With all the emphasis on water filtration, these days and the new technologies always changing, one ingredient stays the same, it’s Activated Carbon. Activated Carbon sources have been mostly made from coal and wood but other new sources are being introduced in the water filtration industry with great success. One stands out. What is the Best Source of Activated Carbon?
The best source of activated carbon depends on the specific application and requirements. Common sources include coconut shells for high porosity, coal for cost-effectiveness, wood for adsorption capacity, and agricultural waste for sustainability. Each has unique properties suited to different needs.
Activated Carbon, “the Natural Wonder” is made from Carbon, one of the most abundant elements found on Earth. It exists in all organic compounds and is found in all forms of life. It plays a crucial role in the health, stability, and life of the planet.
What is the Best Source of Activated Carbon
Activated Carbon is a form of Carbon or Charcoal mixed and processed with a controlled amount of Oxygen.
I t’s used in various methods and applications to purify water and air in products like water filters and air filters. It’s used in the food and beverage industries. Activated Carbon can remove pollutants and improve odors.
t’s used in various methods and applications to purify water and air in products like water filters and air filters. It’s used in the food and beverage industries. Activated Carbon can remove pollutants and improve odors.
It can be taken orally in the advent of poisoning and remove chlorine and other byproducts of drinking water to improve taste besides contaminants, like heavy metals, pesticides and bacteria, and emissions from Industries.
Activated Carbon is a Natural Wonder. It can clean water where the sources of drinking water are polluted and scarce. It saves lives by removing contaminants that would be harmful to populations of people around the globe.
When Carbon is processed to make Activated Carbon at controlled high temperatures, it opens up millions of pores between the atoms of the surface of the Carbon.
This porous surface area creates an ability for the super tiny holes that are different size trap and filter impurities from air and water while allowing water and air to move through.
Activated carbon is the most common in-home water purifier. A large internal surface area of activated carbon makes it a very good adsorbent for many contaminants in drinking water. The sources of activated carbon are mostly, coal, coconut shells, and wood.
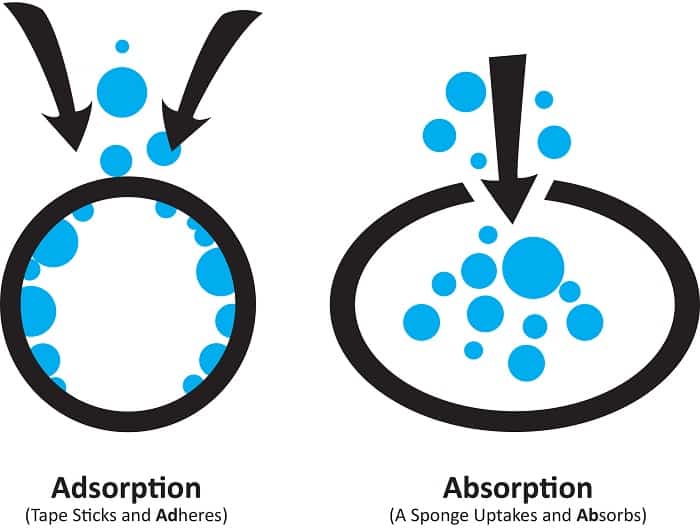
Activated Carbon Adsorption
Adsorption (Activated Carbon) is a method that is effective in removing certain organics (such as unwanted taste and odors, micropollutants), chlorine, fluorine, or radon from drinking water or wastewater. However, it is not effective for microbial contaminants, metals, nitrates, and other inorganic contaminants. activation thermal process, where volatile components are removed from the carbon-laden material (raw material) in the presence of oxygen increases it and makes it a lot better for the job adsorption
Contaminants in water are adsorbed (or adhered to) to the surface of carbon from a solution as a result of differences in adsorbate concentration in the solution and filters using Activated Carbon in the carbon pores. This is done by the process of Adsorption. Simply, the contaminants stick to the surface of the Carbon.
Activated Carbon Absorption
Activated carbon absorption is a process where contaminants in air or water adhere to the porous surface of activated carbon. The high surface area and numerous pores of activated carbon provide ample sites for molecules to bind to. As contaminants come into contact with the activated carbon, they are adsorbed onto its surface through chemical attraction. This process effectively removes a wide range of impurities, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), odors, chlorine, and other chemicals, resulting in cleaner air or water. Activated carbon absorption is commonly used in various applications such as water treatment, air purification, and industrial processes.
Difference Between Carbon Adsorption and Absorption
Carbon adsorption and absorption are two distinct processes involving the interaction of carbon with other substances.
- Adsorption refers to the adherence of molecules onto the surface of a solid material, such as activated carbon, without any significant penetration into its structure.
- In contrast, absorption involves the uptake of molecules into the bulk of a material, where they are dispersed throughout its volume.
While both processes are used for removing contaminants from air or water, adsorption typically involves a reversible attachment of molecules to the carbon surface, whereas absorption often results in irreversible binding within the carbon matrix. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate method for specific purification or filtration needs.
The difference is that in Absorption one thing absorbs another a sponge will absorb water in a bucket of water. In Adsorption, the material will stick to the surface of something else. This is what happens in a water filter using Activated Carbon.
The process of absorbing or assimilating substances into cells or across the tissues and organs through diffusion or osmosis, as in the absorption of nutrients by the digestive system, or absorption of drugs into the bloodstream. Both processes are an important function in all forms of science and Biology.
Contaminants that are organic, have high molecular weights, and are neutral, or non-polar, in their chemical nature are readily adsorbed on activated carbon.
For this Adsorption to happen the Contaminates and Chemicals that are physically adsorbed onto the surface of the Activated Carbon must be dissolved in water.
They need to be smaller in size than the Carbon pores and accumulate. Besides the physical reaction of Adsorption onto Activated Carbon, there could be a Chemical reaction.
Most water filters sold today have bragging rights to a statistic that 99.99% of Chlorine is removed by the Activated Carbon in the filter. The smallest and cheapest water filters are Faucet filters or Water Filter Pitchers can do this. Depending on the Raw Carbon materials that were used to start out in the process of Activating Carbon, it will depend on the result you will get.
Activated Charcoal Powder
Activated Carbon comes in different forms for different applications.
- Powdered: Powdered activated carbon (PAC): consists of fine particles capable of passing through smaller pores. Due to its small particle size and tendency to create dust, it is generally used as part of a processing machine such as a filter rather than a stand-alone product. It can also be pre-wetted to control dust, or mixed with other compounds into extruded water-dispersible pellets for Wastewater treatment or Industrial applications.
- Granular activated carbon (GAC): The next size up, granular activated carbon has a proportionately smaller external surface area than PAC. Smaller GAC is particularly suited to liquid phase applications, while larger GAC is better for vapors and gases. GAC is recyclable, making it advantageous over PAC for applications that use a lot of activated carbon.
- The carbon block is mainly comprised of activated carbon granules and a binding agent that allows the carbon granules to maintain a static position relative to each other. Carbon block immobilizes carbon particles to promote uniformity of performance, stopping water from channeling, which is common with GAC. GAC typically is packed in a loose bed that is contained in an enclosed cartridge or pressure vessel. Mostly used in POU -(Point of use Water Filters)
- Extruded activated carbon (EAC): PAC or powdered char can be mixed with a binder and formed into cylindrical pellets known as extruded activated carbon. Used in Strip Towers and Industrial Emissions
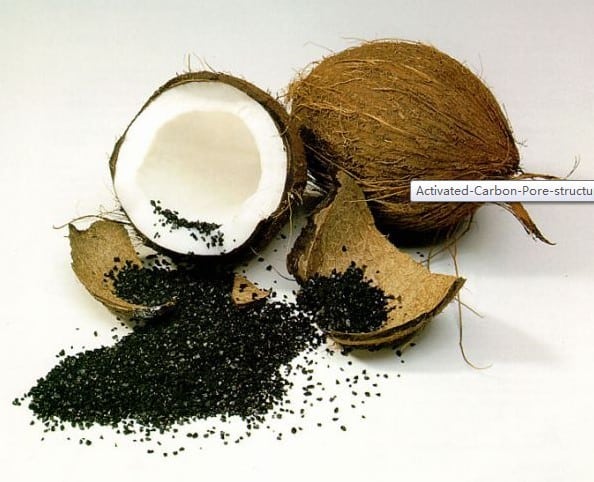
Activated Coconut Filter Working Principle
The working principle of an activated coconut filter relies on the porous structure of activated carbon derived from coconut shells. When water passes through the filter, contaminants are attracted to the large surface area of the activated carbon due to its high adsorption capacity.
The porous structure traps impurities, organic compounds, and chemicals, effectively removing them from the water. Additionally, activated coconut filters can also remove unpleasant tastes and odors from the water, enhancing its quality. This process results in cleaner, clearer, and better-tasting water suitable for various applications, including drinking and cooking.
Adsorption- The pores within activated carbon have a size range. It is important that different-sized pores exist, as they can filter out different contaminants as water moves through them. The extensive internal surface created by the pores allows water to pass through many cavities of varying sizes. Pores range:
Micro-pores: These pores are less than 2 nanometers (one nanometer is one-billionth of one meter)
Meso-pores: These range in size from 2 to 50 nanometers
Macro-pores: The largest pores are from 50 to 2,00 nanometers (1,000 nanometers equals one micrometer)
The attraction between dissolved contaminants and the carbon itself could result because the contaminant itself is hydrophobic — that is, it naturally separates from water. This means the carbon surface is more attractive to the molecule. Alternatively, the molecule could simply exhibit a natural attraction toward carbon. Sometimes both scenarios are present at once.
Hydrophobicity is an important factor in activated carbon filtration, as the majority of organic pollutants in our water exhibit this quality. While they do not bind with the highly polar water molecule, they do bind with carbon, which is non-polar. This is why activated carbon is uniquely capable of removing otherwise difficult volatile organic chemicals, byproducts of disinfection, herbicides, and pesticides.
On Land:
Dig a hole
fill it with green vegetation
put a container in the middle of the hole
Cover the hole with plastic
Collect condensation from the inside of plastic in the container
On Sea:
Use a Bowl
Fill it with Seawater
put a cup in the middle of the bowl
Cover the bowl with plastic
Collect condensation into a cup ………………………………………………………………………………………………. Read more
What is the Best Activated Carbon
Wood Activated Carbon has a broad range of pore diameters. Since these carbons have both a fine and wide pore diameter, they are well-suited for general de-chlorination and the removal of a wider variety of organic chemical contaminants from water, including the larger color bodies.
It produces different performance characteristics in industrial applications typically catered to with coal or coconut products. Their high surface area seen as a significant percentage of mesopores and macrospores generates a fairly low density along with an environmentally friendly and renewable supply of raw materials. Wood-Based Powder Activated Carbon is used for decolorizing sugar liquors, juices, soybean, and food industries.
- Wood base activated carbon has a high surface area characterized by both mesoporous and micropores and has
- excellent decolorizing properties owing to its signature porosimetry.
- Relatively low density
- Renewable source of raw material
Coconut Activated Carbon-based carbon tends to exhibit greater microporosity, which is more suited for the removal of low concentrations of organics such as in drinking water applications. This property can be deduced when comparing iodine numbers on the activated carbons.
The very large internal surface areas characterized by microporosity along with high hardness and low dust make these coconut shell carbons particularly attractive for water and critical air applications as well as point-of-use water filters like this whole house water filter called Fleck 5600 Whole House Well Water Filtration System: 1.5 Cubic ft Coconut Shell Carbon + KDF85 MediaGuard Iron Filter and Safety Respirators. The Advantages include:
- A very high surface area characterized by a large proportion of micropores
- High hardness with low dust generation
- Excellent purity, with most products exhibiting no more than 3-5% ash content.
- Renewable and green raw material
Coal Bituminous Activated –have a broad range of pore diameters. Since these carbons have both a fine and wide pore diameter, they are well-suited for general de-chlorination and the removal of a wider variety of organic chemical contaminants from water, including the larger color bodies. Demand is typically high for this relatively low cost
- filter media for both gas and liquid applications.
- Coal-based activated carbon has a high surface area characterized by both mesoporous and micropores.
- Consistent density
- Hard materials with minimal dust generation.
- Economical
According to Research done on *Kalpaka Industries in Nadu, India Porosity plays a vital role in choosing the right type of carbon. While Coconut activated carbon contains many micropores , Coal activated carbon contains mainly mesoporores as well as micropores whereas wood activated carbon contains mesoporous and macropores only.
If the molecular size of the impurities are less than 100 angstroms then coconut carbon can be preferred. Likewise if the molecular size of the impurities are between 100 and 1000 angstroms we can use coal carbon. And if the molecular size of the impurities are greater than 1000 angstroms Wood carbon can be considered.
Cost wise coconut activated carbon is little bit expensive compared to coal & wood activated carbon. ”If we are to fill up a vessel of a given volume, the weight of coconut activated carbon required is more due to its high density”. But at the same time there is a negligible loss of material during back washing for coconut activated carbon due to its high hardness. Thus operation cost is low. Wettability is very high, and ash content is very low in Coconut activated carbon.
Since it is a renewable source. It is preferable for drinking water treatment and RO water applications. Having said that Coconut activated carbon is best suited for drinking water products. Coal activated carbon is used in drinking water projects.
Apart from that, there are few other industrial applications like Effluent treatment and Waste water treatment. This type of carbon can be best suited for odor removal and cost effective applications. Wood carbon is mainly used in POWDER applications where “decolorization” plays a vital role
What is the Best Way to Filter Well Water?
Use a Whole House Water Filtration system that contains:
- Pre-Filter Sediment Removal
- Water Softener
- Carbon Filter (kills Bacteria)
- Pre-micro-sediment
- Reverse Osmosis-(Dissolved Contaminants to .01 microns in size)
- Polishing-Coconut Fiber-UV treatment (kills Virus & Cyst)
- Minerals-added that were stripped ..…………………………………………………………………………………. Read more
Activated Carbon Filter for Drinking Water
Coconut shell represents one of the newest and most promising options for activated carbon block filters. The density of micro-pores is much higher in coconut than in other forms of activated carbon, meaning it has more surface area and more general porosity. It contains 50 percent more micro-pores than bituminous coal.
This makes Coconut better able to adsorb volatile organic chemicals, which are otherwise difficult to remove from water. Coal performs the best with the overall removal of a wide variety of contaminants and they cost less and the demand is high. It can be applied to gas and liquid. Wood has a high-density area with many mesoporous and macrospore pores not as desirable as the smaller micro-pores that the Coconut and the Coal have but plenty of them.

With Activated Carbon water pollutant adsorption, as it passes over the positively charged carbon surface, the negative ions of the toxins are drawn to the surface of its particles. The use of Activated Carbon is specific to different types of various applications that are designed for all doing the same job but applied according to their needs.
On the whole, Carbon is “The Natural Wonder” and through the process of Activation plays a very critical role in drinking water purification as described by:
- Adsorbs disinfection by-products like THM
- Adsorbs VOCs
- Adsorbs pesticide and herbicide
- Removes halogens from water
- Improves the appearance of drinking water
- Improves the taste of water
The truth is each one of these Carbon sources in a Carbon Block filter is the best defense we have against chlorine by-products, chemicals, and contaminants that end up in our drinking water.
Coconut Activated Carbon is new, sustainable, and efficient and could replace Coal in the near future as the most used Home Water Filters. Whichever you choose, Use a Carbon Filter in your Home to protect your family from the unseen dangers that may or may not affect you.
How long does the LARQ bottle work?
Depending on your household and local water quality, the LARQ filter should last up to 3 months of use or filter up to 60 gallons (227 liters) of water ………………………………… Read more

References:
Nikhilesh Mukherj Author and Consultant
Mumbai, Maharashtra, India Chemicals
The University of Calcutta