Tide tables tell you three important things for any given place: time of high tide, time of low tide, and heights of each along with what’s called slack tide. What is Slack Tide?
Slack tide is a brief period during the tidal cycle with minimal water movement. It occurs between the ebb and flow phases when tidal currents momentarily pause, resulting in calm waters. This phase is vital for activities like boating, offering reduced current challenges.
Slack tide is the time when the water stops flowing into an inlet and begins to flow out. Many things can influence this including local conditions, seas/waves/wind direction, the geography of the tidal passage/inlet or water body and how confined it is, its shape, volume and depth, etc.
Introduction:
As the Earth’s oceans pulsate daily, a fleeting moment of stillness known as slack tide offers a unique spectacle. This elusive phase, where waters briefly surrender their vigorous flow, remains an enigmatic pause in tidal movement that both mariners and marine enthusiasts strive to comprehend. This article delves into the intricacies of slack tide, unpacking its definition and exploring the profound implications it bears on tidal dynamics and maritime activities. Join us as we navigate the calm and the currents, revealing the secrets of slack tide and its pivotal role in the ebb and flow of our coastal waters.
The Concept of Slack Tide and Its Impact on Water Movement
Slack tide is a pivotal point in the tidal cycle characterized by minimal water movement. It occurs twice during each cycle, marking the transition between the ebb and flow of tidal currents. The phenomenon is significant for maritime activities as it provides a brief window of reduced current intensity, making navigation and fishing more manageable.
At slack tide, the opposing tidal forces momentarily balance, resulting in a temporary standstill of water, creating a calm and tranquil period. Understanding the concept of slack tide is crucial for optimizing various water-based endeavors and ensuring safety during tidal transitions.
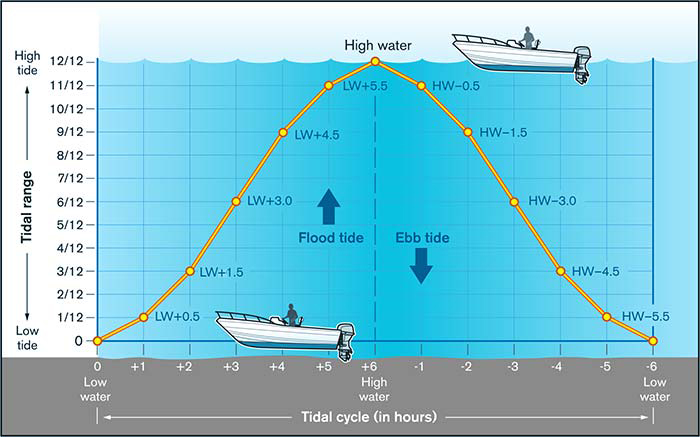
Slack tide is a fascinating phenomenon that is integral to understanding the ebb and flow of our world’s oceans. At its most basic, slack tide refers to a period when there’s notable tranquility in the water, with little or no current movement observable.
During slack tide, the water is at its least active state, which occurs in the short window of time between the ebb (outgoing tide) and flow (incoming tide). It’s an interval that both marine creatures and mariners pay close attention to due to its impact on the marine environment and navigation.
The occurrence of slack tide happens roughly twice in a lunar day for each coastal area, corresponding with the times of high tide and low tide. When the tide is at its highest or lowest point, there is a brief pause – slack water – where the water does not move significantly in either direction.
This pause is pivotal for many marine activities, including fishing, as fish tend to be least active at slack tide, possibly making them easier to catch, or allowing for a well-needed respite for fishing gear setup.
During slack tide, the usual tug-of-war between gravitational pull and the centrifugal forces that generate tides come to a momentary standstill. This natural balance is temporary but critical for the health of various tidal ecosystems.
The lack of strong water movement anywhere allows sediment to settle and can enable easier passage for vessels that require stable conditions to navigate or dock.
Moreover, slack tide is a crucial window for divers, as diving during peak water movement can be treacherous with strong currents. Understanding slack tide anywhere in all countries around the world can thus ensure safer diving excursions. Exploring the depths when the water is slack often leads to clearer visibility and a more enjoyable experience, as the slack water reduces sediment disturbance.
In terms of its effect on tide movements, slack tide acts as a natural reset. It’s akin to the calm breaths between the more tumultuous inhale and exhale of the ocean’s tidal rhythm. Being aware of when slack tide occurs is beneficial for planning several ocean-related activities and ensuring safety. Tidal charts often provide information anywhere in the world on when slack water will happen, but local knowledge can be equally important, as geographic features can influence the timing and duration of slack tide.
For anyone interested in the complexities of tidal movements, the concept of slack tide is a key component. Whether you’re a sailor reading the ebb and flow, a marine biologist studying tidal ecosystems, or simply an enthusiast of oceanography, slack tide represents a period of tranquility that significantly impacts water movement. The balance between tidal and slack periods is essential to the rhythm of life in coastal and marine environments, influencing both human activity and the behaviors of marine species.
The times of high and low tides, as well as tidal heights above or below chart datum (the numbers showing depths on your chart) for each day, can be determined from several sources, such as weather broadcasts, tide tables, navigation programs, some charts, and books such as Eldridge Tide and Pilot Book, published annually. If you’re coastal cruising, keep a print version of the tide tables aboard for times when electricity and Internet connections are unavailable.
How Tidal Changes Influence Slack Water in Marine Environments
Tidal changes significantly influence slack water in marine environments. During high and low tides, tidal currents are at their peak, causing water movement. Slack water occurs in between these phases when the tidal forces balance, leading to a temporary pause in horizontal water motion. The duration of slack water varies based on the location and local tidal conditions. Understanding how tidal changes impact slack water is essential for sailors, fishermen, and other maritime activities, as it allows for strategic planning and safe navigation during these transitional periods.
Tidal changes, driven by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun, play a pivotal role in shaping the characteristics of slack water in marine areas. The tide is the regular rise and fall of the ocean’s water, governed largely by the moon’s influence and to a lesser extent, the sun. When the tide reaches its highest or lowest point, the water movement temporarily diminishes, creating what’s known as slack tide. This slack period signals a brief respite where the current is minimal before the water begins to flow in the opposite direction.
In coastal areas, the current is a powerful factor influencing navigation, sediment transport, and marine life behavior. Understanding when the tide is reversing directions is crucial for mariners because it affects vessel maneuverability. Predicting slack water often involves consulting tide tables, which provide essential data on the expected times and heights of high and low waters. It’s during slack tide that the current’s kinetic energy wanes, and consequently, the water movement slows to a nearly imperceptible pace, having significant implications for anyone who navigates these waters.
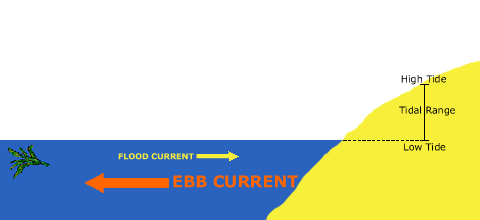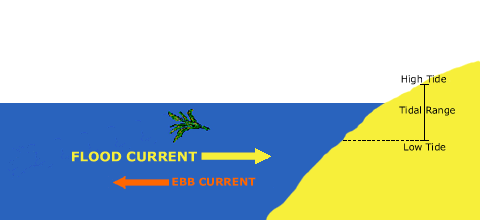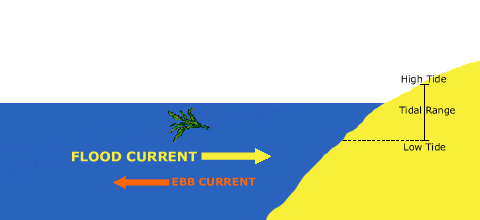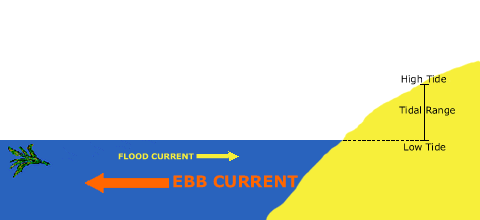
Tidal currents are at their strongest shortly after the water begins moving from slack high tide or slack low tide, increasing in speed until they reach the maximum flow, known as peak ebb or flood currents.
The duration of slack, when the tide is reversing directions, varies in duration based on the topography and contours of the ocean floor as well as the volume of water affected by the tide. In certain areas, these slack periods can be brief while in others, they might extend longer, allowing for a window of calm water.
Mariners and anglers alike pay close attention to slack tide because the calm water provides safe and efficient conditions for travel and favorable periods for fishing, respectively.
Slack tide is when currents are at their weakest, making it easier for fish to feed and for boats to pass through narrow straits and inlets without battling strong tidal flows. Additionally, the lack of current helps in reducing the mixing of water layers, which can result in clearer water conditions and improved visibility underwater.
The rhythm of tidal changes in the world is the subsequent impact on water movement with the moon playing the lead role. As the Earth rotates, different locations anywhere in the world experience bulges of water that contribute to the tide, and the resulting currents are ever-shifting. Therefore, slack water is not a static event; its occurrence and characteristics are influenced by both celestial mechanics and the unique geographical features of different areas. Recognizing the subtle interplay between these variables is essential for anyone who seeks to navigate or understand the dynamic environment of tidal waters.
Navigating High and Low Tides: The Role of Slack Tide for Fish and Boaters
Navigating high and low tides involves understanding the crucial role of slack tides for both fish and boaters. During high tide, water levels rise, and tidal currents intensify, while low tide sees a decrease in water levels and changing currents.
Slack tide, occurring between these phases, provides a brief period of reduced water movement, facilitating easier navigation for boaters. For fish, slack tide is opportune for feeding as the calmer waters make it easier to locate prey. Boaters often use slack tide strategically for smoother transitions and safer journeys, emphasizing its importance in marine navigation and fishing activities.
Navigating the dynamic environment of coastal waters requires an understanding of tides and particularly the phenomenon of slack tide. As high and low waters transition, slack water becomes a critical period for both fish and boaters. This phase of the tidal cycle, often referred to as slack tide, marks a moment when the water is not flowing noticeably in either direction. Some Roles of Slack Tide for Boaters:
- Facilitates optimal fishing conditions
- Provides a period of calm water for boaters
- Allows for safer navigation in challenging areas
- Enables strategic positioning for fishing
- Reduces the risk of accidents or collisions
- Enhances the overall boating and fishing experience
- Offers opportunities for relaxation and enjoyment on the water
- Supports sustainable practices by minimizing disturbance to marine habitats
- Promotes conservation efforts by reducing fuel consumption and emissions
- Contributes to the preservation of marine ecosystems and biodiversity
It occurs shortly after high tide when the current changes direction, and also following low tide just before the flow resumes. Boat handlers pay close attention to this period as the reduction in current makes for easier docking, launching, and navigating through narrow passages that might otherwise be difficult due to stronger water movement. Some Roles of Slack Tide for Fish:
- Facilitates feeding opportunities for fish
- Reduces the energy expended by fish during tidal changes
- Allows fish to conserve energy and rest
- Creates ideal conditions for ambush predators
- Enables fish to adjust position in the water column
- Provides a temporary respite from strong currents
- Promotes feeding activity near structure or cover
- Offers a window of opportunity for feeding in otherwise turbulent waters
For fish, the slack tide can be a time of increased feeding activity, as the high water’s slowdown often causes smaller creatures to become more vulnerable to predation. The slack in the tide lessens the effort fish must expend against strong currents, allowing them to focus on foraging. Consequently, fishing during slack tide can be advantageous, as the high concentration of feeding fish improves the chances of a successful catch. Anglers well-versed with experience in the rhythm of the tides know that slack water anywhere, particularly after a high tide, can signal an opportune time to cast their lines.
Slack tides also affect the movement of sediment and nutrients in the water, which can have implications for marine environments. The temporary lull in water motion allows for the settling of particulates, often enriching the sea floor with a fresh layer of nutrients. It’s during the slack after high tide when the suspended materials in the water column begin to settle. The slack of the water is not just a standstill; it’s a transition, a breath between the ebb and flow of the tide’s constant motion. Some Roles of Slack Tide for Sediment and Nutrients:
- Facilitates sediment settling and deposition
- Allows for nutrient redistribution and mixing in the water column
- Supports the transport of organic matter and detritus
- Enables the accumulation of sediment in depositional zones
- Promotes the exchange of nutrients between benthic and pelagic habitats
- Provides opportunities for nutrient uptake by benthic organisms
- Influences sediment stability and erosion processes
- Contributes to the cycling of nutrients within marine ecosystems
- Supports primary productivity and the growth of benthic and pelagic organisms
- Plays a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem health and resilience
Boaters navigating during slack tide need to be conscientious of the potential for rapid changes. As the slack tide comes to an end, the growing current can catch inexperienced boaters off guard. Boat handling during the transition from slack water to the incoming or outgoing tide demands attentiveness. Moreover, planning a boat trip around the slack tide can make for smoother sailing and safer travel through areas prone to strong tidal currents.
Understanding the slack tide is essential for anyone with experience looking to master their interaction with the seas. The slack of the water’s movement at high and low tide events represents not only a pause in the tidal strength but also a shifting point that can greatly influence marine activity. Slack tides offer a window of calm in the ocean’s relentless cycle, a time that can be strategically used by both fish and boaters for their respective activities. By acknowledging the slack tide’s role in tide movement and marine life behavior, we can improve our navigation and fishing practices, harnessing the power and pause of the water to our advantage.
Your Questions About Slack Tide Answered: A Reply to Common Inquiries
One frequent question is its impact on navigation, and the answer lies in the reduced water movement during this phase, making it an opportune time for smoother journeys. Additionally, many inquire about its significance for fishing, as slack tide provides a calm window for fish feeding, influencing angling strategies.
Slack tide, a brief pause in tidal currents, is a common subject of inquiry. One frequent question is its impact on navigation, and the answer lies in the reduced water movement during this phase, making it an opportune time for smoother journeys. Additionally, many inquire about its significance for fishing, as slack tide provides a calm window for fish feeding, influencing angling strategies.
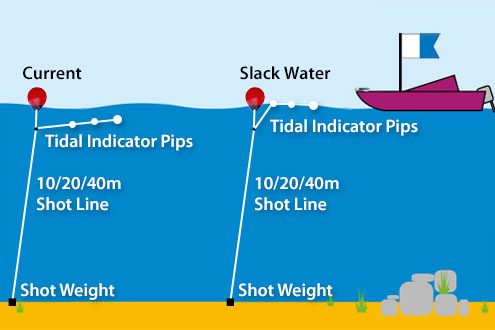
Slack tide, a term that’s often a source of confusion for many, is a short period in a tidal cycle where the water is completely unstressed and there’s minimal tidal current.
During slack tide, the water doesn’t flow perceptibly inward or outward; the current reaches zero and a temporary calm ensues. Understanding slack tide events is crucial for navigators and fishers as it signifies a lull in the otherwise continuous stream of tidal movement. It’s the point where the tide switches from ebb to flood or vice versa.
This natural pause in the water’s motion can influence both sea life and human activities. Slack water, the alternative term for slack tide, might be considered a nautical breather—a moment of equilibrium before the sea sways again. Whether you’re reading tide tables or planning a voyage, knowing when slack tide occurs can greatly assist in ensuring safe and effective sailing.
Isn’t it fascinating how slack tide, though brief, has a profound impact on water movement? It provides an opportunity for sediments to settle, creating a clearer water column, which can be particularly beneficial for marine organisms.
Slack tide also offers fish a respite from fighting the current, which is why many anglers time their expeditions to coincide with Slack water, hoping to capitalize on fish behavior during this period.
Moreover, safe navigation is a prime concern, and sailors rely on the slack tide to pass through narrow channels or dock with reduced risk—a slack current is easier to manage compared to a strong, shifting tide. For boaters, understanding the timing of slack tide can be the difference between a smooth journey and a challenging one.
So, how do you predict when slack tide will happen? It’s all in the tables—the tide tables, that is. These tables are essential tools that provide predictions of water levels and times for high and low tides, including the occurrences of slack tides. Experienced boaters check these tables regularly to reply aptly to the dynamic conditions of the sea. A slack current may not last long, but its importance can’t be overstressed, especially in areas with significant tidal ranges.
Therefore, slack tide, with all its tranquility, marks a period of transition in the ebb and flow of the tides, affecting the movement of water in profound ways. It’s a phenomenon that commands respect and attention, especially among those who tread upon or within the undulating blanket of the sea.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, grasping the concept of slack tide events is crucial for mariners, fishers, and coastal enthusiasts. This brief, peaceful interlude in the relentless ebb and flow of the tides marks a period when the water is neither rising nor falling, and as such, it plays a significant role in navigation, fishing strategies, and underwater activities. With a deeper understanding of slack tide, its timing, and its effects, individuals can plan their coastal activities more effectively, ensuring safety, maximizing success, and fostering a greater appreciation for the natural rhythmic dance of our planet’s oceans.

References:
Local Tides and Currents-Weather for Sailing
FAQ’s
Q: How often does slack tide occur?
A: Slack tide occurs roughly twice in a lunar day for each coastal area, coinciding with the times of high tide and low tide when the water movement is temporarily diminished before reversing direction.
Q: Why is slack tide important for maritime activities?
A: Slack tide is crucial for activities like fishing, as it may make fish easier to catch due to their reduced activity. It also allows sediment to settle, leading to clearer water for activities like diving. Moreover, navigating or docking vessels is easier during slack tide due to the lack of strong water currents.
Q: How can one predict when slack tide will happen?
A: Slack tide predictions are often found in tide tables, which provide data on expected times and heights of high and low waters. Local knowledge and geographical features can also influence the timing and duration of slack tide.
Q: Does slack tide affect marine life behavior?
A: Yes, marine life behavior is influenced by slack tide, as it allows for a period of reduced current in which fish can feed more easily and be caught by anglers. Additionally, the settling of sediment during slack tide can enrich the sea floor with nutrients, affecting the marine ecosystem.
Q: What should boaters be aware of when navigating during slack tide?
A: Boaters should be aware of the potential for rapid changes as slack tide ends and the current begins to grow. It’s a safe time for easier docking, launching, and traveling through strong current areas, but attentiveness is required during the transition from slack to incoming or outgoing tide.


