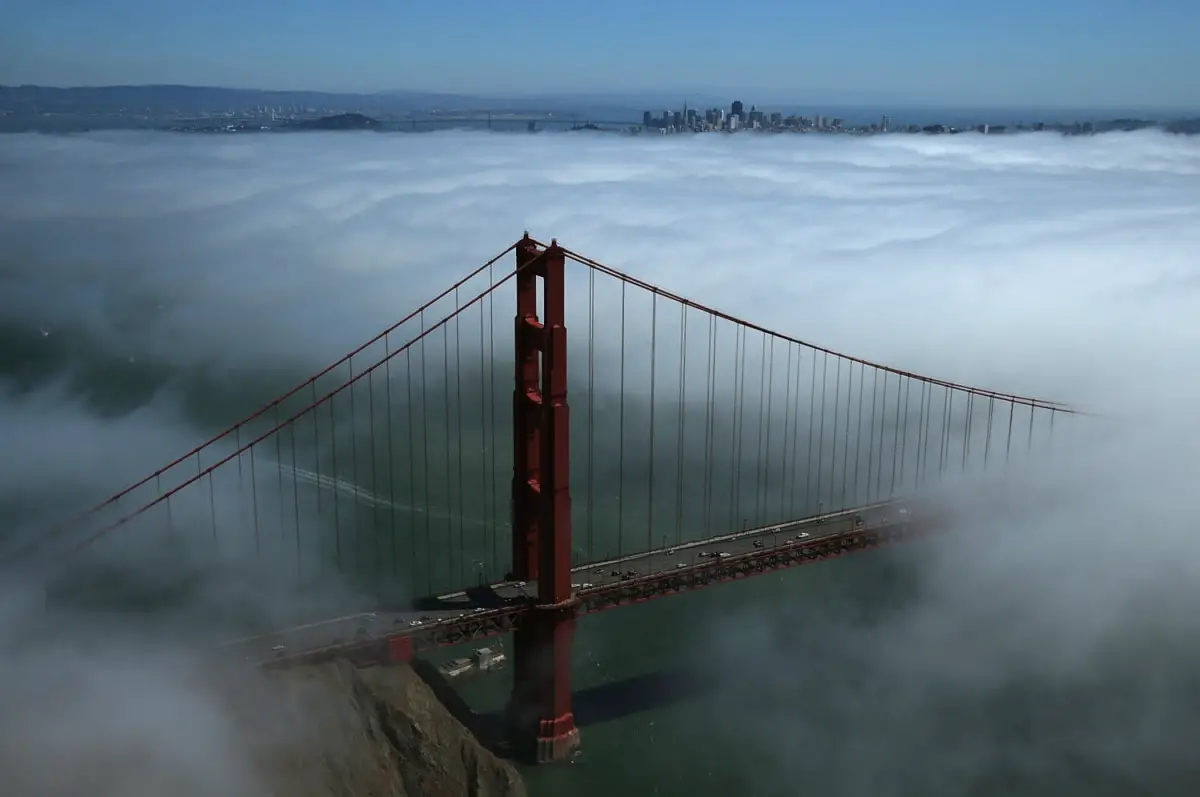
The Sacramento River is a major source of water for the millions of residents in the state and other states through which the river passes it’s well known for four distinct runs of Chinook salmon: fall run, late fall run, winter run, and spring run. Where Does Sacramento River Start and End?
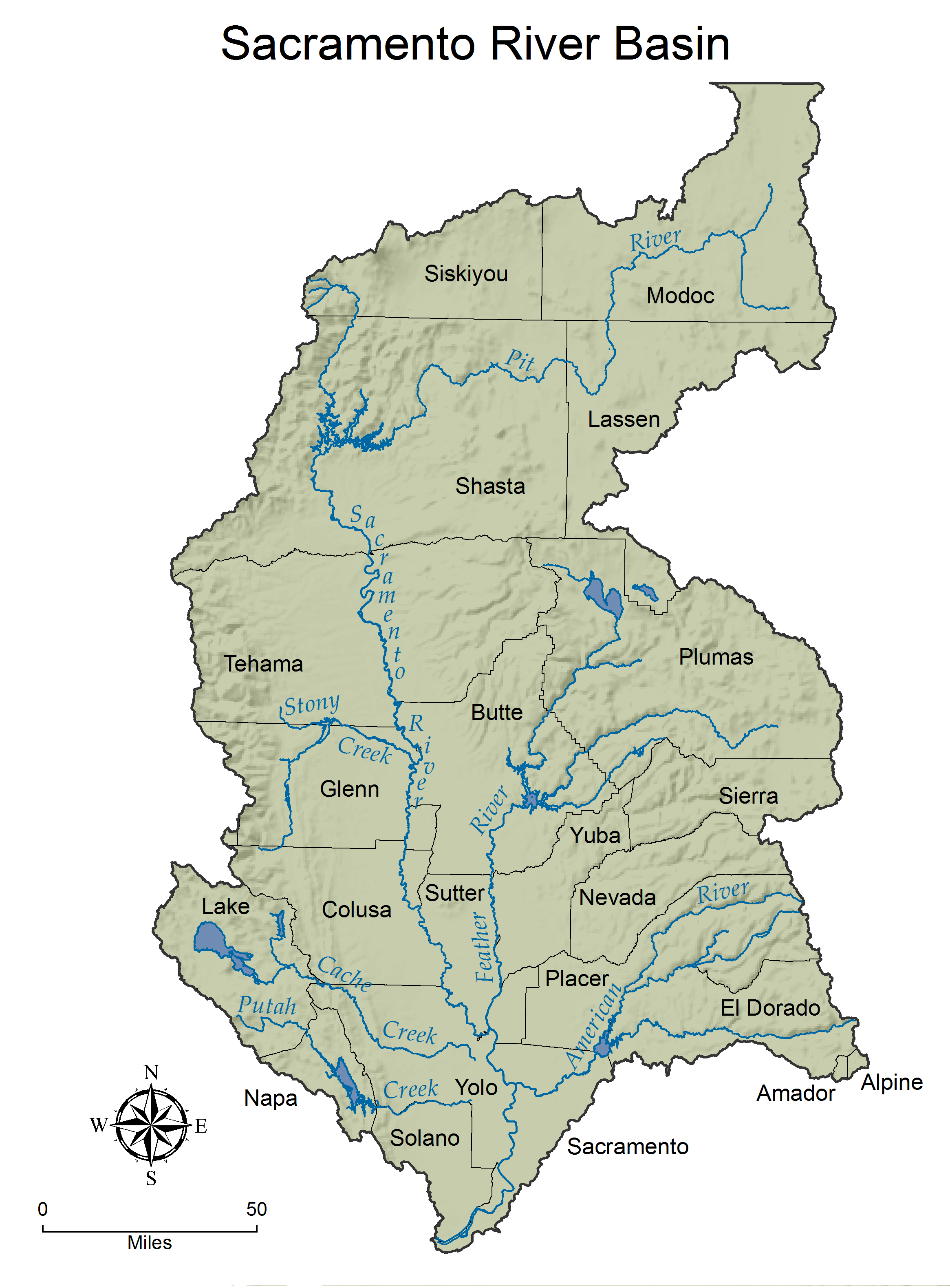
Sacramento River, the largest river in California originates in the mountains of far northern California near Lake Shasta and then flows 382 miles south-southwest through the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta the Central Valley past the city of Sacramento & empties into the Pacific Ocean at San Francisco.
The name Sacramento was originally given to the Feather River by Gabriel Moraga in 1808. It was the scene of the Gold Rush of 1849 the great Sacramento Flood of 1850, and a history of floods ever since flowing through one of the world’s richest agricultural regions.
Introduction:
Often referred to as the lifeline of California, the Sacramento River holds tremendous geographical significance. This article unravels the exact location of the Sacramento River within the sprawling city of Sacramento, California, and will shed some light on the intricate network of other rivers enriching this region. In providing comprehensive geographical detail and context, the material aims to give readers not just a pinpointed location, but also an inherent good of the Sacramento River’s relationship with the city and its other bodies of water.
Where Does the Sacramento River Start and End
The Sacramento River in California
When you’re in the state of California, more precisely in Sacramento Valley, you can’t miss the Sacramento River. From its headwaters near Mount Shasta at Mount Shasta City Park, this magnificent river, full of salmon, flows through the west of the California Central.
It’s a true gem for all of us who cherish the science of the river basin, the management that ensures its water quality, the fisheries that depend on it, and the conservation that protects its habitat.
Exploring the Sacramento River is an experience like no other. Its glittering water is not only a great site for fishing but it’s also important to California’s entire water management system. You will read more about that later. The river’s flood plains, its diverse species of fish and wildlife, and its critical role in the complex ecological environment of California’s Central Valley are something that can be appreciated by everyone.
At first glance, you might think this is just another river in Sacramento, but when you know that it rises in the Klamath Mountains of Northern California and flows straight down to the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, you’ll realize there’s much more to it than meets the eye. That is because the Sacramento River is the main artery of the California water system and it plays a vital role not just for the residents of Sacramento but everyone reliant on California’s river watershed.
Want to know more about the Sacramento River? It’s simply a highway of life – a habitat to numerous species of fish, with salmon making the much-anticipated run each year, bringing an influx of fishing enthusiasts to the area.
Fisheries thrive thanks to its perfect water quality. However, ensuring that quality isn’t simple. It takes planning, informed decision-making, and stringent water quality management techniques. It’s a science, a process that demands the attention of City and State officials.
As you follow the river south, you’ll touch down in Sacramento’s heart, where the American River joins. Here, it’s not only about Sacramento’s River, but the Joaquin River and other rivers too.
Each played their part, contributing their waters to make up the beautiful Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, eventually making their way out to the San Francisco Bay. The array of rivers affects the quality of life and the region’s water quality.
California’s heartland, more known to us as the Central Valley, houses these remarkable natural resources. Here, the Sacramento River is not just a river, it’s a lifeline. Here, west of the highway, you won’t find just Sacramento, but its entire ecosystem surviving and thriving, all thanks to the continuous efforts towards its conservation. It’s all about the balance, the perfect harmony between nature and humans, the fishes and us.
If you’re interested in fishing, if habitat conservation and species management align with your interests, or even if you’re simply an observer fascinated by the Sacramento River’s beauty. Its effect on the valley and California as a whole is not only worth a read. So read, and explore, the secrets and the science that shapes the Sacramento River, one of the greatest river systems in all of California.
The Feather River and its Connection to the Sacramento River
The Feather River is a significant tributary of the Sacramento River, contributing to the larger watershed system in Northern California. It originates in the Sierra Nevada and flows through the eastern part of the Sacramento Valley. One of its major tributaries, the Yuba River, joins the Feather River near Marysville.
The confluence of the Feather and Sacramento Rivers occurs near the city of Sacramento, where the Feather River adds its waters to the Sacramento’s flow on its journey to the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta and ultimately to the San Francisco Bay. The Feather River plays a crucial role in the broader hydrology and ecology of the Sacramento River system.
The Feather River, ain’t just a static landscape feature in Sacramento, California, but it’s also a vital lifeline for a diverse array of fish species, most notably the chinook salmon. As a critical component of the watershed in Sacramento, the Feather River plays a pivotal role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. It’s one of the many rivers that feed into the more prominent Sacramento River, forming a complex network of waterways that are symbolic of California’s rich, aquatic biodiversity.
 The Feather River is among the most significant contributors to the Sacramento River’s fishery systems. It facilitates the migration of chinook salmon, which move up the river to spawn, hence playing a fundamental role in the reproductive cycle of this species.
The Feather River is among the most significant contributors to the Sacramento River’s fishery systems. It facilitates the migration of chinook salmon, which move up the river to spawn, hence playing a fundamental role in the reproductive cycle of this species.
The river provides the salmon with a conducive habitat and ample food resources, essential prerequisites to ensure a robust, healthy population. The integration of varied elements such as velocity, temperature, and turbidity of the rivers offers an optimal environment for the growth and maturation of fish populations.
But the river isn’t just beneficial to the fish. Since Sacramento is fairly arid, the river also acts as a crucial source of water for the surrounding vegetation. Its significance is far beyond aesthetic appeal.
The extensive watershed provided by the Feather River helps sustain the climatic balance by facilitating the percolation of water, ensuring a stable water table in the region.
While the benefits of the river are well known, they’ve also resulted in a bevy of challenges, particularly conservation-related. The ecosystem of the Sacramento River, along with its many tributaries, including the Feather River, is under constant threat from overfishing and pollution.
Ramped-up conservation efforts are the need of the hour, to ensure the survival of unique fish species like the chinook salmon and to preserve the beauty and functionality of the rivers.
All said the bond between the Feather River and Sacramento River isn’t just geographical. Their connection is a deep-rooted one, borne out of shared aquatic life, common threats, and intertwined fates.
The conservation of the watershed will indeed play a monumental role in the future of these rivers and the wide array of flora and fauna they support.
The Sacramento River and the Feather River and two arteries that together keep Sacramento, California, richly pulsating with life.
Highway Information for the Sacramento River Watershed
The Sacramento River watershed is intersected by several major highways, facilitating transportation and connectivity across the region. Interstate 5 (I-5) runs parallel to the Sacramento River, providing a major north-south route through California.
State Route 99 (SR-99) is another significant highway in the area, connecting cities within the Sacramento Valley. State Route 70 (SR-70) runs along the Feather River, intersecting with the Sacramento River in the northern part of the valley. These highways play a crucial role in connecting communities, supporting commerce, and facilitating travel within the Sacramento River watershed. Travelers can use these routes to explore the diverse landscapes and communities that make up this important watershed in Northern California.
The Sacramento River, one of California’s most iconic rivers, rises majestically in the Klamath Mountains of Northern California near Mount Shasta. Ultimately, it weaves its way through California’s Central Valley before merging into the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta. It’s important to consider the intricate network of highways that crisscross this vast watershed when discussing the Sacramento River’s place in the state of California and, indeed, within the broader context of the Sacramento Valley.

The River Basin of the Sacramento River, apart from helping to shape California’s expansive Central Valley, also plays a pivotal role in contributing to the welfare and productivity of the state’s highway system.
It’s important to know what highway information is relevant concerning the water quality and management of the Sacramento River’s watershed. This confluence of roadways, rivers, and other bodies of water, such as creeks, ultimately has a profound impact on the river’s quality, and by extension, the quality of California’s water supply.
The Sacramento River’s water quality does not operate in isolation, rather, it’s part of a complex ecosystem consisting of numerous tributaries, watersheds, and, of course, the highways that traverse the river basin.
These highways, such as Route 5, which runs parallel with the Sacramento River from its headwaters near Mount Shasta to the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, play an integral role in managing Sacramento’s water resources.
Highway runoff can carry contaminants into the watershed and thereby affect water quality. As such, management of the state’s highways, particularly those within the Sacramento River basin’s catchment, is critical. The California Water Resources Control Board and various other agencies work together to monitor, manage, and improve this delicate balance between transportation and water quality management.
Flood management also plays an integral role in the Sacramento River’s watershed. When you read about the historic floods within the Sacramento Valley, you’ll find that many of them originate from the Sacramento River and its tributaries. The river’s path, which rises in the Klamath Mountains of Northern California, flowing through the Sacramento Valley and onto the delta, runs parallel to a complex network of highways again emphasizing the importance of managing the interaction between these natural and man-made assets.
The Sacramento River’s watershed is not only a key natural resource of the State of California but also an integral part of the state’s transportation and water management plans. To truly appreciate the incredible journey the Sacramento takes from its headwaters near Mount Shasta to the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, you must also understand the network of highways that zigzags across this river basin, the challenges this brings to maintaining water quality, and the need for ongoing and effective management from Sacramento’s water agencies.
Rivers, valleys, and creeks that run through the heart of the Central Valley are an essential part of California’s water system, underscoring the importance of understanding the complex relationship between this river and the highway system that intersects its watershed.
Where does the Missouri River Start and End?
The Missouri River a tributary of the Mississippi starts in Three Forks, Montana, as the confluence of 3 major rivers, Madison, Jefferson & Gallatin & ends in St. Louis, Missouri. Crossing South Dakota, North Dakota, Nebraska, Iowa, Colorado, and Kansas, & at 2,540 mi. is the longest river in the US .………………………………………………………………… Read more
Species Thriving in the Sacramento River Watershed, California
The Sacramento River watershed in California is home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. Native fish species, such as Chinook salmon and steelhead trout, thrive in the river, playing a crucial role in the ecosystem. Riparian habitats along the riverbanks support various bird species, including waterfowl and migratory birds, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the Sacramento River watershed.
The Sacramento River, and its watershed a magnificent gem of the state of California, is a haven for numerous species thriving in its unique habitat. This river, teeming with a rich array of fish species, serves as a testament to the natural diversity alive in Sacramento, California.
In this pulsing vein of water, several species of salmons, prominent among which is the Chinook salmon, find a conducive environment due to the river’s commendable water quality.
It’s important to understand that the water quality in the Sacramento River is not merely a happy occurrence; it is the result of hefty conservation efforts. California’s science and conservation-based approaches have contributed significantly to preserving the river’s quality, making it a sanctuary for these precious species.
The American River, another noteworthy waterway in Sacramento, too, follows suit, ensuring a haven for the intriguing members of the underwater life
Fisheries in the Sacramento River are a busy public sector. They revolve around the vibrant fish that inhabit these waters, particularly the salmon. Fishing, for both commercial and recreational purposes, is a significant activity here. Conversely, it is the indispensable role that these species play in the food chain, especially the Chinook salmon, the largest member of the Pacific salmon family, that helps maintain the river’s rich diversity.
Beyond doubt, these species are a crucial component of the ecosystem in the Sacramento River. The fish help to uphold the delicate balance of life in this thriving environment, highlighting the interconnectedness of life in California’s river systems.
However, the relevance of the river and the species it nurtures extends beyond pure science. The crucial link that bridges nature, culture, and commerce in Sacramento, the river, signifies an embodiment of the city’s essence and conservation practices.
Species thriving in the Sacramento River are highly dependent on the water quality that has been upheld through rigorous conservation methods. It’s an evocative vision of the science of persistence. It’s a clear testament to how investing in conservation pays dividends in preserving biodiversity.
Ensuring the adequate health of a river system as rich as the Sacramento River requires vigilance, dedication, and a strong focus on preservation taken seriously by the folks here in The City of Sacramento. The delicate intricacies of the river’s water quality are of paramount importance, a fact reiterated by the diverse array of life that it enables.
The Sacramento River undoubtedly holds a place of pride within Sacramento, California, showcasing the enviable water quality and richness of species that have made their home within its waters. The interconnectedness of rivers, both the Sacramento River and other connected rivers like the Feather River, accentuates the holistic health of these ecosystems. This interconnectedness showcases the mitigation of their challenges as a celebration of unity, a triumph over adversity.
In conclusion, species thriving in the Sacramento River are a precious testament to the beauty and resilience of nature. The rivers, the Chinook salmon, the water quality, and the conservation all echo the harmony of life that thrives in this spectacular aspect of the State of California. It’s a tale of a river teeming with life, of a fishing industry sustained by its science, striving to preserve it, and of a city whose story is incomplete without its river.
Name: The Sacramento River topographic map, elevation, and terrain.
Location: Sacramento River, United States (38.05942 -122.46042 41.29161 -121.50121)
Average elevation: 2,746 ft
Minimum elevation: -23 ft
Maximum elevation: 10,456 ft
Basin Size: 26,500 sq mi
About 80% of the City’s of Sacramento water supply is surface water and comes from the Sacramento and American rivers. The remaining 20% of H2O comes from a system of about 28 groundwater wells that pull water from an underground layer that acts like a reservoir.
Presently there are 1,100 miles of Delta levees that protect farms, cities, schools, and people from flooding and related hazards. But Delta islands are as much as 25 feet below the level of the surrounding water. Many of the levees that protect the islands are fragile, leaving them vulnerable to earthquakes and other seismic activities as well as flooding.
More than half a million people call the Delta home, living in 14 cities and towns in six counties. It is home to the community of Locke, the only town in the United States built primarily by early Chinese immigrants during the early 20th century.
Where does the Missouri River Start and End?
The Missouri River a tributary of the Mississippi starts in Three Forks, Montana, as the confluence of 3 major rivers, Madison, Jefferson & Gallatin & ends in St. Louis, Missouri. Crossing South Dakota, North Dakota, Nebraska, Iowa, Colorado, and Kansas, & at 2,540 mi. is the longest river in the US .………………………………………………………………… Read more
Conclusion:
The Sacramento River is a prominent geographical feature in Sacramento, California. It stands out among other rivers in the US enhancing the natural beauty of the city and the state. It flows seamlessly through the central part of the city, creating a picturesque landscape that residents and tourists love. Being uniquely positioned, it contributes immensely to the life and economy of Sacramento. Beyond just a water source, it represents the natural heritage of the city and a cherished part of its history. Therefore, the Sacramento River is not just located in Sacramento, but it is intricately woven into the city’s identity.
Where is the Philadelphia Schuylkill River?
The Philadelphia Schuylkill River begins in Tuscarora & Minersville Schuylkill County PA. meeting in southern Schuylkill County the river then flows southeast for 137 mi. through Schuylkill, Berks, Montgomery, Chester, & Philadelphia Counties in PA draining into the Delaware River at Philadelphia ………………………………………………………. Read more

References:
California Through My Lens- The Headwaters of the Sacramento River, Mount Shasta
The Nature Conservatory-The Sacramento River
FAQ’s
Q: Where is the Sacramento River located?
A: The Sacramento River is located in the Sacramento Valley within the state of California. More specifically, it rises in the Klamath Mountains near Mount Shasta and flows through the west of the California Central, eventually reaching the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta.
Q: What is the significance of the Sacramento River’s water quality?
A: The quality of the Sacramento River’s water is crucial to the fisheries that depend on it, particularly the salmon populations, and also for the overall conservation of its habitat. Water quality management techniques ensure the river remains a healthy environment for these species and contribute to the river’s role in California’s entire water management system.
Q: How does the Sacramento River contribute to California’s Central Valley’s ecosystem?
A: The Sacramento River plays a critical role in the complex ecological environment of California’s Central Valley. Its flood plains, diverse species of fish and wildlife, and role in the region’s water management system all contribute to the health of the local ecosystem.
Q: How does the Feather River contribute to the Sacramento River’s ecosystem?
A: The Feather River is a significant contributor to the Sacramento River’s fishery yield and facilitates the migration and reproduction of chinook salmon. It also provides a crucial source of water for the surrounding vegetation in the arid Sacramento region and helps maintain the climatic balance.
