoir on the Colorado River, straddling the border between Utah and Arizona, United States. Most of Lake Powell, along with Rainbow Bridge National Monument, is located in Utah. Lake Powell sits at an elevation of 3,700 feet and is surrounded by a dramatic backdrop of deep sandstone walls.
Lake Mohave is located south of the Hoover Dam along the Colorado River at the southern end of the Lake Mead National Recreation Area. It’s known for its abundance of sandy coves and mix of the peaceful Black Canyon and high-octane open waters.
With Lake Powell at 3,700 ft. in the north collecting snowmelt from upper Colorado in Utah Lake Mead drops in elevation of 1,112 feet the Mohave Reservoir is last at 647 feet in elevation keeping the mighty Colorado River moving southward. Still, the amount of water in the system continues to drop.
Continuing a 22-year downward trend, water levels in Lake Mead stand at their lowest since April 1937, the water level at Lake Mead in Nevada, USA, was 1052.78 feet above sea level and 166.82 feet below Full Pool as of its last reading updated weekly, & Lake Mead is up 3.13 feet from one year ago………………………………………read more
What Were Lake Mead’s Water Levels in 2023
Lake Mead’s water levels rose slowly throughout 2023, although the measurements were lower than in the previous two years. Water level measurements began at 1,046.97 feet in January and ended at 1,068.18 feet in December.
The lake has experienced record lows in water levels in recent years, with the first water shortage announced in 2021 after years of chronic overuse and drought.
Lake Mead’s water levels stayed high again last month amid a historic water shortage, rising again and passing January’s mark to become the highest point in nearly three years. According to measurements taken at the end of February by the Bureau of Reclamation, Lake Mead’s water levels were reported to be 1,076.52 feet, higher than levels taken at the end of January, when they were measured at 1,072.67 feet.
Prior to this year, the most recent highest level was recorded in April 2021, when it was measured at 1079.30 feet. The lake’s water levels remained high in the month following the heavy winds, rain and snow that moved through California in January from an atmospheric river weather event, also known as a “Pineapple Express.”
Earlier this month, a blizzard pounded Eastern California and the mountains along the Nevada border in a powerful storm that dumped heavy snow and brought howling winds with gusts that hit 190 mph.
Although water levels remain high for now, experts previously told Newsweek that it would depend on future storms to fill the reservoirs in Lake Mead and Lake Powell in Utah and Arizona.
Lake Mead Water Levels Today
Current updated water levels at Lake Mead water shortage and experiencing record-low can be found here at Lake Mead Water DataBase this site includes an interactive detailed map and a ton of information and is the most complete set of Colorado River water-related information you can find on the web. This site started with a water supply at Lake Powell and now includes Powell and 6 other major lakes on the Colorado River.

The American West is facing its most severe drought in human history. Research suggests conditions are drier now than they have been for at least 1,200 years, and, compounded by the effects of climate change, will likely persist for another decade.
Prolonged periods of lower precipitation along with climate change mean there is less water collecting in Lakes Mead and Powell, and less snowpack in the Rocky Mountains to melt during warmer months and push the river downstream.
Located along a stretch of the Colorado River, Lake Mead spans hundreds of miles over the border of eastern Nevada and western Arizona. It works conjunctively with Hoover Dam to supply water and power to 25 million people and is a lifeline for major cities and agricultural hubs throughout the region now experiencing record-low water levels.
Both Hoover Dam and Lake Mead are integral components of the complex system that divides and allocates the Colorado River. The river stretches 1,400 miles from Colorado’s Rocky Mountains to the Gulf of California and provides water to roughly 40 million people in the U.S. and Mexico.
To access the Lake Mead water databases and Lake Powell water levels along with the other news on the Colorado River features we have developed, just use the navigation menu at the top. Simply select the area that you want to review and navigate the menu to the specific item you want to see, as you would in any other application. Try it out for yourself. It supports dozens of indigenous tribes and 11 national parks and irrigates 5.5 million acres of farmland.
Where Does Lake Mead Get Its Water From?
Lake Mead is fed by the Colorado River and three smaller tributaries: the Virgin and Muddy Rivers and Las Vegas Wash. Gregg Basin and Temple Basin are fed by the mainstream of the Colorado River, which now enters Lake Mead at the northern end of the Gregg Basin……………………………………………..read more
References:
The USGS-The Colorado River Basin
National Park Service-America’s First National Recreational Area


