If you have ever fished waters in the southern American states then you may have caught or seen the mysterious Garfish that is a scary sight indeed as it travels through the lakes and muddy backwaters of the south. What are Ideal Water Conditions for Garfish?
Gars prefer warm, shallow, well-vegetated freshwater habitats in slow-moving rivers and lakes. Some gars also frequent brackish water. Gars have a primitive swim bladder that they can use as a lung to breathe air, which allows them to survive in waters with low levels of dissolved oxygen.
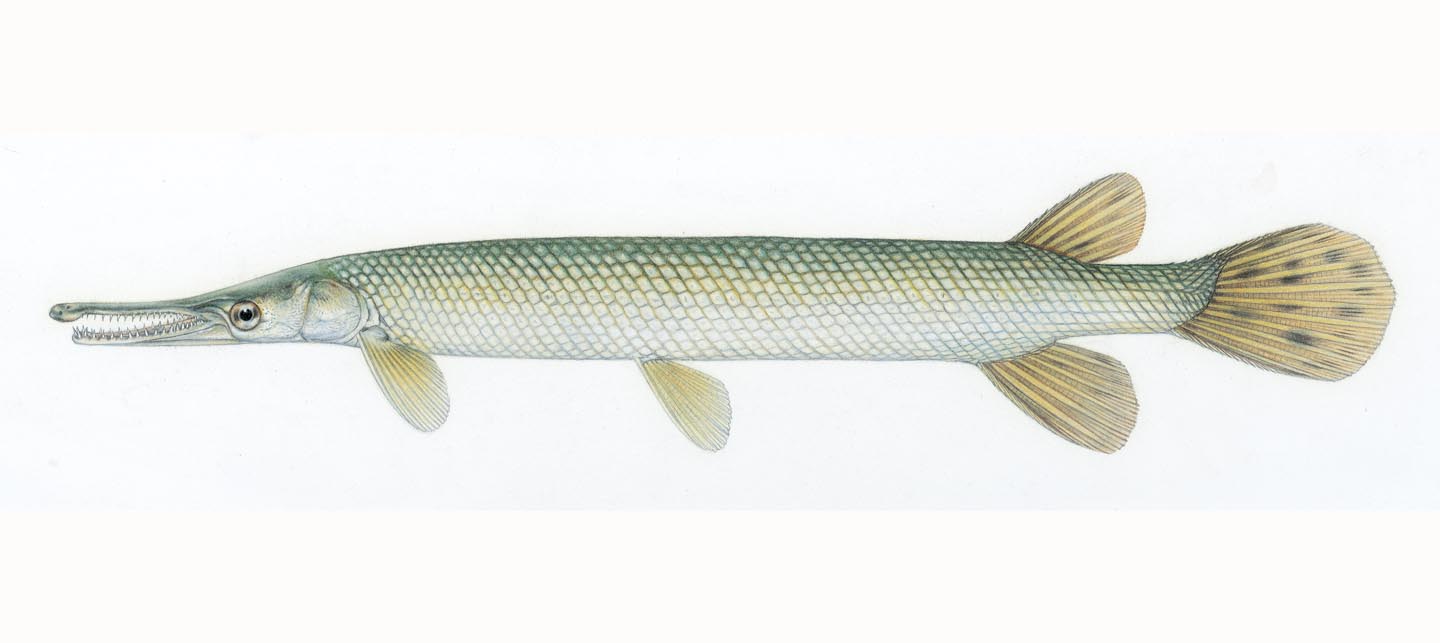
Gars are large, freshwater fish belonging to the Lepisosteidae family, which consists of 7 species of gar: alligator, Cuban, Florida, longnose, shortnose, spotted, and tropical. Gars have long, cylindrical bodies covered in hard, shiny, diamond-shaped scales.
Introduction:
Gars are found across much of the eastern portion of North America. Although gars are found primarily in freshwater habitats, several species enter brackish waters, and a few, most notably Atractosteus Aristarchus, are sometimes found in the sea. Some gars travel from lakes and rivers through sewers to get to ponds.
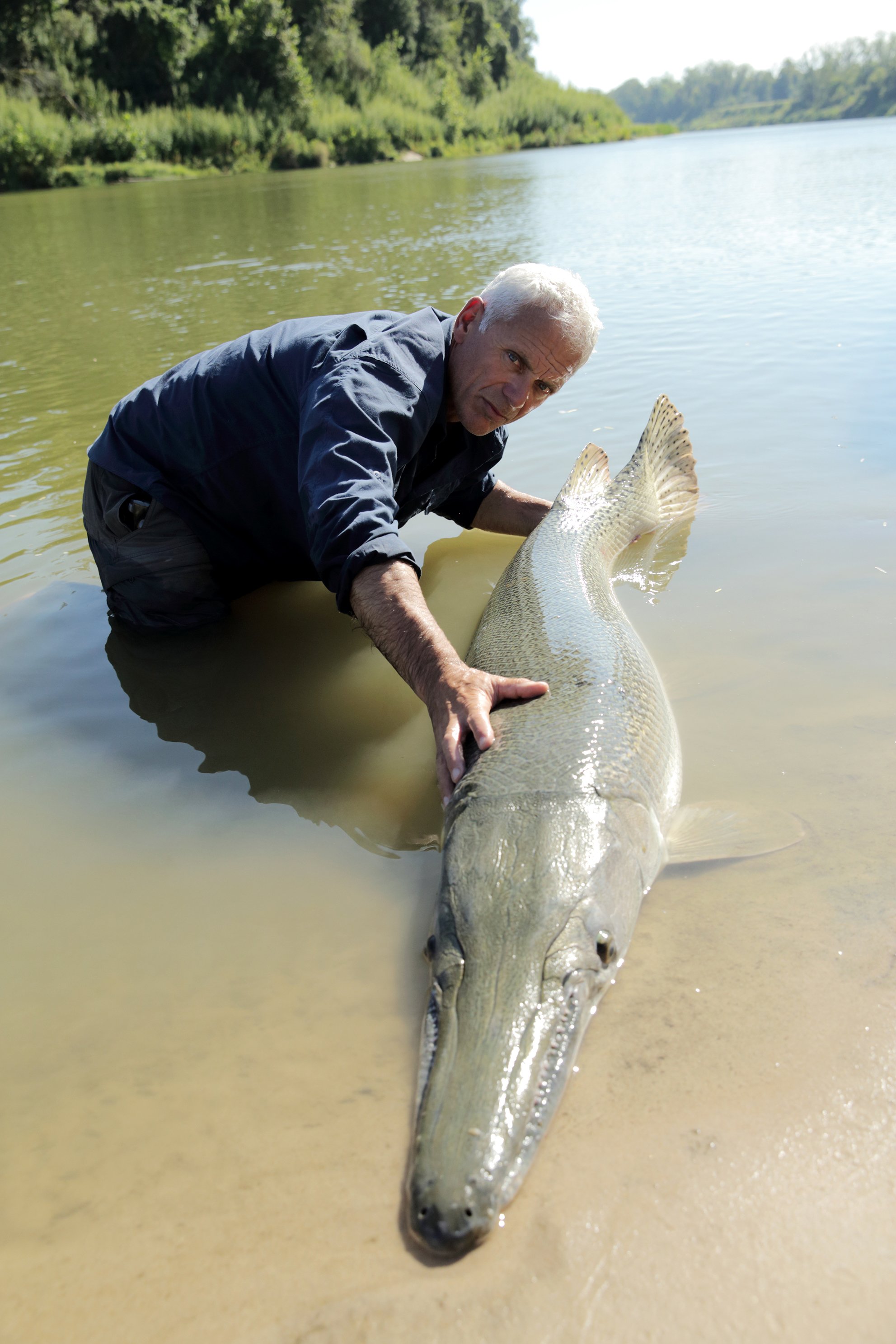
They are one of the most distinctive freshwater fish species. Alligator gars are the largest of all gar species with a head that looks very much like an alligator’s. They can be distinguished from all other gars species by the two rows of teeth in the upper jaw, their short-broader snout, and their size when fully grown.
The body is long, slender, and olive greenish-brown in color and sometimes blackish. Along the upper sides and back mainly darker, the belly is ordinally white or yellowish. The large black spots toward the rear and sides blend into the head and align with the tail fin. The younger the Gar, the lighter stripe and marking they have which include the well-marked spots. Feeding Habits – They mainly feed on fish but are known to eat ducks and other water birds. Age and Growth – They are one of the monsters of fresh waters. They can reach lengths of up to 10 feet and weights of more than 200 pounds.
What is Ideal Water Conditions for Garfish
Garfish, also known as needlefish or garpike, inhabit a variety of aquatic environments, primarily in coastal and estuarine areas. Their habitats include:
- Shallow Coastal Waters: Garfish are commonly found in shallow coastal regions, often near sandy or muddy bottoms. They prefer areas with abundant vegetation where they can find food and shelter.
- Estuaries and Lagoons: Estuarine environments, where freshwater meets saltwater, are favored habitats for Garfish. They thrive in these transitional zones, taking advantage of the rich food sources and diverse ecosystems.
- Mangrove Forests: Mangrove habitats provide an ideal setting for Garfish due to the intricate root systems that offer shelter and protection. They are often found darting among the mangrove roots, hunting for prey.
- Seagrass Beds: Garfish are frequently associated with seagrass meadows, where they forage for small fish and crustaceans. These habitats offer both food and refuge from predators.
- Nearshore Reefs and Rocks: Along coastlines with rocky formations and coral reefs, Garfish can be found patrolling the shallows, especially around structures where they can hide and ambush prey.

Importance of Habitat Diversity for Garfish Survival:
Habitat diversity plays a crucial role in the survival and well-being of Garfish populations for several reasons:
- Food Availability: Different habitats offer varied food sources, ensuring Garfish have access to a diverse diet year-round. This reduces competition for resources and increases overall food availability.
- Shelter and Protection: Garfish rely on vegetation, submerged structures, and natural features for shelter from predators and adverse environmental conditions. Habitat diversity provides a range of hiding spots and refuge areas.
- Reproductive Success: Certain habitats, such as estuaries and mangroves, provide suitable breeding grounds for Garfish. The presence of diverse habitats ensures that Garfish can fulfill their reproductive needs and sustain healthy populations.
- Migration and Movement: Garfish often move between different habitats throughout their life cycle, depending on factors such as water temperature, salinity, and food availability. Having diverse habitats allows for seasonal migrations and ensures connectivity between populations.
- Resilience to Environmental Changes: Habitats with high diversity are more resilient to natural disturbances and anthropogenic impacts. If one habitat is affected by pollution or habitat degradation, Garfish populations can potentially relocate to nearby suitable habitats.
In conclusion, habitat diversity is essential for the survival and ecological resilience of Garfish. Conservation efforts should prioritize the preservation and restoration of diverse aquatic habitats to ensure the long-term sustainability of Garfish populations.
Ideal Water Temperature for Garfish
References:
Texas Parks & Recreation: Are Gar Safe to Eat?
FAQ’s
Are Garfish poisonous?
- Garfish are not poisonous to humans, but they do have sharp teeth and may inflict injuries if mishandled. Additionally, their eggs are toxic to consume, so caution should be exercised when handling them.
Are Garfish endangered?
- While Garfish populations may face localized threats from habitat degradation, overfishing, and pollution, they are not considered globally endangered. However, conservation efforts are important to ensure the sustainability of Garfish populations and their habitats.